 A subacute to chronic bacterial infection caused by Actinomyces. A common form is cervicofacial (i.e., lumpy jaw).
A subacute to chronic bacterial infection caused by Actinomyces. A common form is cervicofacial (i.e., lumpy jaw).
A fungal disease transmitted to humans from cattle, causing abscesses in the mouth and lungs (pulmonary actinomycosis) or in the ileum (intestinal actinomycosis).
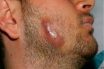
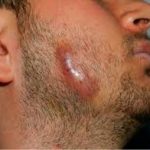
Disease of cattle and humans (in humans, caused by the bacteria Actinomyces Israeli) characterized by the appearance of lumpy abscesses that exude pus through long sinuses. The most common and least severe form of the disease (cervicofacial actinomycosis) affects the face and neck region and is often called lumpy jaw. Less common, more serious forms affect the chest (thoracic actinomycosis) and abdomen (abdominal actinomycosis). Fever, chills and sweats, and weakness may occur in all forms of the disease. Treatment includes incision and drainage of the abscesses and administration of penicillin.
A noncontagious disease caused by the bacterium Actinomyces israelii, which most commonly affects the jaw but may also affect the lungs, brain, or intestines. The bacterium is normally present in the mouth but it may become pathogenic when a tooth is extracted, causing the slow formation of abscesses and ulcers. Prolonged treatment with penicillin is usually effective but it may be necessary to drain the abscesses.
A chronic infectious condition caused by an anaerobic micro-organism, Actinomyces israelii, that often occurs as a commensal on the gums, teeth and tonsils. Commonest in adult men, the sites most affected are the jaw, lungs and intestine, though the disease can occur anywhere. Suppurating granulomatous tumours develop which discharge an oily, thick pus containing yellowish (‘sulphur’) granules. A slowly progressive condition, actinomycosis usually responds to antibiotic drugs, but improvement may be slow and surgery is sometimes needed to drain infected sites. The disease occurs in cattle, where it is known as woody tongue.
An infectious bacterial disease in animals and humans. Infection may be of the cervicofacial, thoracic, or abdominal regions, or it may be generalized.
Actinomycosis, an infectious disease caused by Actinomyces israelii or similar actinomycete bacteria, is characterized by the resemblance of these bacteria to fungi. The condition primarily affects various areas such as the mouth, jaw, chest, and pelvis, giving rise to specific pathological conditions.
The jaw area is commonly afflicted by the predominant form of actinomycosis. This manifests as a distressing swelling accompanied by the discharge of pus and distinct yellow granules through small skin openings. Inadequate oral hygiene practices can potentially contribute to the development of this particular type of infection.
Actinomycosis can also affect the pelvic region in women, leading to symptoms such as lower abdominal pain and irregular bleeding between menstrual periods. This particular form of the infection was primarily associated with a type of intrauterine device (IUD) that lacked copper and is no longer utilized. In rare cases, actinomycosis can affect the appendix or lungs. Fortunately, the majority of actinomycosis cases can be effectively treated with antibiotics, resulting in successful resolution of the infection.
A condition instigated by a fungal infection, typically leading to the affected area, frequently in the jaw region, forming pus and discharging through multiple openings, releasing a yellow discharge containing granules. In the past, it was considered untreatable, but it now shows positive responses to high doses of penicillin.