False Heather Facts
| False heather Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | False heather |
| Scientific Name: | Cuphea hyssopifolia |
| Origin | Mexico, Guatemala and Honduras |
| Shapes | 3-lobed oblong-ovoid, dehiscent, leathery or berrylike capsules about 3.5 mm long containing 5-8 small seeds |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for high cholesterol, triglycerides, dermatitis, fever, cough, stomach disorders, malaria, indigestion, dysentery, wounds, bruises, and muscle pain |
| Name | False heather |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cuphea hyssopifolia |
| Native | Mexico, Guatemala and Honduras |
| Common Names | False Heather, Hawaiian Heather, Elfin Herb, Elfin Plant, Cuphea, Clammy Cuphea, Corail, Tarweed, Mexican Heather, Heather, Elfin bush |
| Name in Other Languages | Assamese: Pānikā phula (পানিকা ফুল) Bangladesh: Rani Phool Brazil: Cuféia Chinese: Xì yè xuějiā huā (細葉雪茄花) Creole: Radie raide Cuba: Cufia English: Mexican-heather, False heather, Elfin bush, Hawaiian heather, cuphea, elphin herb, elphin plant, tarweed Finnish: Sinitulitorvi French: Corail, Jean gaiac German: Falsches Heidekraut Greek: Koféa (Κοφέα) Portuguese: Falsa-érica Samoan: Aoa Spanish: Romerito, cufia, yerba de la dicha, yerba de la suerte Swedish: Isopskufea Vietnamese: Cẩm tú mai |
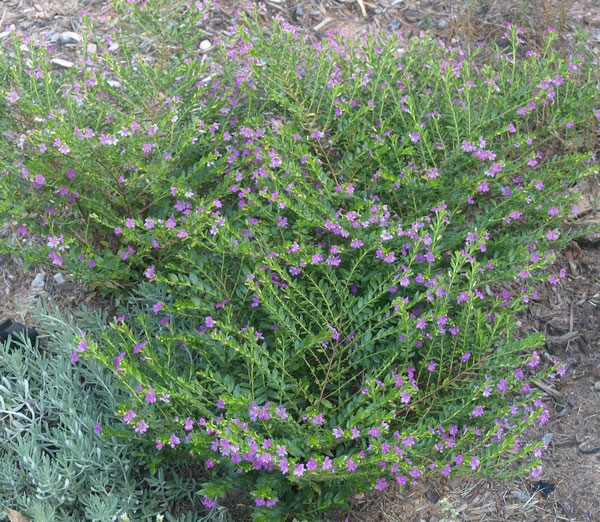
| Plant Growth Habit | An erect to spreading, low-branching, compact, free-flowering, evergreen subshrub |
| Growing Climates | In the under storey of deciduous and semi-deciduous lowland, mid-elevation forests, in oak forests, edges of creeks and rivers, in humid forests, in disturbed areas and moist forests |
| Soil | Can grow in a variety of soil, including clay, sandy, and loam. They can also grow in the slightly acidic to slightly alkaline and neutral soil as well. A nutrient-rich soil that can allow the excess water to quickly move out (well-draining) is the best soil for Mexican Heather plants |
| Plant Size | About 60 cm (24 in) tall and 90 cm (35 in) wide |
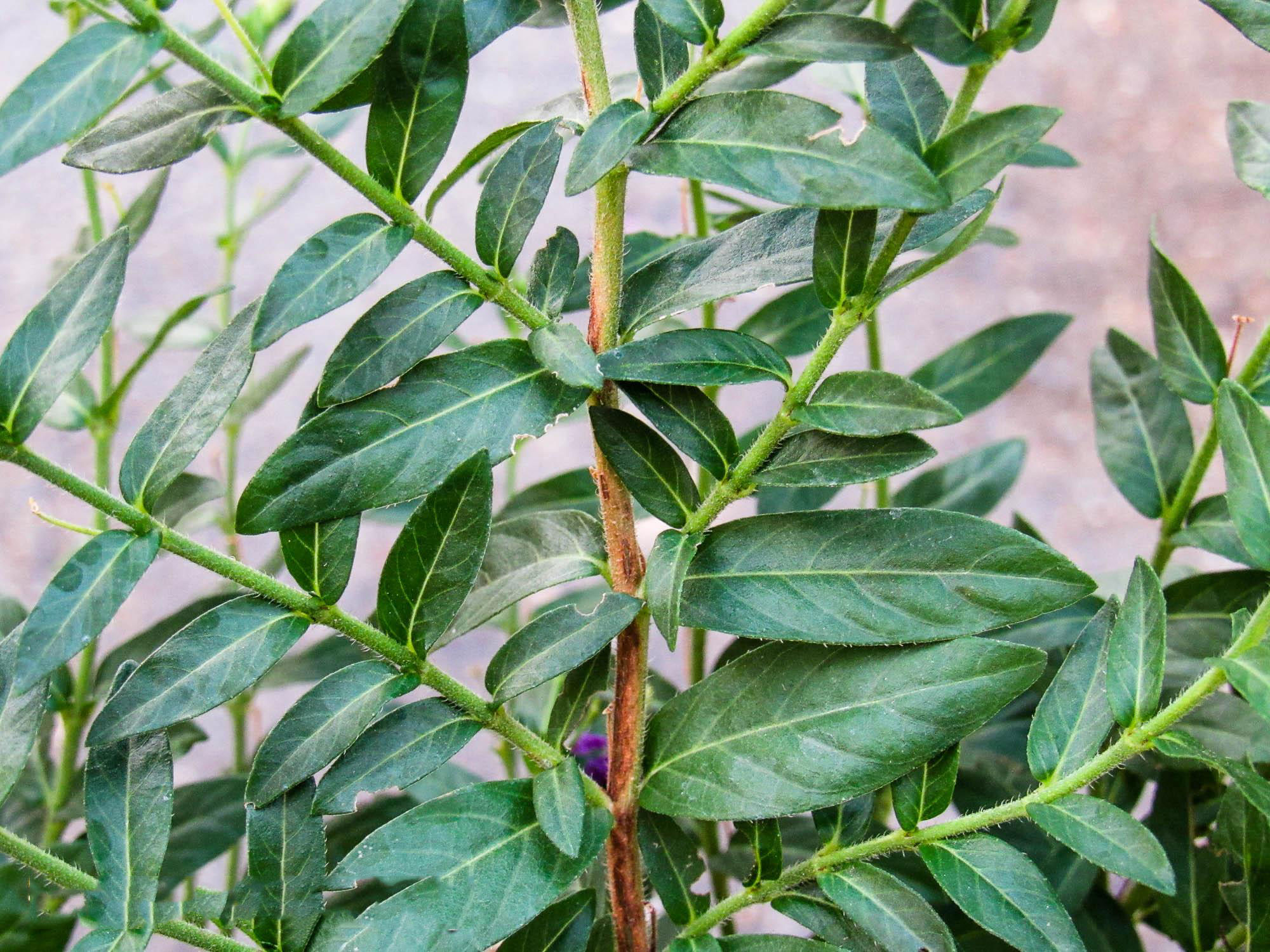
