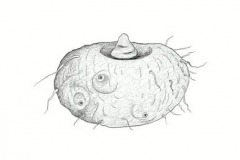
Cheeky Yam, Corpse Flower, Corpse Plant, Elephant Foot Yam, Elephant Yam, Stink Lily, Telinga Potato, Voodoo Lily, White-Spot Giant Arum, Sweet yam and pungapung are some of the most popular common names of the plant. Genus epithet ‘Amorphophallus’ means deformed phallus, an allusion to the shape of the inflorescence and tubers. Species epithet ‘paeoniifolius’ means having leaves like Peony (Paeonia), and is named after ancient Greek physician Paeon, who was thought to be the first to use plants medicinally.
Plant Description
Elephant Yam is a stout deciduous, herbaceous aroid shrub that may grow about 1.5 m tall. The plant is found growing in secondary forest, shrub forests, coastal monsoon forests and thickets or highly disturbed areas and in dappled shade or fully exposed areas and grasslands in arid valley areas. The plant prefers friable, deep loamy non alkaline soil. It is hardy in tropical areas when planted in rich, well-drained soil in a sheltered, humid position. It does best in partial shade. It yields to waterlogging and heavy clayey soil; hence, good drainage is needed.
It is a stem less herb, with tuberous roots. The tuber is underground stem. It is sub-globose, depressed, bulbiferous, dark greyish-brown, warty and 18 to 25 cm in thickness. Rootlets are thin. Petiole is radically developed from the depressed portion of the globose tuber side by side with the spathe and spadix. Spathe is broadly campanulate, light green with whitish patches outside, dark-purple at base. Spadix is stout, with pistillate region at the base, staminate above and upper most sterile, sub globose or amorphous, dark purple, irregularly lobed appendix, spongy, broader than long and whitish within. After cutting into two halves; elephant’s foot yam looks same as the elephant’s foot. After getting ripe its edible root yam gets pink-brown and the upper shoot gets grown and leafy green.
Leaves
Leaf blade is divided into hundreds of small leaflets, with whole cluster reaching 1.5 -3.0m across. Leaflets are 3-lobed, each lobe divided into pinnatisect segments. Several leaves may be produced from accessory tubers. Leaf stalk is up to 1 m or more, background color pale to dark green with large and small pale blotches and numerous tiny dark dots. Leaves die down after blooming, and regrow from tuber during next season.
Flowers
The plant blooms annually around the beginning of the rainy season. Flower bud arises from the corm as a purple shoot, and later blooms as a purple inflorescence. The pistillate (female) and staminate (male) flowers are on the same plant and are crowded in cylindrical masses as an inflorescence. The top part is responsible for secreting mucus that gives off rotten, pungent smell that is used to entice pollinating insects, the middle part of the inflorescence consists of staminate, and the base of the inflorescence contains pistillate. Stigmas of the female flowers will be receptive on the first day of the bloom, when the pungent smell draws pollinating insects inside, and the inflorescence closes, trapping them for a night to allow the pollen deposited on the insect to be transferred to the stigmas.
Later in the second day, the female flower is no longer receptive to pollens, the male flowers start to bloom, and the inflorescence opens again. This allows the pollen to be deposited on the emerging insects to pollinate other flowers, while preventing the pollen from the same inflorescence fertilizing itself, preventing inbreeding. While the flowers are in bloom they also produce heat. They die after five days.
Fruit
In 24–36 hours, after the first bloom of the inflorescence, the inflorescence’s female flowers start developing into cylindrical berries crowded on the spadix, about 1.5 cm in diameter. Fruits are initially green maturing to bright red as they mature. These bright red fruiting bodies and other parts of the inflorescence start wilting away.
History
Elephant foot yam is used as food in Island Southeast Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia, New Guinea, Oceania, and Madagascar. Its origin and center of domestication was previously considered to be India, where it is most widely utilized as a food resource in recent times. But a genetic study in 2017 have shown that Indian populations of elephant foot yams have lower genetic diversity than those in Island Southeast Asia, thus it is now believed that elephant foot yams originated from Island Southeast Asia and spread westwards into Thailand and India, resulting in three independent domestication events. From Island Southeast Asia, they were also spread even further west into Madagascar, and eastwards to coastal New Guinea and Oceania by the Austronesian migrations. Though they may have spread south into Australia without human intervention.
