They are referred to as a “typical fruit from Papua” and are called Ton or Taun on the island of Papua New Guinea, Buah Matoa in Indonesia, and Kasai in Western Malaysia. The tropical fruits can be found throughout Indonesia and are highly variable in their appearance, with fruits in shades of green, red, purple, and brown. The flavor of matoa fruit is like the mixture of rambutan, lychee and longan fruit, with juicy texture and very sweet and is a popular fruit for eating.
Plant Description
Fiji Longan is a small to large, evergreen tree that grows about 12-50 m high with a large, spreading crown with a spread of 10–20 m across. Bole is cylindrical, straight up to 7 m high and diameter up to 30 cm with fawnish to reddish bark. The plant is found growing in common in lowland forest, forest edges, open woodlands, lava flows, and often cultivated in villages of the Pacific Islands, lowland riverbanks, humid woodlands, swampy forests, often on alluvial sites and along or near rivers and streams, but also on hillsides. The plant thrives on a wide range of soils but does best on slightly acidic to neutral, well drained, fertile sandy, loamy and clayey soils, but will tolerate mildly alkaline soils of pH 7–8 and even soils with impeded drainage.
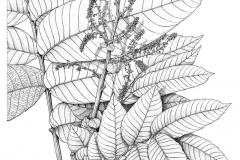
Leaves
The plant has alternate, stalked, compound leaves that are more than 1 m long. Each leaf consists of 4–15 pairs of leaflets, and lacks a terminal leaflet. The papery to leathery leaflets are egg-shaped to drop-shaped, slightly to distinctly sickle-shaped. When young, the leaflets are bright red in color, turning dark green when mature, hairless to covered with hair, 6–40 cm long and 2–13 cm wide, and with toothed margins. The lowest pair of leaflets is smaller than others, round, ear-shaped or cushion-shaped, 0.4–3 by 0.3–5 cm, appearing like a stipule, and with one of the leaflets reduced.
Flowers
The plant is monoecious, producing both male and female flowers in the same individual. The flowers are about 2–2.5 mm across, generally white to green-yellow, and occur on branched flowering stalks that are 15–70 cm long. Flowering normally takes place from July – October.
Fruits
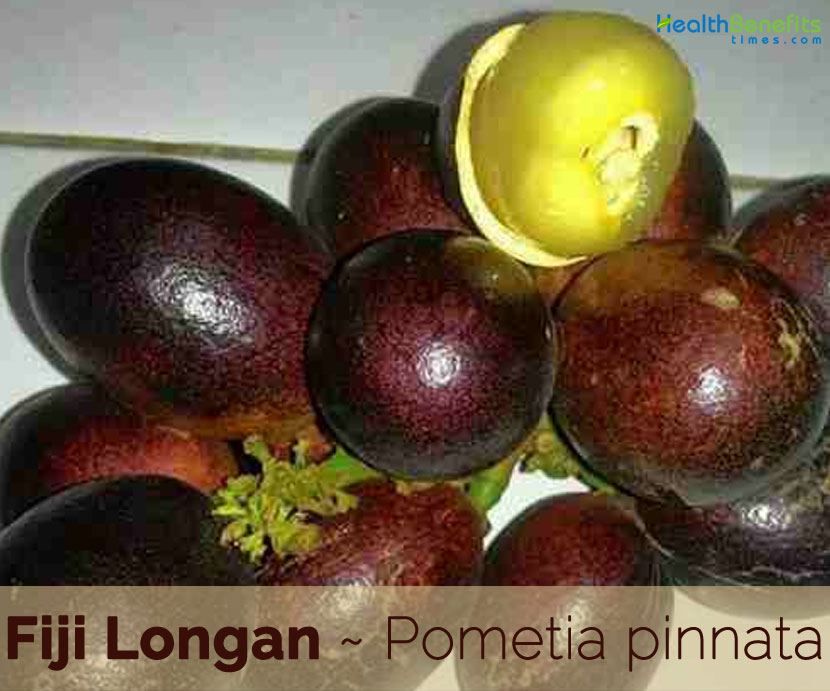
Fertile flower are followed by ellipsoid to round fruit that is 1.5-5 cm long and 1-3 cm wide. Pericarp is thin or moderately thick, smooth, greenish-yellow, reddish-brown, purplish, dark red or black, enclosing a gelatinous, sweet, juicy, white translucent, pulpy aril lode which partly encloses a single large seed with curved embryo. The seed is egg-shaped, unequal sided, up to 2.5 cm long and 1.5 cm wide, brown, and with a white covering (aril).