| Stem | Stems with ascending trichomes, reddish-brown or white, sometimes also tiny hairy; internodes generally 1/2 the length of the underlying leaves |
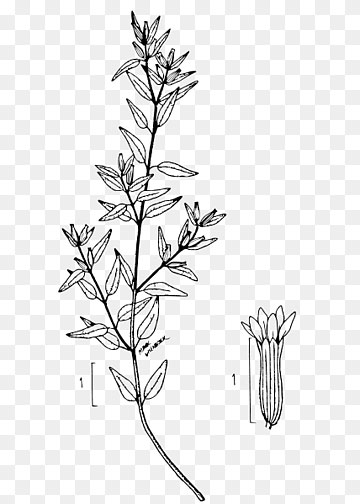
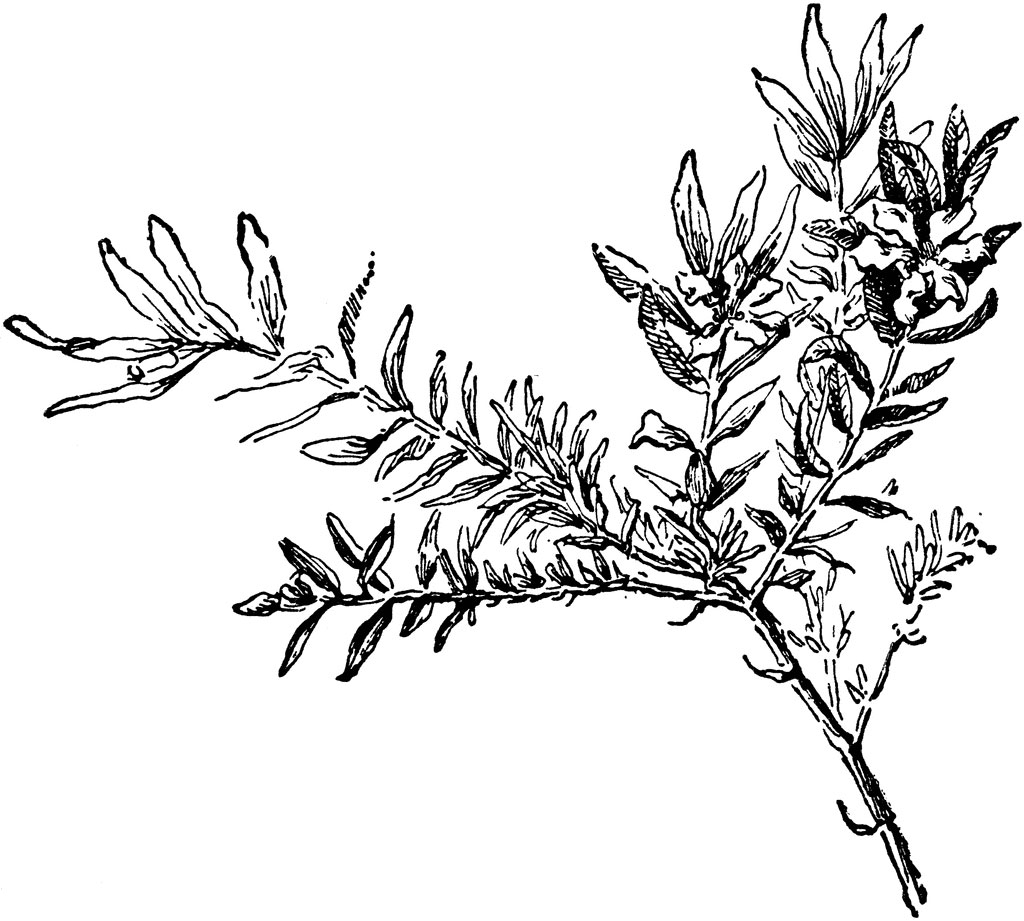
| Leaf | Simple, subsessile (with slight stalks), opposite, pinnately-veined, oblong, sometimes elliptic, glossy, medium to dark green, 10 to 30 mm long and 1.5 to 4 mm wide, with pubescent (covered with hair) undersides |
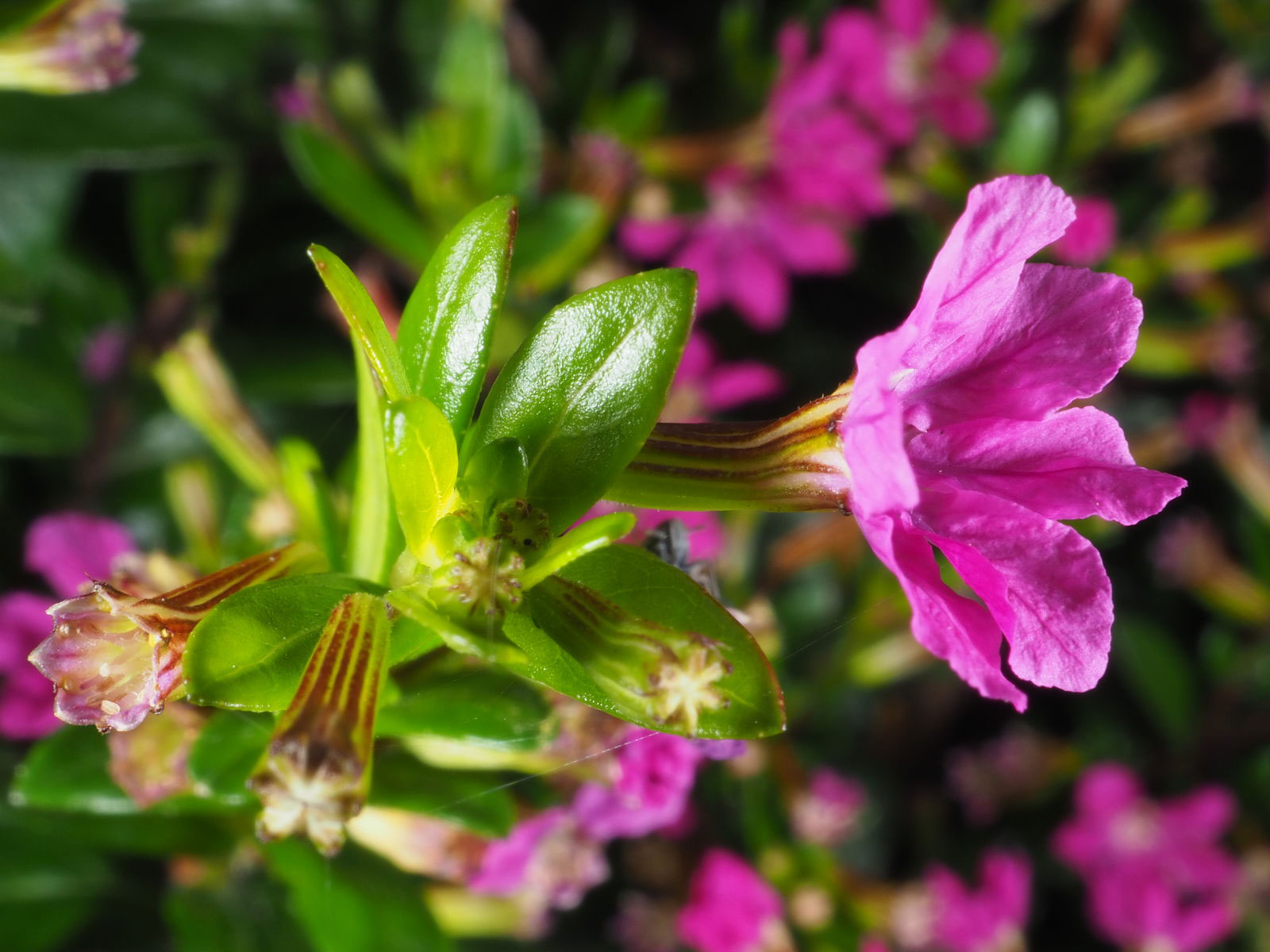
| Flower | Solitary, alternate in the axils of new leaves, trumpet-shaped, pedicels 2 to 7 mm long, ending in 2 persistent bracts. Floral tube is 5-8.5 mm, the base rounded to slightly descending, the mouth blunt, not extended ventrally, the dorsally green or purplish tube, glabrous or the veins sparsely setose, rarely also finely hirsute |
| Fruit Shape & Size | 3-lobed oblong-ovoid capsules about 3.5 mm long containing 5-8 small globose seeds, each about 1 mm in diameter |
| Seed | Seeds are reddish brown, sub orbicular, each about 1 to 1.5mm in diameter and pitted |