Health benefits of Elephant Yam
Mentioned below are the best health benefits of Elephant Foot Yam
1. Lowering Cholesterol
Elephant foot yam is known to have a great effect in lowering the levels of bad cholesterol in the body. It is widely used as a slimming food. Omega-3-fatty acids present in it help in increasing the levels of good cholesterol in the body, while reducing the levels of low-density lipoproteins and very low-density lipoproteins. Elephant foot yam consists of very low about 0.2-0.4% of fat and high levels about 1.7-5% of fibers, making it an ideal food in the process of weight reduction.
2. Cardiovascular Health
Elephant Yam is really very helpful in maintaining good cardiovascular health. There are various reasons that show the goodness of this vegetable for heart health and they are.
3. Anticoagulant and Anti Inflammatory
As an effective anticoagulant, elephant foot yam can be helpful in reducing the risks of heart attacks. It also helps in relieving the clots formed in arteries and veins. This action can also be helpful in reducing high blood pressure and further complications like coronary artery disease.
4. Cancer Prevention
As we all know that Elephant Yam is loaded with dietary fiber therefore it is quite beneficial in the prevention of colon cancer. Additionally, this vegetable is also rich in vitamin A content. This vitamin is advantageous in preventing lung and oral cavity cancers.
5. Slow down ageing
The powerful antioxidants present in elephant foot yam is said to be effective in slowing down the aging process. It also helps in keeping away risks of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and strokes. Another important constituent of elephant foot yam is vitamin C that also aids in slowing down of the aging process. It slows down the process of aging by making one’s skin blemish-free and wrinkle-free.
6. Diabetes
You all know this fact that Elephant Yam has a low glycemic index and therefore people with diabetes can freely enjoy it without any fear of blood-sugar spike.
7. Detoxification
It is a powerful detoxifier. The high fiber content in elephant foot yam shows toxin detoxification in the liver. Elephant foot yam is best known for its hepato-protective activity. It helps in proper cleansing of other internal organs including intestine and stomach, making them free of pathogens.
8. Anti-Inflammatory
It is also used in the treatment of hemorrhoids and piles. It is also suggested in the treatment of arthritis. It also helps in reducing muscle spasms. Other applications of its anti-inflammatory activity can be found in rheumatism, elephantiasis, glandular swellings and others.
9. Memory and Concentration
Being a rich source of Omega-3-fatty acids and also other essential minerals like zinc, selenium, magnesium, phosphorous, elephant foot yam help in improving brain functioning and aids in the improvement of memory and concentration.
10. Boost Immunity
Fiber contents of elephant foot yam are great supplements for probiotics. It not only cleanses toxins and pathogens out of the body, but also builds up good bacteria to improve immunity. Elephant foot yam is also said to be possessing antibacterial agents which help in keeping away infections. It also shows wide cytotoxic and immune-modulatory activity.
11. Cures Piles
Piles are really very painful. It is mainly caused due to chronic constipation, too much straining, excessive sitting and eating spicy, oily and unhealthy foods. There are many other causes of piles or hemorrhoids. You can cure this problem by using Elephant Yam. All you have to do is to cut Elephant Yam in small and thin pieces and dry them in sunlight. Make a powder out of them. Take half to one teaspoon of this powder with water twice daily. You should make a balanced and healthy diet menu to prevent this painful problem.
12. Women Health
Elephant foot yam is said to be estrogen boosting food. This benefit makes Elephant Yam an excellent food for those who want to increase the estrogen level. Vitamin B6 and antispasmodic properties of this yam helps prevent and cure the symptoms of PMS or Pre Menstrual Syndrome. If you are a pregnant or lactating mother then you must take the approval of your doctor before consuming this vegetable.
13. Cooling effects
Elephant foot yam shows a cooling effect in the body. It helps in reducing high blood pressure and also facilitates, smooth flow of blood across arteries and veins. It reduces stress and is highly recommended to be included in the meals especially, in hotter regions for its cooling effect. This can be accounted for elephant foot yam’s nervous system depressant activity, which results in sedation and decreased loco motor activity.
