The genus name Galinsoga is derived from Ignacio Mariano Martinez Galinsoga, an 18th century Spanish botanist and physicist who identified the plant and transported it from the Andean regions of Peru to the Madrid Botanical Gardens. Parviflora is a Latin word which means small flower (parvo = small, and flor = flower), a reference to the small size of its flowers. The English name ‘Gallant Soldier’ could be a corruption of the ‘galinsoga.’ In Britain, its name Galinsoga is occasionally popularly rendered as “gallant soldiers”, and then sometimes altered to “soldiers of the Queen”. In Malawi, where the plant is naturalized, it is known as ‘Mwamuna aligone’ which translates to ‘My husband is sleeping’.
Gallant Soldier Facts
| Gallant Soldier Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Gallant Soldier |
| Scientific Name: | Galinsoga parviflora |
| Origin | Central America, South America, Europe, West Indies, Mexico, Australia, Africa and Asia |
| Colors | Initially green turning to black as they matures |
| Shapes | 1.5 to 2.0 mm long, inversely cone-shaped or inversely pyramid-shaped dry capsule |
| Health benefits | Support for diarrhea, fever, vomiting, boils small pox, eczema, toothache, colorectal cancer, eye diseases and beetle bites |
| Name | Gallant Soldier |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Galinsoga parviflora |
| Native | Central America, South America, Europe, West Indies, Mexico, Australia, Africa and Asia. However it is widely naturalized in other countries. |
| Common Names | Dumb-nettle, galinsoga-weed, gallant soldier, lesser quick-weed, little flower quick weed, potato-weed, small-flower quick weed, smooth Peruvian-daisy, yellow-weed, chick weed, ciliate galinsoga, galinsoga, quick weed, small-flower galinsoga |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Knopkruid Albanian: Galinsogë lulevogël Amharic: Yeshewa aremi (የሸዋ ኣረም) Angola: Okalumeonglo Argentina: Albahaca silvestre, Botón de oro, picao bravo, saetilla, small flower galinsoga Australia: Chick weed, potato weed, yellow weed Azerbaijani: Xırdaçiçək qalinsoqa Belarusian: Halinsoha dribnokvitkova (галінзога дробнакветкавая) Brazilian: Botao-de-ouro, fazendeiro, picao branco Bulgarian: Dribnotsvitna halynzoha (дребноцветна галинзога), dribnotsvitna peruansʹka laykuchka (дребноцветна перуанска лайкучка) Canada: Small-flowered galinsogayellow galinsoga Catalan: Galinsoga, herba de la bola, herba del Mas de la Pastor Chile: Pacuyuyo Chinese: Niú xī jú (牛膝菊), Xiǎomǐ jú (小米菊) Colombia: Guasca Costa Rica: Mielcilla Créole Réunion: Petit piquant, Piquant blanc, Herbe piment Croatian: Sitna konica Czech: Pěťour malokvětý, Pěťour maloúborný Danish: Håret kortstråle , Betonie, Bredbladet Timian, Drue-Kortlæbe, Håret kortstråle, Klase-Kortlæbe Dominican Republic: Yerba boba Dutch: Kaal knopkruid, klein knopkruid Ecuador: Burrionera English: Kew weed, small-flowered quickweed, potato weed, gallant soldier, small-flower galinsoga, Dumb-Nettle, Galinsoga-Weed, Small Flowered Galinsoga, Yellow-Weed, Chickweed, Kew weed, Smooth galinsoga, French soldier, Peruvian daisy, quickweed Estonian: Paljas võõrkakar Ethiopia: Abadabbo Finnish: Tarhasaurikki, Nurmiajuruoho, Rohtopähkämö French: Galinsoga, galinsoga parviflore, galinsoga à petites fleurs, herbe piment, scabieuse des champs, sournette blanche, Galinsoga glabre, Piquant blanc German: Kleinblütiges Franzosenkraut, kleinblütiges Knopfkraut, Kleinkorbfranzosenkraut, Kleinblütiges Franzosenkraut, Zranzosenkraut Haiti: Herbe aiguiles Hebrew: Galinesogah ketannat-perachim, glinsugh ktns-prkhim (גָּלִינְסוֹגָה קְטַנַּת-פְּרָחִים), Galinsoga kitnat-prahim Hindi: Marchia, pardesi Hungarian: Gyakori gombvirág, kicsiny gombvirág Indonesia: Balakatjioet losih, bribel Italian: Galinsoga, galinsoga comune Japanese: Kogomegiku (コゴメギク), hakidamegiku Kenya: Macdonaldi Kinyarwanda: Baonoka, Barzazi, Chimari, Rumari Korean: Byeol kkot