| Propagation | By seed, cuttings, layering or division |
Plant Description
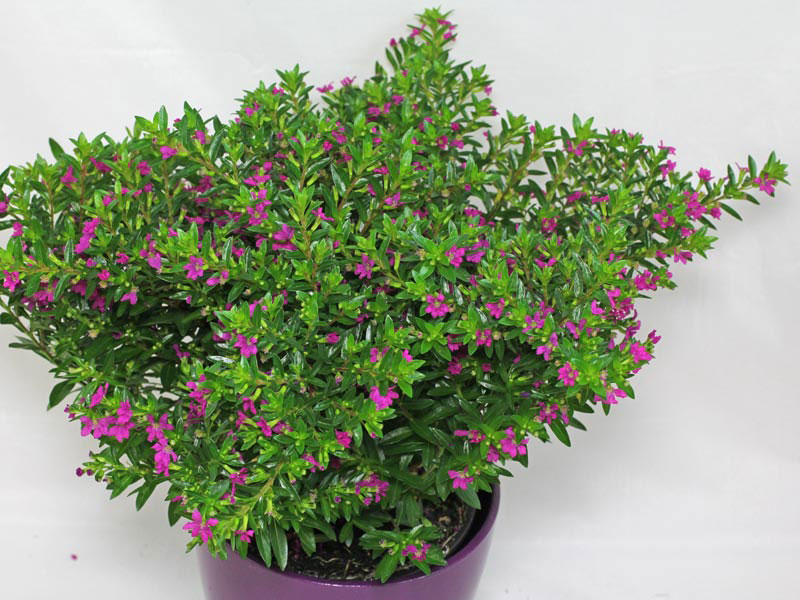
False heather is an erect to spreading, low-branching, compact, free-flowering, evergreen subshrub that normally grows about 60 cm (24 in) tall and 90 cm (35 in) wide. The plant is found growing in the under storey of deciduous and semi-deciduous lowland, mid-elevation forests, in oak forests, edges of creeks and rivers, in humid forests, in disturbed areas and moist forests. The plant can grow in a variety of soil, including clay, sandy, and loam. They can also grow in the slightly acidic to slightly alkaline and neutral soil as well. A nutrient-rich soil that can allow the excess water to quickly move out (well-draining) is the best soil for Mexican Heather plants. It is moderately salt-tolerant, adaptable to various soils with good drainage in full sun and tolerates high summer heat and some drought but grows best with regular moisture. It is a perennial in zones 9 and higher but is generally grown as an annual.