14. Good for Digestion
Eating Elephant Yam regularly can help you improve your digestive health. This yam is loaded with antispasmodic, inflammation fighting, carminative, appetizing, digestive and stomachic properties. These effects help improve digestion and appetite. This vegetable is effective in curing abdominal cramping, flatulence, bloating, dysentery, worm infestation, ulcers, excessive stomach acid and many other stomach related issues. Regular consumption of Elephant Yam can help alleviate various types of gastrointestinal problems including constipation, irregular bowel movements, upset stomach and piles.
15. Slimming food
Elephant yam is a low calorie food which is fully packed with dietary fiber. High fiber content and nutrients make Elephant Yam a good slimming food for those who are looking to lose weight. Eating fiber rich food will keep you full for longer and as a result you’ll eat less. You can really enjoy nicely cooked vegetable without any fear of weight gain. Some people drink a mixture of bitter gourd and Elephant Yam vegetable juice. This juice is said to be a great weight loss aid. However, too much intake of this juice may be dangerous. So, always consult with your physician or reputed Ayurvedic practitioner before using this juice for weight loss.
16. Skin and Hair Care Benefits
It has an awesome store house of skin friendly nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, beta-carotene, vitamin C, vitamin B6 and various minerals. These all nutrients not only help prevent signs of aging but also keep your skin glowing and younger looking. Elephant Yam is also a storehouse of anti-oxidants that help keep skin soft, tight and healthy looking.
Vitamin A and other nutrients present in Elephant Yam are helpful in promoting hair growth and stomach hair fall. Deficiency of beta-carotene is responsible for dry hair, split ends and flaky scalp. So, consume this vegetable regularly to get an adequate shot of beta carotene. Vitamin B6 of yam is helpful in preventing and curing hair graying.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U10Gn1AA9Qw
Traditional uses and benefits of Elephant Yam
- Tubers are used as appetizer, aphrodisiac, expectorant, irritant and anti-catarrhal and for liver complaints, tumors, inflammation, hemorrhoids, vomiting, cough, bronchitis, asthma, piles, abdominal pains, dyspepsia and acute rheumatism and for treating spleen enlargement in Indian traditional medicine.
- Corm is thought as carminative, restorative, stomachic and tonic.
- It is dried and used in the treatment of piles and dysentery.
- Corm is used for dropsy, urinary diseases, dyspepsia, toothache, rheumatism, boils, fistula, colitis, hemorrhoids, diuretic, piles, elephantiasis and glandular swellings in Sri Lanka.
- Tuber is widely used in South India as folk medicine to treat acute rheumatism, tumors, lung swelling, asthma, vomiting and abdominal pain.
- Traditionally, Elephant Yam tuber is used for the treatment of enlarged spleen, rheumatism and tumor in India.
- Elephant Yam was one of seven plant species that was found to be most important and frequently used by traditional healers in Palakkad district of Kerala, India, for dermatological infections/diseases and gastrointestinal disorders.
- Leaves were the most frequently used plant parts, and most of the medicines were prepared in the form of paste and administrated orally.
- Tubers (corms) are used for treatment of boils and hemorrhoid and poultices used as anti-rheumatic in Philippines.
- Root is carminative, restorative, stomachic and tonic.
- It is dried and used in the treatment of piles and dysentery.
- Fresh root acts as an acrid stimulant and expectorant, it is much used in India in the treatment of acute rheumatism.
- Tuber is used to prevent sagging belly in women and enlargement of the bladder.
- They are also used to trim the body and clear the complexion, to prevent palpitations in older people, and to stop the formation of excess fat and solidified fatty deposits in the body.
- Paste of the tuber is applied externally to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
- Paste of the tuber mixed with honey and clarified butter is applied to alleviate filaria.
- For piles, Elephant Yam and Mahua flowers are pounded and taken twice a day for one month.
- Corm and the seeds are used as irritants and relieve the pain of rheumatic swellings when applied externally.
- Crushed seed relieves tooth-ache.
- It is used for treating Intestinal disorders, Gall Bladder Pain and Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Elephant Yam
- Elephantiasis: Tuber of Elephant Yam is made into paste after adding with ghee and applied over the leg affected with elephantiasis and swelling of the joints.
- Indigestion: Juice of Elephant Yam is consumed in a dose of 10 ml to treat piles, intestinal worms, indigestion and hepatomegaly.
- Amenorrhea: Tuber of Elephant Yam is boiled and consumed in a dose of 15-20 g to treat amenorrhea.
- Asthma: Cold infusion of tuber of Elephant Yam is given in a dose of 15-20 ml to treat cough and asthma.