Health Benefits of Fiji Longan
Listed here are some well-known health Benefits of Fiji Longan for beauty and your body
1. Reduce Coronary Heart Disease
Vitamin C in Fiji Longan is supposed to help reduce heart disease. Additionally, if your diet is not healthy, you can use the Fiji Longan as a companion (fruit) as a counterweight.
2. Help control high blood pressure
Even not only the fruit flesh, extracts of seeds and leaves are also proven to help reduce high blood pressure. Fiji Longan extract consists of diuresis, which surges the amount of fluid released from the body. When too much fluid in the body, blood pressure will automatically increase. So, if the fluid level returns to normal, it can make blood pressure drop. Research from Bandung states that at a dose of 100 milligrams per kilogram of body weight, this Fiji Longan extract can remove water and salt through urine so that a person’s blood pressure can go down. Even so, all the benefits of this Fiji Longan must still be studied further. However, it never hurts to try fruit with this unique taste, because it has fiber and nutritional content that is not inferior to other fruits.
3. Prevents the Development of Cancer
Cancer occurs when free radicals are free to access your body. Antioxidants are the real deal for free radicals because they will fight it and prevent the development of cancerous cells. As rich of vitamin C and vitamin E, Fiji Longan is excellent source of powerful antioxidants.
4. Maintain Skin Health
The content of vitamin E in the Fiji Longan also has an important role in maintaining skin health by maintaining and improving skin moisture and elasticity. Together with some of the phytochemical compounds contained in the fruit of Fiji Longan, vitamin E is able to increase the regeneration of skin cells.
5. Cure dysentery
To treat dysentery using Fiji Longan, you can utilize the fruit leaves Fiji Longan to get the properties. Fiji Longan fruit marinade leaves already believed long ago as remedy dysentery.
6. Stress Relief
Fiji Longan fruit is a healthy snack you could consume in daily basis because it is so rich of vitamin E which is essential stress relief. Whenever you feel stressful, sometimes your appetite is also improving, snacking with Fiji Longan fruit is not going to cause weight gain but instead it will relieve your stress effectively.
7. Increases Endurance
During a workout you need endurance and to improve your work productivity you need to expand your endurance as well. Body endurance is closely related to your current stamina and the sugar compound found in Fiji Longan fruit is excellent energy booster to increase your endurance.
8. Improve Male and Female Fertility
Fiji Longan fruit contains vitamin E. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant and important to protect and increase fertility health. For women, vitamin E contains antibodies that can protect eggs and increase fertility by 20 to 30 percent, and can prevent membrane splits during pregnancy. As for men, vitamin E can improve sperm quality and motility in men.
9. Fights Viral Infection
Viral infection is not going to be fatal but fighting it is not an easy case at all. The best thing to fight this infection is by making sure your immunity system is in excellent state and consuming Fiji Longan which is rich of vitamin C and antioxidants are a perfect protection against viral infection.
10. Improve Immune System
Fiji Longan fruits consist of vitamin C. Vitamin C has been known to prevent free radicals and helps to increase endurance. If you increase endurance, would be protected from virus attacks the disease.
Traditional uses and benefits of Fiji Longan
- Masticated bark is applied to burns in Papua New Guinea.
- Both leaf and bark extracts are used, either individually or in combination with other plants, to treat a wide range of ailments, including stomach complaints, diarrhea, dysentery, pain relief (bones, muscles, joints, chest, headache), colds, flu, diabetes, and mouth ulcers in Fiji.
- In the Solomon Islands an oral medicine is prepared from the bark to protect babies from the devil.
- An infusion of the bark was used to treat diarrhea in children, stomach trouble, serious coughs accompanying fever and constipation, and the leaves were also used medicinally in Tonga.
- It was used as a traditional treatment for chicken pox, with the patient being bathed in an infusion (hot water extract) of the bark in parts of Sarawak (Malaysia).
- Malays boil leaves and bark and used decoction in a bath for fever.
- Bark is used for festering sores in Java.
- The Fijian longan is often used in traditional medicine in the Pacific Islands.
