Common-cypress, Italian cypress, Mediterranean cypress, Pyramidal-cypress, evergreen cypress, graveyard cypress, Tuscan cypress, pencil pine, funeral cypress are few of the popular common names of the plant. Genus name is the Latin name for Italian cypress (Cupressus sempervirens.) Specific epithet means ever green. The term cypress has been derived from the old French word ‘cipres’ that was introduced from Latin ‘cyparissus’. While most species of cypress are trees, some are also shrubs. The tree has been planted as a timber crop in areas from the warm temperate zone to the tropics, often being grown in east Africa. It is widely grown as an ornamental.
Cypress Facts
| Cypress Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Cypress |
| Scientific Name: | Cupressus sempervirens |
| Origin | Eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, southern and coastal Bulgaria |
| Colors | Green when young and shining yellowish-gray when ripe |
| Shapes | Male cones are 4 to 8 mm, the female are 25 to 40 mm. They are elliptical-oblong (rarely globose), with 8 to 14 short and obtusely spiked scales |
| Health benefits | Reduces Inflammation, Respiratory Issues, Varicose Veins, Skin Conditions, Treats Fungal Infections, Hair Health, |
| Name | Cypress |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cupressus sempervirens |
| Native | Eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, southern and coastal Bulgaria, southern coastal Croatia, southern Montenegro, southern Bosnia and Herzegovina, southwestern Macedonia, southern Greece, southern Turkey, Cyprus, northern Egypt, western Syria, Lebanon, Malta, Italy, Palestine, Israel, western Jordan, South Caucasus, and also a disjunct population in Iran |