Stem
The plant has stems with ascending trichomes, reddish-brown or white, sometimes also tiny hairy. Internodes are generally 1/2 the length of the underlying leaves.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, subsessile (with slight stalks), opposite, pinnately-veined, oblong, sometimes elliptic, glossy, medium to dark green, 10 to 30 mm long and 1.5 to 4 mm wide, with pubescent (covered with hair) undersides. They are arranged alternately in the length of the stems giving the plant a fernlike appearance. They are glabrous or almost glabrous on the upper surface, the lower midrib or the leaf margins are sometimes strigous, the base is rounded to acute or attenuated. The apex is acute, rare once obtuse. Petiole is up to 2 mm or absent; upper stem leaves not reduced.
Flowers
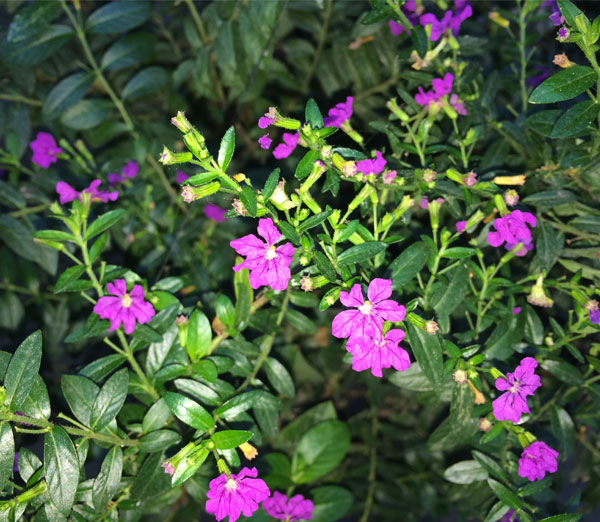
Flowers are solitary, alternate in the axils of new leaves, trumpet-shaped, pedicels 2 to 7 mm long, ending in 2 persistent bracts. Floral tube is 5-8.5 mm, the base rounded to slightly descending, the mouth blunt, not extended ventrally, the dorsally green or purplish tube, glabrous or the veins sparsely setose, rarely also finely hirsute. Six petals, purple, 3 to 3.5 mm long. Sepals crinkled, rarely absent. Calyx is 5 to 8 mm long; floral tube pale green, sometimes turning purplish toward apex, glabrous or slightly pubescent. The plant blooms profusely from summer to frost. False heather flowers range from the typical purple and lavender to the less frequently seen white, pink and deep rose varieties.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by Fruits are 3-lobed oblong-ovoid, dehiscent, leathery or berrylike capsules about 3.5 mm long containing 5-8 small seeds. Seeds are reddish brown, sub orbicular, each about 1 to 1.5mm in diameter and pitted. Plants may be propagated by cuttings, layering or division. They seed freely, and new seedlings that appear may be easily transplanted.
Traditional uses and benefits of False Heather
- It is used medicinally in Mexico and in Bangladesh.
- In Brazil, it is used to treat high cholesterol and triglycerides.
- In French Guiana, stem and leaf are macerated in rum and rubbed onto sprains.
- Leaf infusion is used for colds and chills.
- In Bangladesh, it is used as tonic and insect repellent; also used for dermatitis, fever, and cough.
- The leaves and flowers of are used as a tonic and in the treatment of fevers and coughs.
- The plant is a rich source of phenolic compounds which have been shown to have a strong antioxidant activity.
- In town, infusions of the aerial parts of false heather are used for treating stomach disorders.
- Decoction is taken as a remedy for malaria.
- An infusion is used to relieve feverish states or even to calm a cough.
- Flowers are anti-phetic, anti-tussive and balsamic, being very effective for respiratory ailments.
- It is also used as a wound healer, as well as for snake bites.
- False heather is used to treat indigestion, dysentery, wounds, bruises, and muscle pain.
- Plant often used in prevention of organ stones, subsidence of consumption and fever, curing of infections especially with eyes, healing of poisonous bites and stings.
Other Facts
- It is widely grown and sold as an ornamental plant.
- The leaves and flowers of are used as an insecticide.
- Industrial oils made from these fatty acids have a range of uses, including as a de-foaming agent; a booster for soaps and detergents; and in health and beauty products.
- They can also be used in foods, mostly as vegetable shortenings.
References:
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/cuphea_hyssopifolia.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=12632
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/118210
https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=a113
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CPHHY
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2748114
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cuphea_hyssopifolia
http://www.stuartxchange.org/Kupea
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=27104#null
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CUHY
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Cuphea+hyssopifolia
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/676/#b
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Mexican%20Heather.html