a jae bi (별꽃아재비) Latvian: Sīkziedu sīkgalvīte Lithuanian: Smulkiažiedė galinsoga Malagasy: Anambitro (Moyen-Ouest) Malayalam: Mukuthipoovu Malawi: Mwamuna aligone Manipuri: Hameng shampakpi Mexico: Piojito, rosilla chica Nepali: Chitlange jhar (चित्लांगे झार) New Zealand: Galinsoga Netherlands: Knopkruid Norwegian: Peruskjelfrø, Bakketimian, Betonie, Firtann Pakistan: Khanna Peru: Pacpa yuyo, paco yuyo, waskha, chuminca Polish: Zółtlica drobnokwiatowa Portuguese: Erva-da-moda, picão-bravo, fazendeiro, Botão-de-ouro, picão-branco Romanian: Busuioacă de cîmp, busuioacă parviflora, Busuioc salbatic , Busuiocul dracului Rundi: Kirandura, Kurituka Russian: amerikanka (американка), galinzoga melkotsvetkovaya (галинзога мелкоцветковая), galinsoga melkotsvetkovaya (галинсога мелкоцветковая) Serbian: Konnitsa (коница), obychnaya kuritsa (обична коница), Konica Slovak: Pätúr drobnokvetý, žltnica maloúborová Slovene: Drobnocvetni rogovilček South Africa: Quick weed Spanish: Chumica, galinsoga, moderna, soldado galante, albahaca silvestre, escabiosa, botón de oro, rosilla chica, Cundinamarca y Boyacá, Guascas, Pajarito, Sogamoso y oriente de Boyacá, albahaca silvestre, estrellita, mercurial, pacoyuyu fino, saetilla, chuminca, guasco, mielcilla, pacuyuyo Swedish: Gängel, Druvgamander, Humlesuga, Lundgamander, Stortimjan, Gängel, Tarhasaurikki, tandgängel Tamil: Mookuthi poo (மூக்குத்தி பூ), Mūkkutti (மூக்குத்தி) Turkish: Beşpat çiçeği Ukrainian: Halinsoha dribnotsvita (галінсога дрібноцвіта), Tridax parviflora, Halinzoha dribnokvitkova (Галінзога дрібноквіткова), Halinsoha dribnokvitkova (Галінсога дрібноквіткова), Nezbutnytsya (Незбутниця) USA: Littleflower quickweed Uganda: Kofume Venezuela: Canilla de blanca Zimbabwe: Kew weed |
| Plant Growth Habit | Erect, upright, leafy, fast growing annual herbaceous plant |
| Growing Climates | Urban areas, trails, open rocky sites or pastures, open areas, dry deciduous forests, shola forests, arable land, waste places, pavements in towns, roadside, upland crop field, weedy field, margins of field, gardens, fallows, ruins and railway embankments |
| Soil | Prefers light and slightly moist places and neutral to slightly acidic soil rich in nutrients |
| Plant Size | About 10-100 cm tall |
| Root | Pivoting and it has many side roots that are long and thin |
| Stem | Erect or ascending, leafy, and finely ridged and grooved. It has few to many branches and is hairless or sparsely to moderately covered with appressed and sometimes spreading hairs |
| Leaf | Leaves are oval yellowish-greenish, pointed, opposite and toothed with hairs on the leaf margins and stems. Leaf blade is ovate or ovate-oblong, 1–6.5 cm long and 0.5–4.5 cm wide, margin shallowly serrate. |
| Flowering season | May to October |
| Flower | Flowers are small with five white petals, three-lobed at the tips, with yellow central disc florets |
| Fruit Shape & Size | 1.5 to 2.0 mm long, inversely cone-shaped or inversely pyramid-shaped dry capsule |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to black as they matures |
| Propagation | By Seed |
| Plant Parts Used | Flowers, leaves, stem |
| Precautions |
|
Plant Description
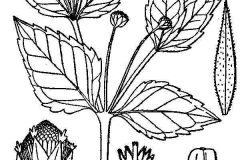
Gallant Soldier is an erect, upright, leafy, fast growing annual herbaceous plant that normally grows about 10-100 cm tall. The plant is covered with sparse, fine, dense (in upper part), accumbent, simple hairs, with admixture of glandular hairs. The plant is found growing in urban areas, trails, open rocky sites or pastures, open areas, dry deciduous forests, shola forests, arable land, waste places, pavements in towns, roadside, upland crop field, weedy field, margins of field, gardens, fallows, ruins and railway embankments. The plant prefers light and slightly moist places and neutral to slightly acidic soil rich in nutrients. The plant is pivoting and it has many side roots that are long and thin.