- It is used to treat deep pains in the bones, migraine headache, to aid expulsion of placenta after childbirth, to relieve rheumatic aching of muscles and joints, to relieve fever, as a remedy for flu and cold, to cure diarrhea, stomach trouble, cough, fever, constipation, and diaper rash.
- Leaves are antimicrobial.
- Decoction of the leaves or bark is used medicinally against fever and sores.
- An infusion of the leaves is rubbed onto the heads of infants or is given internally to treat unclosed fontanelles.
- An abundant, thin, red gum obtained from the inner bark is considered to have many medicinal properties.
- An infusion of the bark is used as an emetic for mouth infections, colds and mucous congestion, and to treat abdominal pains.
- Decoction of the bark is used to treat mouth cancers.
Culinary Uses
- The arillode of ripe fruit is sweet and is eaten fresh.
- The oily seeds are boiled or roasted and eaten.
Other facts
- Trees are occasionally planted as fences, boundary markers, avenue trees, shade trees and as wind-breaks and used in urban greenings.
- Tree provides a very good general purpose hardwood timber that is particularly well suited to light construction, moldings, interior joinery and framing, non-impact tool handles, furniture, for canoes, boats and ship construction, agricultural and sports implements, paddles, flooring, plywood and veneers.
- Wood is also used to produce excellent charcoal.
- Canoe putty is extracted from the inner bark.
- An extract of the leaves was formerly used to dye hair black in Fiji.
- Leaves are used against rice-pests.
- Gum obtained from the inner bark is used to waterproof canoes.
- A hair shampoo is made from the bark.
- Timber can be used for furniture and cabinet work but must be dried to sufficiently low moisture content.
- Each stem of the fruit contains 23-76 pieces weighing between 0.5 – 1.0 kg.
Precautions
- Be careful with allergic reaction because it is not a kind of fruit you commonly find in the market. If you are allergic to lychee or longan fruit, perhaps avoiding this fruit is a wise move.
- If you are not familiar with this fruit, don’t try to consume kind of fruit that looks like Fiji Longan fruit because the chance it is not Fiji Longan fruit is higher and probably could be harmful for your body.
References:
http://old.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Pometia_pinnata.PDF
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pometia_pinnata
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Pometia+pinnata
http://isoplexis.uma.pt/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=35395
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/tro-28601407
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/261424
https://www.monaconatureencyclopedia.com/pometia-pinnata-2/?lang=en
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Pometia_(PROSEA)
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/PMEPI
https://florafaunaweb.nparks.gov.sg/Special-Pages/plant-detail.aspx?id=3084
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/42815
Comments
| Fiji Longan Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Fiji Longan |
| Scientific Name: | Pometia pinnata |
| Origin | Andaman Islands, China (Yunnan), Fiji, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Nicobar Islands, Niue, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Salomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Tonga, Vanuatu, Vietnam and Wallis and Futuna Islands |
| Colors | Greenish-yellow, reddish-brown, purplish, dark red or black (depending on variety) |
| Shapes | 3–5 cm long and wide, round to broadly ellipsoid; pericarp thin or moderately thick, smooth |
| Flesh colors | Semi-transparent white to yellowish flesh |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Health benefits | Improve Immune System, Fights Viral Infection, Improve Male and Female Fertility, Increases Endurance, Stress Relief, Cure dysentery, Maintain Skin Health, Prevents the Development of Cancer, Help control high blood pressure, Reduce Coronary Heart Disease |
| Name | Fiji Longan |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pometia pinnatan |
