 A type of skin cancer arising from blue-black moles.
A type of skin cancer arising from blue-black moles.
A dark tumour which develops on the skin from a mole, caused by exposure to strong sunlight.
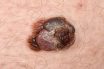
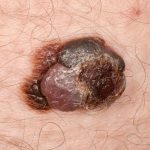
A skin cancer that begins in the melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin. Melanomas are usually dark brown or black and can resemble dark freckles or moles. Typically, they are unevenly colored, irregular-shaped tumors that bleed easily.
Most serious form of skin cancer; often characterized by black or dark brown patches on the skin that may appear uneven in texture, jagged, or raised.
Malignant tumor of the skin that originates from pigmented cells, usually a mole.
A type of skin cancer with life-threatening potential, this condition originates from melanocytes, which are pigment-producing skin cells containing melanin.
The most severe form among the three skin cancer types, with the other two being basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. If not addressed, this cancer can be life-threatening.
Malignant melanoma is a cancer originating from melanocytes, the cells responsible for melanin production. It often results from prolonged exposure to intense sunlight. Predominantly, middle-aged and elderly individuals with light skin and fair hair who have lived in sun-rich environments for extended periods are at risk. Experiencing severe sunburn in one’s youth significantly increases the chances of developing melanoma later on.
The number of new instances and fatalities from this skin cancer in the UK is rising annually, likely because of individuals sunbathing and vacationing in sunlit regions.
Tumors often form on exposed skin areas but can appear anywhere on the body, even within the eye. A melanoma typically emerges from a pre-existing mole. If a mole alters its color, enlarges, or shows an uneven border, it might be affected. Other symptoms include a mole that becomes raised, bleeds, crusts over, develops a scab, or feels itchy or inflamed. Such transformations should be brought to a doctor’s attention. In some cases, melanoma might appear on unaffected skin. Without treatment, this cancer can penetrate deeper skin layers and swiftly metastasize to other body areas.
Detecting the cancer early is crucial to avoid its dangerous spread. The diagnosis is made through a skin biopsy, where tissue from the growth and a bit of the adjacent skin are extracted for microscopic analysis. Nearby lymph nodes might also be examined; finding cancerous cells in these samples suggests the cancer has metastasized.
The melanoma will be surgically excised. If the cancer has metastasized from its original location, treatments like radiotherapy or chemotherapy might be required. Immunotherapy, which uses substances like interferon or interleukin-2, can also assist the body in combatting the cancer.