| Common Names | Common-cypress, Italian cypress, Mediterranean cypress, Pyramidal-cypress, evergreen cypress, graveyard cypress, Tuscan cypress, pencil pine, funeral cypress |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Cypress Albanian: Selvi, qiparis Arabic: Shajar alsuruw (شجر السرو ), sru almutawasit (سرو المتوسط), Saro, Shajarat el-Saro, Saro al-bahr al-abiadh Armenian: Nochi (նոճի), Nochi mshtadalar (Նոճի մշտադալար) Azerbaijani: Sərv, Adi sərv Basque: Nekosta, Altzifre arrunt, nekosta arrunta Belarusian: Kiparys (кіпарыс), Kiparys viečnazialiony (Кіпарыс вечназялёны) Bengali: Saralabargīẏa cirahariṯ br̥kṣabiśēṣa (সরলবর্গীয় চিরহরিৎ বৃক্ষবিশেষ) Bosnian: Cempres Bulgarian: Kiparis (кипарис), Obiknoven kiparis (Обикновен кипарис) Catalan: Xiprer, Xiprer mediterrani, Xifrer, Xiprer comú, Xiprer negre Cebuano: Sipres Chichewa: Paini Chinese: Bǎi (柏), di zhong hai bai mu Croatian: Cempres, zimzeleni čempres Cuba: Ciprés; ciprés fúnebre; ciprés piramidal Czech: Cypřiš, cypřiš stálezelený, Almindelig Cypres, cypřiš vždyzelený Danish: Cypress, almindelig cypres Dominican Republic: Cinta Dutch: Cipres, Italiaanse cipres English: Common-cypress, Italian cypress, Mediterranean cypress, Pyramidal-cypress, evergreen cypress, graveyard cypress, Tuscan cypress, pencil pine, funeral cypress Esperanto: Cipreso, Mediteranea cipreso Estonian: Küpress Filipino: Saypres Finnish: Sypressi, Välimerensypressi French: Cyprès, Cyprès d’Italie, Cyprès sempervirent, Cyprès commun, Cyprès méditerranéen, cyprés vert, cyprès de Provence, cyprès fastigié, cyprès femelle, cyprès pyramide, cyprès toujours vert Galician: Ciprés, Alcipreste común Georgian: Cypress, maradmts’vane k’vip’arozi (მარადმწვანე კვიპაროზი) German: Zypresse, Echte Zypresse, Mittelmeer-Zypresse, Trauerzypresse, Italienische Zypresse, Atlas-; Zypresse, Immergrüne, gemeine Zypresse, immergrüne Zypresse, Säulenzypresse Greek: Kyparíssi (κυπαρίσσι), kypárissos aeithalís (κυπάρισσος αειθαλής) Gujarati: Sāyaprasa (સાયપ્રસના) Haitian Creole: Pichpen Hausa: Cypress Hebrew: בְּרוֹשׁ, Brosh matzui, tzrifi, ברוש מצוי,צריפי, ברוש מצוי Hindi: Sanauvar, Saro (सरो) Hmong: Cypress Hungarian: Ciprus, Európai valódi