Stem
The stem is erect or ascending, leafy, and finely ridged and grooved. It has few to many branches and is hairless or sparsely to moderately covered with appressed and sometimes spreading hairs. The upper part of the stem does not have glandular hairs.
Leaves
The leaves are simple, opposite, broad, long-stalked at the base, nearly sessile at the top. It is ¾ inches to 4¼ inches (2 to 11 cm) long, and ⅝ inches to 2¾ inches (15 to 70 mm) wide, sometimes wider. They are on slender, up to 1½ inches (4 cm) long leaf stalks (petioles). The leaf blades are lance-shaped to broadly egg-shaped and unlobed. They are mostly angled or short-tapered at the base and are angled or tapered to a sharp point at the tip. The upper and lower surfaces are sparsely to densely covered with short, slender, more or less spreading hairs. Three main veins are visible on the upper side. The margins are coarsely toothed with obscure, rounded teeth that amount to little more than bumps, and they have a fringe of short, slender, more or less spreading hairs.
Flower
The inflorescence is an irregularly branched cluster (panicle) or loose cluster of flower heads, or sometimes just a single flower head, at the end of the stem and branches, and rising from the upper leaf axils of the main stem. Each flower head is on a 1⁄32 inches to 1½ inches (1 to 40 mm) long stalk (peduncle). The peduncle is covered with minute gland-tipped hairs.
Each flower head is small, just ¼ inches to ½ inches (6 to 12 mm) in diameter. At the base of each head there is a 3⁄32 inches to ⅛ inches (2.5 to 4.0 mm) long, 3⁄32 inches to 3⁄16 inches (2.5 to 5.0 mm) in diameter, hemispherical to bell-shaped, cup-like whorl (involucre) of 5 to 8 bracts (phyllaries) in two series. All of the phyllaries are green and are usually hairless. The inner series of 4 to 6 bracts are longer and broader than the outer 1 or 2 bracts. Each phyllary is fused to two thin dry (chaffy) bracts on the upper part of the peduncle (receptacle). The outer phyllaries have a thin white margin. They are dropped with their chaffy bracts as an intact unit with the fruits developing from the ray florets. The inner phyllaries are persistent.
The flower head has usually 5 widely spaced ray florets, sometimes just 4 or up to 8, and 15 to 35 disk florets. Both ray florets and disk florets are fertile. Each ray floret is usually dull white, with a tube-like portion at the base and a 1⁄16 inches to ⅛ inches (2 to 3 mm) long, widely spreading portion (lamina). The lamina has three teeth at the tip. There is no tuft of bristles (pappus) at the base, or just a minute one, much shorter than the corolla tube, that cannot be seen without a hand lens. Sometimes the rays are pink, and flower heads with both ray colors can appear on the same plant. The disk flowers are yellow. The corollas are 1⁄32 inches to 1 ⁄16 inches (0.8 to 1.5 mm) long and have 5 minute lobes. Flowering normally takes place in between May to October.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by black, 1⁄16 inches to ⅛ inches (1.5 to 2.0 mm) long, inversely cone-shaped or inversely pyramid-shaped (with the narrow end at the base) dry capsule (cypsela). At the base of each cypsela there is a yellowish pappus, usually shorter than the cypsela that spreads outward as the cypsela matures. The seeds germinate quickly, and there are usually two or three generations each year. This is the feature that gives the plant one of its other common names quick weed. One plant produces up to 300,000 seeds. Weight of 1000 seeds is 0.21 g. Vegetation period lasts 30-45 days. Spread by pappose seeds, which are carried by wind.