| Native | Andaman Islands, China (Yunnan), Fiji, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Nicobar Islands, Niue, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Salomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Tonga, Vanuatu, Vietnam and Wallis and Futuna Islands |
| Common Names | Fijian Longan, Dawa, Island Lychee, Oceanic Lychee, Pacific Lychee, Kasai, Megan, Taun, Fiji longan, Kasai tree, Kava, langsir, matoaTaun tree |
| Name in Other Languages | Borneo : Dipangah, Kasai, Kayu sapi, Kuang, Lantupak, Matoa, Pangak, Pitanah Burmese: Paga-nyet-su ava Chinese : Fan long yan (番龙眼) Cook Islands : Tava Dutch: Matoa English: Fijian longan, Kasai, Megan, Taun, Fiji longan, Island lychee, Kasai tree, Oceanic lychee, Pacific lychee, Kava, langsir, matoaTaun tree Fiji : Dawa, Dawa Moli, Dawa Sere, Dawadawa, Tavisivesi, Tawa Vesi Ni Wai, Vesi Wai, Vesivsei, Ndawa, tawa Filipino: Tugaui French : Bois De Pieu, Le Pomet, Lychee Sauvage, Bois de pieux, Kava, Karva, Lichi sauvage, Nandao, Pomet, Pometier French Polynesia : Kava India : Kasai (कसै), khasai (ख़सै), pometi panna (पोमेतिअ पिन्नता) Indonesia : Kalasina, Kablauw, Iwa, Kayu Sapi, Langsir, Leungsir, Langsek Anggang, Matoa Lao: Sino-Tibetan Malay: Kasai, Kasai daun besar, Kasai daun kecil, Kayu sapi, Lengsir, Matoa, Sibu Malaysia : Asam Kuang, Kasai, Kasai Daun Besar, Kasai Daun Kecil, Sibu, Enselai, Kasai Niue : Tava Papua New Guinea : Koiawo, Dame, Okamu, Taun, Ohabu, Bas, Cuhinh, Tze Philippines : Agupanga, Malugai, Tugaui Portuguese: Kassai Rotuman : Fao, Fava Russian : Pometiia (Пометия), pometiya peristaya (пометия перистая), fidzhiĭskiĭ longan (фиджийский лонган) Samoa : Kava, Tava Solomon Islands : Nyia, Tava, Nodae, Tauna, Igi, Ako, Dawa, Tao, Gema, Mede, Taoa, Awa, Tava, Piraka Taba Spanish : Longán De Fiji, matoa Tagalog: Agupanga, Malugai, Tugaui, Tungai Thai : Daeng-Ná am, Dængn̂ả (แดงน้ำ) Tonga : Tava, Tava Kula, Tava Moli, Tava Toua Vanuatu : Rao, Tava, Dava, Ndava, Netva, Tava, Netowe, Tewen, Tien, Wuten, Nandao, Burklata, Ndalawa, N’Dalaoa, Dra, Nendo, Nendro, Vujarie, Vujaria, Jaria, Jariea, Ah, Jarie, Ha, Kao, Nsai, N’Seire, Jarie, Ndao, Nandem Vietnam : Truong, Truong Maat Wallis And Futuna : Tava |
| Plant Growth Habit | Small to large, evergreen tree |
| Growing Climates | Common in lowland forest, forest edges, open woodlands, lava flows, and often cultivated in villages of the Pacific Islands, lowland riverbanks, humid woodlands, swampy forests, often on alluvial sites and along or near rivers and streams, but also on hillsides |
| Soil | Thrives on a wide range of soils but does best on slightly acidic to neutral, well drained, fertile sandy, loamy and clayey soils, but will tolerate mildly alkaline soils of pH 7–8 and even soils with impeded drainage |
| Plant Size | 12-50 m high with a large, spreading crown with a spread of 10–20 m across |
| Bole | Cylindrical, straight up to 7 m high and diameter up to 30 cm with fawnish to reddish bark |
| Leaf | Alternate, stalked, compound leaves that are more than 1 m long. Each leaf consists of 4–15 pairs of leaflets, and lacks a terminal leaflet. The papery to leathery leaflets are egg-shaped to drop-shaped, slightly to distinctly sickle-shaped. |
| Flowering season | July – October |
| Flower | 2–2.5 mm across, generally white to green-yellow, and occur on branched flowering stalks that are 15–70 cm long |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Ellipsoid to round fruit that is 1.5-5 cm long and 1-3 cm wide. Pericarp is thin or moderately thick, smooth, greenish-yellow, reddish-brown, purplish, dark red or black, enclosing a gelatinous, sweet, juicy, white translucent, pulpy aril lode |
| Fruit Color | Greenish-yellow, reddish-brown, purplish, dark red or black (depending on variety) |
| Flesh Color | Semi-transparent white to yellowish flesh |
| Seed | Seed half to three-quarters of the size of the fruit, covered by an arillode of up to 4 mm thick, shiny brown or red-brown |
| Propagation | By seed |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, bark |
| Health Benefits |
|