 Neutropenia; can be acute or chronic depending on the duration of the illness.
Neutropenia; can be acute or chronic depending on the duration of the illness.
A reduction in the absolute number of circulating granulocytes (a category of white blood cells) that often leads to an increased susceptibility to bacterial and fungal infections and even death. The atypical antipsychotic clozapine and the mood stabilizer carbamazepine may produce this condition and require hematological monitoring.
A condition of the blood marked by a sudden decrease in the number of granulocytes (a type of white blood cell); occurs in lesions of the throat or other mucous membranes or as a side effect of the administration of certain drugs or radiation.
An acute disease in which the white blood cell count drops to extremely low levels and is characterized by high fever and infection, usually of the mouth and throat region.
A usually fatal disease where the number of granulocytes, a type of white blood cell, falls sharply because of a bone marrow condition.
Considerable decrease in leukocytes resulting from depression of granulocytes formed in the bone marrow.
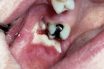
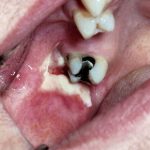
Acute blood disorder, often resulting from radiation or drug therapy, characterized by a severe decrease in granulocytes (a type of white blood cell). Rarely asymptomatic, agranulocytosis is usually accompanied by fever, prostration, and ulcers of the mucous membranes of the mouth, rectum, and vagina. Also called agranulosis; granulocytopenia.
Acute, life-threatening immunocompromised state characterized by severe depression or complete absence of disease-fighting white blood cells and by leukopenia, resulting in infections of the skin and mucous membranes.
A disorder in which there is a severe acute deficiency of certain blood ceils (‘neutrophils) as a result of damage to the bone marrow by toxic drugs or chemicals. It is characterized by fever, with ulceration of the mouth and throat, and rapidly leads to prostration and death. Treatment is by administration of antibiotics in large quantities. When feasible, transfusion of white blood cells may be lifesaving.
A condition in which the white cells or leucocytes in the blood of the polynuclear or granular variety become greatly lessened in numbers or disappear altogether. It is usually caused by taking such drugs as amidopyrine, thiourea, sulphonamides, chloramphenicol and the immunosuppressant drugs.
An acute disease marked by a deficit or absolute lack of granulocytic white blood cells (neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils). It may occur in some leukemias or after exposure to certain drugs (e.g., clozapine) or radiation.
In the realm of medical afflictions, an intense state arises an acute condition characterized by a profound suppression of the bone marrow’s capacity to generate white blood cells. This condition manifests through a constellation of symptoms, including overwhelming fatigue, pronounced chills, swelling in the neck, and a sore throat often accompanied by localized ulceration. Referred to as agranulocytic angina or granulocytopenia, this enigmatic ailment underscores the intricate interplay between immune function and the delicate balance within our hematopoietic system.
A critical and potentially life-threatening condition known as neutropenia arises when there is a severe and sudden scarcity of neutrophils, which are white blood cells responsible for identifying and eliminating infectious microorganisms. This deficiency significantly compromises the body’s immune defenses against infections.
Agranulocytosis, a condition characterized by insufficient production of neutrophils in the bone marrow, can occur as an unfavorable consequence of certain medications like carbimazole, which is used in the treatment of thyroid diseases, or as a side effect of certain cancer treatments such as chemotherapy. Common symptoms associated with agranulocytosis include fever and the presence of mouth ulcers.
The treatment for agranulocytosis involves the administration of antibiotic medications, which should be initiated promptly to prevent the progression of severe and potentially life-threatening infections.
A serious illness that results from the suppression of the body’s blood-forming capabilities due to the use of specific drugs or toxins. It is characterized by ulceration and inflammation in the throat or vagina and can be life-threatening in some instances.