History
Galinsoga parviflora was brought from Peru to Kew Gardens in 1796, and later escaped to the wild in Great Britain and Ireland, being temporarily known as the ‘Kew Weed’. The plant is named after the Spanish botanist Ignacio Mariano Martinez de Galinsoga. The species name ‘parviflora’ translates to ‘having small flowers’.
Traditional uses and benefits of Gallant Soldier
- It is used to coagulate bleeding from cuts and wounds.
- In Manipur, India, salted extract of leaves are given for diarrhea, fever, and vomiting; also, for boils and small pox.
- Leaves are mixed with those of Ageratum conyzoides, Drynaria cordata, and ginger and made into a paste and used as remedy for snake bites.
- Its extracts are applied topically to treat eczema, lichens, and poorly-healing wounds.
- Decoction of leaves is used for excess stomach acids in Columbia.
- Whole plant is used as hemostatic and anti-inflammatory in China.
- In the Kakamega county of Kenya, it is used for colorectal cancer: leaves of Ocimum gratissium are usually mixed by Galinga parviflora leaves, Senna didymobotyra and Triumfetta rhomboidea leaves, taken as decoction twice daily for two weeks.
- Leaves and stems are chew to cure colds and sores; applied locally for wound healing.
- Gallant soldier is used for the treatment of nettle stings and similar skin inflammation by rubbing the affected skin with the leaves.
- Leaves are used for wound dressing in Ethiopia.
- Leaves of this plant, along with Ageratum conyzoides, Drymaria cordata and ginger are made into a paste and applied as a remedy for snake-bite by the Khasis and Jaintias of Meghalaya.
- When rubbed onto the body, the plant is useful in treating nettle stings.
- Juice of the plant is applied to treat wounds; it helps to clot the blood of fresh cuts and wounds.
- Plant’s sap / juice when applied directly on fresh wounds stimulates coagulation of blood therefore stopping further bleeding and excessive loss of blood which could lead to anemia.
- The plant is used in traditional preparations for wound healing as well as for the treatment of blood coagulation problems, cold, flu, toothache, and dermatological and eye diseases.
- The chemical constituents are useful for treating snakebites, wounds, eczemas, lichens, flu, and colds.
- Juice of the whole plant is used as a healing agent for treating wounds and body injuries.
- The roots provide effective remedy against beetle bites.
- Plant has been used as an anti-scurvy agent due to its high level of vitamin C.
- The flowers are applied in making preparations for relief of toothache.
Culinary Use
- It can also be used as an ingredient in leaf salads, although it’s subtle flavor, reminiscent of artichoke, mostly develops after being cooked.
- In eastern Africa, the plant is collected from the wild, and its leaves, stem and flowers eaten.
- It is used as pot herb in some parts of the world.
- It is an essential ingredient in Bogota chicken and potato stew/soup called ajiaco.
- Young leaves, stems and flowers are used as ingredient in smoothies, salads, stews or juices.
- It can be dried and grind into powder to be used as soup flavoring.
- Guacas is the indispensable herb flavoring in the traditional Colombian stew, ajiaco Bogotano.
- In Tanzania and Uganda, the leaves and stems are eaten as leafy vegetable.
- Young stems and leaves are cooked and eaten as a vegetable but flower heads and buds are usually removed.
- Gallant soldier is also eaten as a vegetable in South-East Asia.
- In South America the dried leaves (’guascas’) are an essential flavoring for certain dishes.
- Leaves stem and flowering shoots can be consumed raw or cooked and eaten as a potherb, or added to soups and stews.
- It is a bland but very acceptable food; it makes a fine salad either on its own or mixed with other leaves.
- Fresh juice can be mixed and drunk with tomato or vegetable juices.
- Fresh leaves are used for making salad, and the dried whole plant is used in making soups in Latin and North America.
Other Facts
- In Colombia, leaves and stems are used as vegetables.
- Flower heads and buds are reportedly discarded or used as cattle fodder.
- The plant is grazed by livestock and used as a feed for chicken, rabbits and pigs.
References:
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/GASPA
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=37414#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/galinsoga_parviflora.htm
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/229805
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/gcc-96478
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galinsoga_parviflora
http://www.stuartxchange.org/GallantSoldier
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Galinsoga_parviflora_(PROTA)#Vernacular_names
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Quick%20Weed.html
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Galinsoga+parviflora
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=GAPA2