 An inflammatory condition of the tonsils due to bacteria, allergies or respiratory problems.
An inflammatory condition of the tonsils due to bacteria, allergies or respiratory problems.
Inflammation or infection of a tonsil, especially the palatine tonsils. Acute tonsillitis, often caused by bacterial, especially streptococcal, infection, produces sore throat, fever, headache, enlarged lymph glands in the neck region, and difficulty in swallowing. Treatment is by rest, fluids, and antibiotics. Surgery (tonsillectomy) is sometimes performed to prevent recurrent streptococcal attacks.
Acute or chronic bacterial infection of the palatine tonsils and pharynx producing difficulty swallowing, edema and hypertrophy of tonsillar crypts, and blockage of the eustachian tubes.
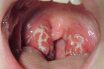
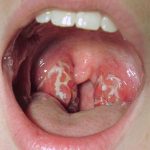
An inflammation of the tonsils, the two small masses of tissue at the back of the mouth, on both sides of the throat. Tonsillitis may occur intermittently and is caused by an infection, most commonly from viruses or the Streptococcus bacteria. The tonsils help filter out and fight bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth and nose. When the tonsils become overwhelmed by infectious organisms, they become inflamed. Tonsillitis is a common childhood illness, most often affecting children between the ages of 5 and 15 years.
Inflammation of the tonsils due to bacterial or viral infection, causing a sore throat, fever, and difficulty in swallowing. If tonsillitis due to streptococcal infection is not treated (by antibiotics) it may lead to rheumatic fever or nephritis.
The inflammation of a tonsil, which is a small cluster of tissue located in the throat.
Tonsillitis arises due to an infection that leads to the inflammation of the tonsils. This condition primarily manifests in children who are younger than nine years old. At times, the tonsils can experience recurrent infections from the very microorganisms they are meant to defend against.
The primary indicators encompass a painful throat and challenges with swallowing. The throat exhibits visible signs of inflammation. Additional prevalent symptoms comprise fever, headache, earache, swollen and sensitive lymph nodes in the neck, as well as unpleasant breath. On occasion, supplementary issues might arise, including temporary hearing impairment or the presence of quinsy, an abscess around the tonsil.
To address tonsillitis, the recommended approach involves ample fluid intake and the administration of an analgesic medication, like paracetamol, to alleviate pain. In certain instances, antibiotic medications might also be prescribed.