ciprus, Európai ciprus Igbo: Fir Icelandic: Cypress Indonesian: Cemara Irish: Cufróg Italian: Cipresso, Cipresso commune, Cipresso femmina, Cipresso italiano, Cipresso orizzontale Japanese: Saipuresu (サイプレス), Hosoitosugi (ホソイトスギ) Javanese: Cypress Kannada: Saipres (ಸೈಪ್ರೆಸ್) Kazakh: Kiparis (кипарис) Khmer: k kaoh (កកោះ) Korean: Saipeuleoseu (사이프러스) Lao: Cypress Latin: Cupressus Latvian: Ciprese Lithuanian: Kiparisas, Visžalis kiparisas Lower Sorbian: Pšawa cypresa Macedonian: Chempres (чемпрес), Običen čempres (Обичен чемпрес) Malagasy: Kypreso Malay: Cypress Malayalam: Saraḷavr̥kṣavuṁ (സരളവൃക്ഷവും) Maltese: Ċipru, Cipress kannella Maori: Kauri Marathi: Surūcē jhāḍa (सुरूचे झाड) Mongolian: Maĭls (майлс) Myanmar (Burmese): Htainn ruu pain (ထင်းရူးပင်) Nepali: Saroo (सरू) Netherlands: Italiaanse cypres Norwegian: Sypress, Ekte sypress, Vanlig sypress Occitan: Autciprés, Cipressièr, Ciprièr, Ciprès Persian: درخت سرو, سرو ناز Polish: Cyprys, Cyprys wiecznie zielony Portuguese: Cipreste, Cipreste-colunar, Cipreste-comum, Cipreste-da-itália, Cipreste-do-mediterrâneo, Cipreste-italiano, Cipreste-piramidal, Cupressus-piramidalis, Cedro-bastardo, Cipreste-comun, Cipreste-de-itália, Cipreste-dos-cemitérios Romanian: Chiparos Russian: Kiparis (кипарис), Kiparis vechnozelënyĭ (Кипарис вечнозелёный) Serbian : Chempres (чемпрес) Sesotho: Kyprese Shambala: Čempres Sinhala: Sayipras (සයිප්රස්) Slovak: Cyprus, cyprus vždyzelený Slovenian: Ciprese Somali: Beroosh Spanish: Ciprés, Ciprés común, Ciprés italiano, Ciprés del Mediterráneo, Vednozelena cipresa, ciprés mediterráneo, arbol de los cementerios Swahili: Cypress Swedish: Cypress, Kretacypress, Äkta cypress Tajik: Cарву Tamil: Puṉṉai (புன்னை) Telugu: Saipras (సైప్రస్) Thai: T̂n sị per s (ต้นไซเปรซ) Tunisian Arabic: سرول Turkish: Selvi, Akdeniz servisi, kara selvi Ukrainian: Kyparys (кипарис), Kiparis víchnozeleniĭ (Кипарис вічнозелений) Upper Sorbian: Prawa cypresa Urdu: صنوبر Uzbek: Sarv Vec: Pigno Vietnamese: Cây bách Welsh: Cypreswydden Yiddish: Seypris (סייפּריס) Yoruba: Firi Zulu: Cypress |