- Hemorrhoids: Dried powder of the tuber of Elephant Yam is mixed with buttermilk in a dose of 3-4 g and consumed to treat hemorrhoids and piles.
- Tumors: Tuber of Elephant Yam is covered with mud, dried under sunlight and later burnt. The ash obtained is consumed in a dose of 5-6 g to treat cases of internal growth like tumors.
- Stings: Make a paste of the leaves of Yam Rhizome. Apply on the affected area.
- Piles: Cut the cleaned Yam Rhizome in small pieces and dry in sunlight. Now finely powder them and store in a container. Take One tablespoon with water twice a day.
- Obesity: Prepare a juice of Bitter Gourd and Yam Rhizome. Drink it once a day for a week. (Caution: Excessive use may cause toxicity.)
- Night sweat: Take equal quantity of Rehmannia, Cornus Florida, White Peony, Yam Rhizome, Hoelen, Water Plantain, Anemarrhena and Phellodendron Amurense. Powder all ingredients together. Have one teaspoon with milk at night.
- Energy Tonic: Take dried form of 10 gram Burdock, 10 gram Chaenomeles Speciosa, 20 gram Mandarin Orange, 10 gram Acorus Gramineus Rhizome, 10 gram China Root, 20 gram Snow Lotus Root, 10 gram Glehnia Root, 20 gram Yam Rhizome, 10 gram Ginseng Siberian Root, 20 gram Stevia Leaves, 10 gram Licorice and 5 gram Clove Bud. Put all ingredients in a grinder. Make powder. Store in a jar. Boil half a teaspoon in a cup of water. Strain. Have it early in the morning. This tonic increases your stamina and feels you energetic whole day.
- Sexual Health: Take equal amount of Morinda Officinalis, Dong Quai, Eucommia, Aconitum Carmichaelii, Goji Berry, Garlic Chives, Ginseng Korean, Cinnamon, Yam Rhizome, Cornus Officinalis, Cnidium, Rehmannia, Cynomorium Songaricum, Cuscuta Chinensis and Horny Goat Weed. Following herbs, in conjunction are beneficial for male and female Sexual energy. It increases vitality and stamina.
- Reproductive problems of Male: Take equal amount of Ginseng Korean, Astragalus, Dong Quai, Rehmannia, Cuscuta Chinensis, Goji Berry, Fennel, Zanthoxylum Piperitum, Morinda Officinalis, Cornus Officinalis, Polyporus Umbellatus, Psoralea, Achyranthes Aspera, Yam Rhizome, Horny Goat Weed, Eucommia, Cinnamon, Paeonia Suffruticosa, Raspberry, Chinese Knotweed, Anemarrhena , Atractylodes Macrocephala, Water Plantain, Senega, White Peony, Anemone Chinensis and Honey. Following herbs, in conjunction are beneficial for Reproductive Problems of Males and act as a powerful kidney tonic.
Culinary Uses
- Tubers eaten after thorough cooking in sayur or as a titbit, sliced, baked or boiled especially in Indonesia.
- Very young shoots still in the bud are used as vegetables in Indonesia.
- Leaves are also used as a tobacco substitute.
- Young petioles of young unexpanded leaves are edible when thoroughly cooked and considered a delicacy in the Philippines.
- Indigenous Sakai eats the tubers after pounding and prolonged cooking in Malaysia.
- Starch from the tuber is used as food for diabetic persons, and the petiole is soaked in water and cooked in Vietnam.
- Tuber may be used as a source of starch and alcohol and have been used to prepare a flour for bread-making.
- Corm is prepared in curries, fried or used as pickles and chutney, while the above-ground parts are also eaten as green vegetable in India.
- In Bangladesh, it is usually eaten as mashed and added to curries and, more rarely, pickles.
- Leaves are also eaten and are used to make a special leaf based curry.
- In Bihar, it is used in oal curry (i.e. Elephant Foot curry), oal bharta or chokha, pickles and chutney.
- Oal chutney is also called Barabar chutney as it has mango, ginger and oal in equal quantities, hence the name barabar.
- In Chhattisgarh, it is eaten as curry and is a delicacy among people.
- It is used to make chips, fries, stews, soups, casseroles, and others just like sweet potatoes.
- It is also widely used in the form of flour to make slices of bread.
