 Continuous contraction of the muscles of the jaw, specifically as a symptom of tetanus, or lockjaw; inability to open mouth fully.
Continuous contraction of the muscles of the jaw, specifically as a symptom of tetanus, or lockjaw; inability to open mouth fully.
Inability to open the mouth due to spasm of the muscles of mastication.
A spasm in the lower jaw, which makes it difficult to open the mouth, a symptom of tetanus.
Prolonged spasm of jaw muscles.
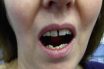
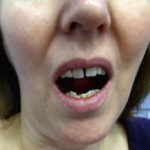
Spasm of the chewing muscles in the jaw. Trismus, also called lockjaw, may be caused by a variety of abnormal conditions or diseases. It is also a result of dental infections, drug reactions, jaw fracture, mumps, or severe strep throat. Usually, a person who has trismus cannot open the mouth more than about 1 inch. It is often the first symptom of tetanus. Treatment varies, depending on the cause.
Spasm of the jaw muscles, keeping the jaws tightly closed. This is the characteristic symptom of tetanus but it also occurs less dramatically with overuse of the phenothiazine drugs and in disorders of the basal ganglia.
Tonic contraction of the muscles of mastication; may occur in mouth infections, encephalitis, inflammation of salivary glands, and tetanus.
Trismus, often referred to as lockjaw, is an involuntary tightening of the jaw muscles that results in the mouth closing tightly. This condition can be a symptom of various issues, including tetanus, tonsillitis, mumps, acute ulcerative gingivitis, or dental problems affecting the molars. Treatment focuses on addressing the root cause.
Lockjaw is an initial symptom of tetanus.