| Plant Growth Habit | Medium-sized evergreen coniferous tree |
| Growing Climates | Woodlands, interior valleys, and coastal mountains, disturbed areas along roadsides, gardens, parks and cemeteries |
| Soil | Thrives better than other species on rocky, dry and compact soils, even if it prefers rich, deep, moist and well aerated soil |
| Plant Size | Up to 35-40 m with trunks of 1 m in diameter, rarely over 2 m |
| Root | Large shallow root system |
| Bark | Thin, smooth and gray for quite a long time, later becoming gray-brown and longitudinally furrowed |
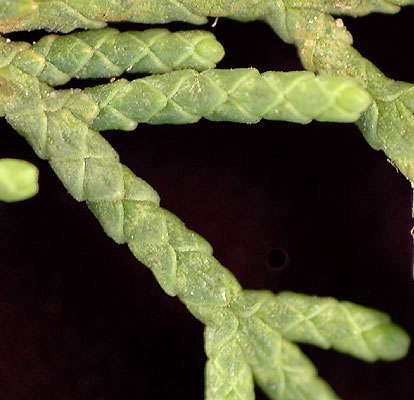
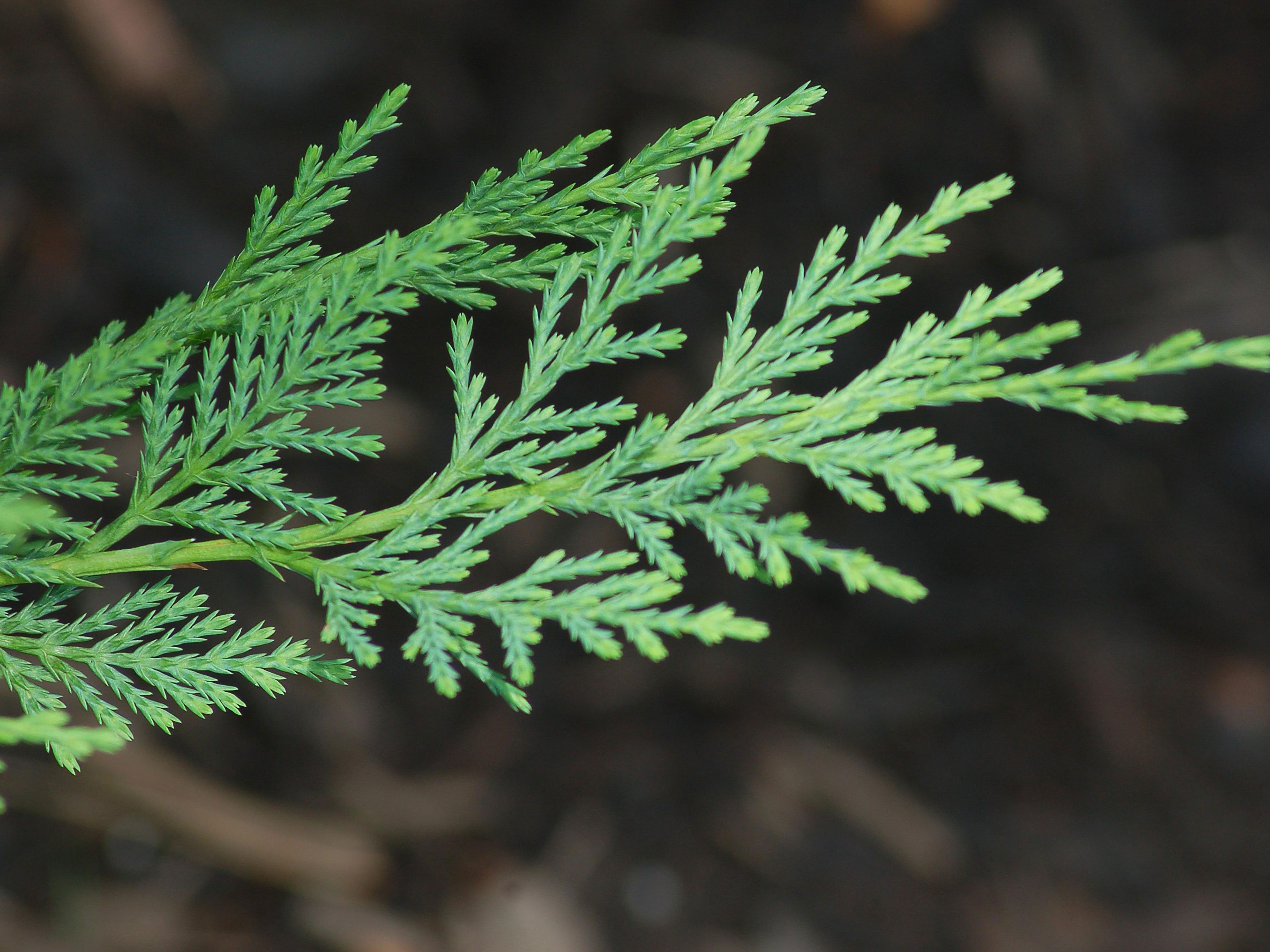
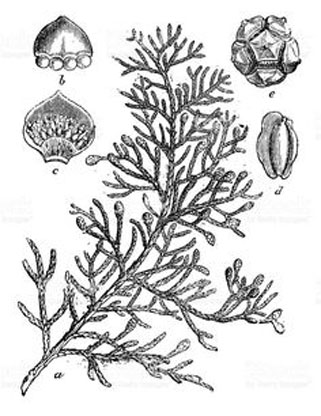
| Leaf | Leaves are scale-like, 2–5 mm long, and produced on rounded (not flattened) shoots. |
| Flowering season | January to February |
| Flower | It is monoecious. The male flower is cylindrical, 3-5 mm long, yellow when ripe. Pollination occurs from mid-winter to early spring. The female flowers are brownish-green and globose, ripening after one year |
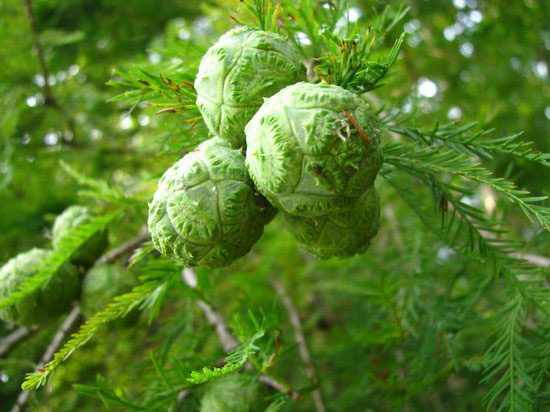
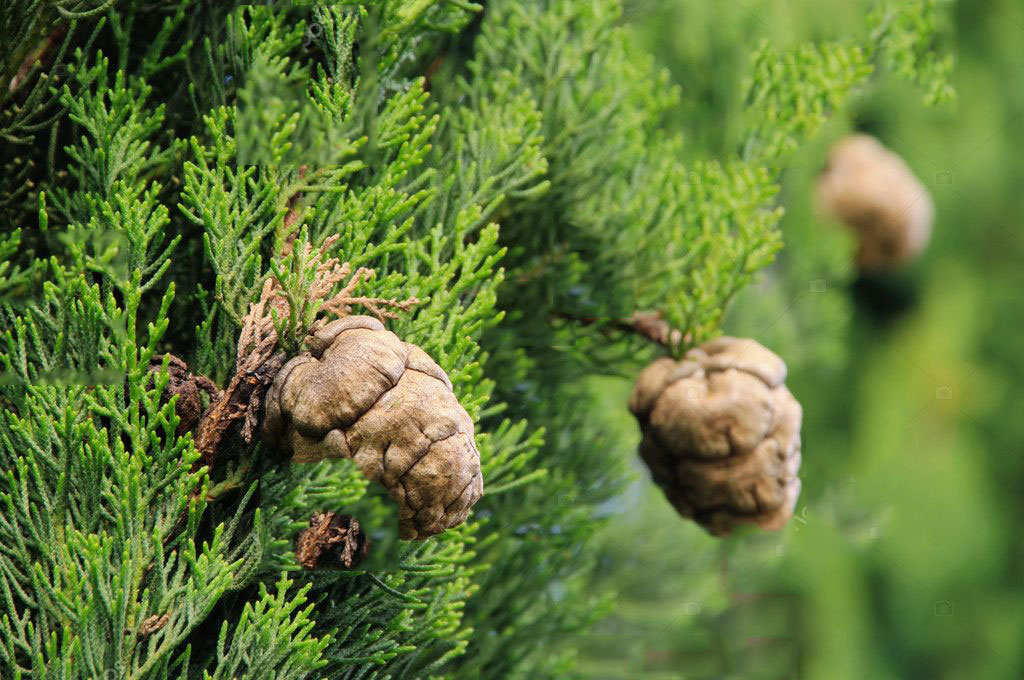
| Fruit Shape & Size | Male cones are 4 to 8 mm, the female are 25 to 40 mm. They are elliptical-oblong (rarely globose), with 8 to 14 short and obtusely spiked scales. There are 8 to 20 seeds on each scale |
| Fruit Color | Green when young and shining yellowish-gray when ripe |
| Propagation | Cutting, seed |
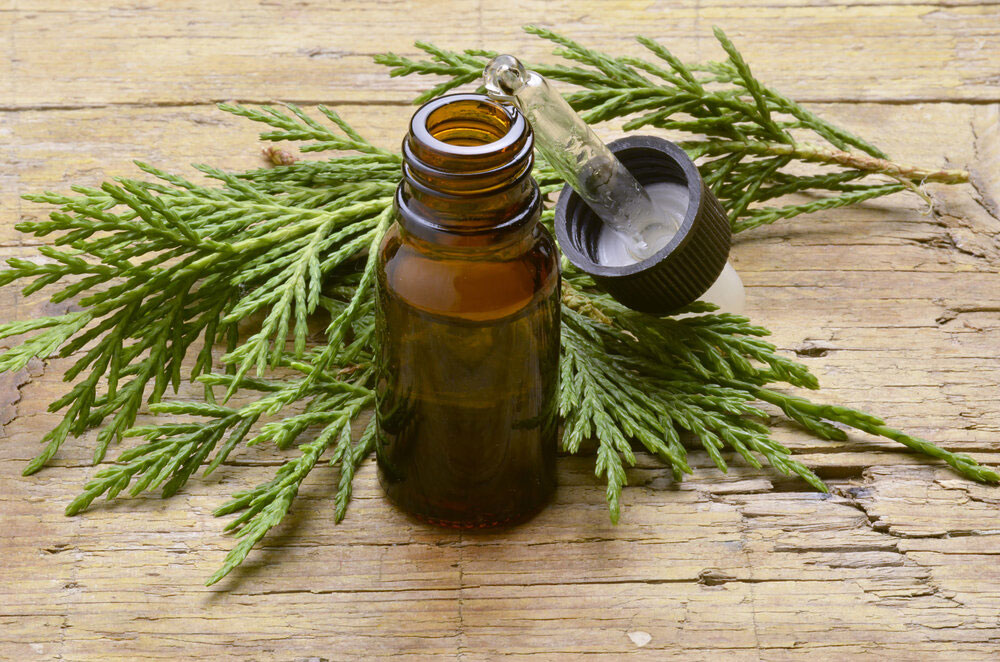
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves , cones, branches, essential oil |
| Seed | 8-20 per each scale, brown and narrowly winged, 3-5 mm long |
| Lifespan | Over a hundred years: in natural stands 200-500 year old |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Precautions |
|
Plant Description
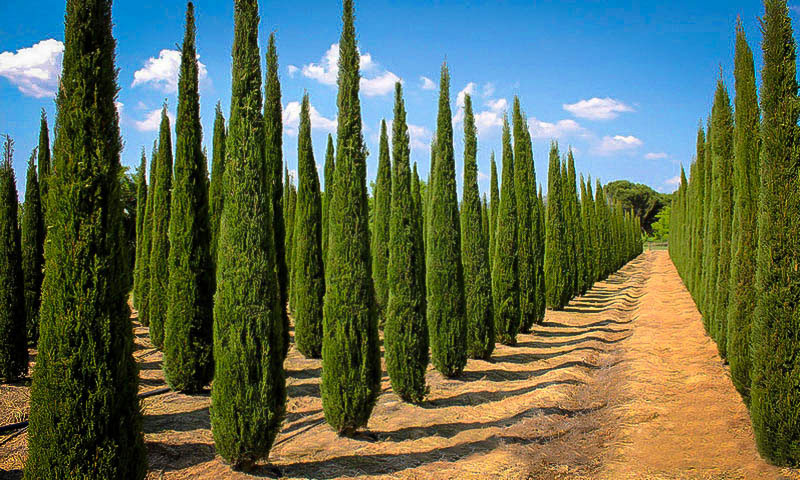