- Young leaves and petioles are cooked and used as a vegetable.
Selection and Storage
Elephant foot yam can be bought from the nearby market. It is readily available in monsoon season. Always try to select fresh, whole, smooth and small vegetable and avoid one that is large and dried. Also, discard one with bruised skin and irregular shape. It can be stored up to one month at room temperature in dry, cool and well ventilated place. You can enjoy it by making bhajia, sabji, pakaude, achaar (pickle) and add it while preparing various dishes.
Recipes
Elephant Yam in dry gravy
Ingredients
- Elephant Yam – 500 gm.
- Oil- 2 tbsp.
- 2 onions– sliced
- Ginger paste- 1 tsp.
- 2 medium Tomatoes – fresh and pureed
- Cumin seeds– 1/2 tsp.
- Asafetida– a pinch
- Garam masala- 1 tsp.
- Turmeric powder- 1/2 tsp.
- Coriander powder- 1/2 tsp.
- Green chili– 2
- Salt– as per the taste
- Lemon juice- 1 tsp.
- Green coriander leaves- chopped (for garnishing)
- Oil- for frying
- Water- 2 cups
Directions
- Cut the Elephant Yam into small cubes. Wash them thoroughly and dry them.
- Take a kadhai. Pour oil in the kadhai. When the oil becomes hot, deep fry the Elephant Yam cubes. When they start turning in golden brown color, remove them. Press the cubes and again deep fry them. Remove it and keep on the tissue paper to soak extra oil.
- In another pan, pour 2 tbsp. oil. Add cumin seed, Asafetida. When the seeds start crackling, add the slice onion.
- When onion starts turning the color and becomes transparent, add the ginger paste. Sauté for 2 minutes and then add turmeric powder, coriander powder. Fry for 2-3 minutes.
- Then add tomato puree and green chili. When oil starts separating from the mixture, add the fried suran cubes and mix them, so that the Elephant Yam pieces are coated well. Add the water as per the requirement.
- Now, add the salt as per taste and the garam masala powder.
- Cook until the gravy thickens. Add lemon juice, stir for one minute and turn off the gas.
- Garnish it with the fresh coriander leaves
- Serve the delicious Elephant Yam with hot chapatis/ rice.
Elephant foot yam stir-fry
Ingredients
- Elephant foot yam –Half yam
- Turmeric powder – ½ tbsp
- Red chili powder – ½ tbsp
- Garlic – 4 cloves[mashed]
- Curry leaves –1 spring
- coriander leaves –2 springs
- Coconut – 3 tbsp
- Asafoetida – ½ tsp
- Tamarind – 1 inch piece
- Mustard seeds – 1 tbsp
- Chana dal – 1 tbsp
- Urad dal – 1 tbsp
- Oil – 2 tbsp
- Salt to taste
- Water as needed
Directions
- Cut black outer layer (skin) of Elephant foot yam.
- Wash & cut into small cubes.
- In a bowl add water, turmeric powder, tamarind & salt mix well.
- Add cubed Elephant foot yam and soak it for 15 min.
- Heat oil in a pan, add mustard seeds let it splutter.
- Add chana dal, urad dal, curry leaves & garlic saute
- Add asafoetida, coconut saute for a min.
- Add soaked Elephant foot yam, saute for 3 min
- Add turmeric & red chili powder saute.
- Add water & salt cook till soft
- Finally add coriander leaves, cut off heat, serve hot with rice.
Other Facts
- Tubers are sliced, sun-dried, pounded to a meal, boiled and fed to pigs, while the older petioles are boiled and used as pig food in the Philippines.
Precautions
- Plant is toxic fresh and, if eaten, makes the mouth; tongue and throat feel as if hundreds of small needles are digging in to them.
- People with a tendency to rheumatism, arthritis, gout, kidney stones and hyperacidity should take especial caution if including this plant in their diet.
- Patients suffering from Asthma/ chronic cold should not consume Elephant Yam.
- Pregnant ladies or breast-feeding women should also consume Elephant Yam only after taking the advice from the doctor.
- Patients suffering from sinus infections should also avoid eating Elephant Yam.
- Intake of elephant foot yam juice may cause side effects like vomiting, nausea, diarrhea and headache.
- It should not be taken by persons with skin diseases and suffering from bleeding disorder or raktapitta.
- Avoid in blisters, dryness and persistent bitter taste in the mouth, red eyes, hot and watery face, and inflammation of the body, skin diseases and high pitta.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=506752#null
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Amorphophallus+paeoniifolius
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=AMPA13
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amorphophallus_paeoniifolius
https://wikivisually.com/wiki/Amorphophallus_paeoniifolius
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=102457
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-8254
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/244525
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Elephant%20Foot%20Yam.html
https://florafaunaweb.nparks.gov.sg/Special-Pages/plant-detail.aspx?id=1659
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/AMUCA
http://www.medicinalplantsindia.com/elephant-foot-yam.html
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Amorphophallus+paeoniifolius
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/180662/#b
Comments
| Elephant Yam Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Elephant Yam |
| Scientific Name: | Amorphophallus paeoniifolius |
| Origin | Tropical Asia. It grows wild in Sri Lanka, the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia and other Southeast Asian countries. |
| Colors | Maturing from green to bright red |
| Shapes | Obovoid berry crowded on the spadix, 1.5 cm diameter, two to three seeded |
| Taste | Sweet, bitter |
| Health benefits | Lowering Cholesterol, Cardiovascular Health, Anticoagulant and Anti Inflammatory, Cancer Prevention, Slow down ageing, Diabetes, Detoxification, Anti-Inflammatory, Memory and Concentration, Boost Immunity, Cures Piles, Women Health, Cooling effects, Good for Digestion, Slimming food, Skin and Hair Care Benefits |
| Name | Elephant Yam |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Amorphophallus paeoniifolius |
| Native | Tropical Asia. It grows wild in Sri Lanka, the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia and other Southeast Asian countries. It is also found in India, southern China, New Guinea, Northern Australia and Polynesia |
| Common Names | Cheeky Yam, Corpse Flower, Corpse Plant, Elephant Foot Yam, Elephant Yam, Stink Lily, Telinga Potato, Voodoo Lily, White-Spot Giant Arum, Sweet yam, pungapung |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic : Batata El-Feel Assamese: Ol, Ol Kochu, Baghraj, Ol/ Ol-kochu, Ol kochu Bengali: Shuran, Ole Bangladesh : Ol Brazil : Inhame Gigante, Toyoeu Burmese : Wa Chinese : Bai Ban Mo, Bai Ban Mo Yu, yóu bǐng mó yù ( 疣柄魔芋), Nán tiānxīng (南天星), Léigōng chòng (雷公銃), Shu Yu, Shan Yao , Xie bn yu, Nan xing tou, Nan yu, Ji zhao yu, Chou mo yu Czech : Zmijovec Zvonovitý Danish : Elefantyams Dutch: Olifantenyam English: Sweet yam, Telinga potato, elephant foot yam, whitespot giant arum, elephant yam, pungapung, telingo-potato, voodoo lily, Cheeky yam, Corpse flower, Corpse plant Fijian : Daiga, Vaaga, Via Gaga, Viamiloa Flemish : Olifantspoot French : Kouniak D’annam, Pomme De Terre De Télinga, amorphophallus campanule German: Elefantenkartoffel, Glockendickkolben Greek : Elephantini Dioscorea Gujarati: Surana Guyana : Hig Tannia Hebrew : Amorpha Hindi: Alu, Jangli Suran, Kanda, Madana Masta, Zaminkand, Suran- Kand, Gandira, Zamin-Kand, Jimikand Indonesia : Badur, Suweg, Iles-Iles, Kembang Bangah, Kembang Bangke, Sobek, Walur, Ileus, Achung Japanese : Konjac, Konniaku, Konnyaku Kannada: Choorana, Choorna Gedde, Gandira, Kanda Gedde, Panjaragedde, Soorana Gedde, Suvarna-Gadde, Suvarna Gedda, Suvarna Gedde, Suvarna-Guddab, Suvarna Gedde Khmer: Toal Kiribati : Babai Konkani: Soorna, Suma Laos : Duk Düa, Houo Ka Bouk, Kabuki Malayalam: Cena, Mulenschena, Schena, Karunakarang, Kizhanna, Cinapavu, Kattuchena, Chena, Cena Karana Malaysia : Hakai, Loki, Lokai, Ubi Kekek Manipuri: Haopan Marathi: Suran Marquesan : Teve Myanmar: Wa Nepali : Wol, ole New Caledonia : Pindu Niuean : Teve Oriya: Farasi, Olua, Owa, Samba, Simba Persian: Zamin-Kand, Zaminkand Philippines : Alu Pahi, Bagong, Anto, Oroi, Pamangkilon, Bagang, Bagong, Tigi-Nga-Magmanto, Tokod-Banua, Apon, Apong- Apong, Pungapung Polish : Dziwidło Dzwonkowate Portuguese : Jararaca Mirim, Batata De Telinga Punjabi: Jimikand, Zimikand Rarotongan : Teve Samoan : Talanu, Teve Sanskrit: Suranah, Alu, Arsaghna, Arshoghna, Arsoghna, Bahukanda, Durnamari, Kanda, Kandala, Kandanayaka, Kandarha, Kandashurana, Kandi, Kandula, Kandvardhana, Kanthalla, Kunda, Ola, Olla, Rutchyakanda, Sala, Sthulakandaka, Sukandi, Surana, Suranah, Suranaka, Suranakanda, Suvitra, Tivrakantha, Vajrakanda, Vajrandi, Vatari Siddha: Karnsa Spanish : Patata De Telinga, suran Sri Lanka : Kidaran Tajik : Batat, Kartoshkai Shirin Tamil: Karakarunai, Karnai Kilangu Kara – karunai, Karnai Kilangu, Karunaikkalang, Karunaikkilhangu, Karak Karunai, Karikkarunai, Anaittantu, Karukkarunaikkilangu, Karunai- K-Kilanku, Karunai-T-Tantu, Karakarunai, Karunai Kizhangu, Karakkaranai, Karuna Kalang, Karak-Karunai, Senai Kizhangu, Boomi Sallaraikilangu, Karunaikkishangu, Kiccilikkizanku, Camattilai, Cenai, Cirramitakkarunai, Curanam, Kantai, Karanai, Karunai, Karunaippala, Malaiyalaccenaikkilanku, Perunkarunai, Pulikkarunai, Taittiyamatanacceti, Taittiyamatanam Telegu: Daradakandagadda, Ghemikanda, Kanda, Kandagodda, Manchi- Kindaguddae, Manchikanda, Poti-Kunda, Potikanda, Thiya-Kandha, Manchi Kanda Thai: Buk Khang, Man-Suran, Ukkhungkhok, buk Tongan : Teve Tulu: Parinki Gadde, Pariṅkigaḍḍè, Sūraṇa Turkish : Amorfotallus Tuvalu : Puluka Unani: Soorana, Zamin-qand, Zamikand Urdu: Hati Yam, Jangli Suran, Zaminqand Vietnam : Khoai Nưa, Nưa Chuông |
| Plant Growth Habit | Stout deciduous, herbaceous aroid shrub |
| Growing Climates | Secondary forest, shrub forests, coastal monsoon forests and thickets or highly disturbed areas and in dappled shade or fully exposed areas and grasslands in arid valley areas |
| Soil | Prefers friable, deep loamy non alkaline soil. It is hardy in tropical areas when planted in rich, well-drained soil in a sheltered, humid position. It does best in partial shade. It succumbs to waterlogging and heavy clayey soil; hence, good drainage is essential |
| Plant Size | About 1.5 m |
| Corm | Depressed-globose, to about 30 cm in diameter, about 20 cm high, dark brown, with distinct annular root scars. The pustular surface of the stem is attractively blotched with paler shades of green |
| Leaf | Leaf usually solitary divided into three major segments, which is further subdivided into oval or elliptic lobes about 6 cm long, leaf stalk up to 1 m or more, background color pale to dark green with large and small pale blotches and numerous tiny dark dots |
| Flower | Flowers small, yellowish crowded into a stout column (spadix), male above and female below; the column is crowned by a reddish-brown bladder like appendage, and the whole inflorescence is subtended by a large red brown bract |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Obovoid berry crowded on the spadix, 1.5 cm diameter, two to three seeded |
| Fruit Color | Maturing from green to bright red |
| Fruit Texture | Starchy |
| Propagation | Offsets of the corm or by fresh seed |
| Flavor/Aroma | Fresh inflorescence emits an odor reminiscent of rotting meat which attracts pollinating carrion flies and beetles |
| Taste | Sweet, bitter |
| Plant Parts Used | Whole plant, dried corm, Rhizome |
| Health Benefits |
|