Cypress is a medium-sized evergreen coniferous tree that grows up to 35-40 m tall with trunks of 1 m in diameter, rarely over 2 m with a conic crown with level branches and variably loosely hanging branchlets. It is very long-lived, with some trees reported to be over 1,000 years old. The plant is found growing in woodlands, interior valleys, and coastal mountains, disturbed areas along roadsides, gardens, parks and cemeteries. It thrives better than other species on rocky, dry and compact soils, even if it prefers rich, deep, moist and well aerated soil. It is a pioneer species, growing quickly when young on most types of soils, including rocky and compact ones, adapted to the Mediterranean climate with dry and hot summers and rainy winters. It can form pure forests or be the dominant tree in pine forests or maquis vegetation. This cypress is widely planted as an ornamental tree, especially the columnar and conical forms, making a characteristic feature of the Mediterranean landscape.
The crown is very variable, from about as broad as it is tall with spreading branches, to the conical or columnar fastigiated form (known also as Italian cypress). The plant has large shallow root system. Bark of the tree is thin, smooth and gray for quite a long time, later becoming gray-brown and longitudinally furrowed. The foliage grows in dense sprays and closely pressed against the twigs. It is dark green in color. The leaves are scale-like, 2–5 mm long, and produced on rounded (not flattened) shoots.
Flower and Fruit
Flowers appear in early spring and may occur on 3-6 year old plants. The cypresses are monoecious wind-pollinated plants. The male flower is cylindrical, 3-5 mm long, yellow when ripe. Pollination occurs from mid-winter to early spring. The female flowers are brownish-green and globose, ripening after one year into brown-grey woody cones, ovoid-shaped, 2-4 cm long, composed of 8-14 opposite scales. Seeds are 8-20 per each scale, brown and narrowly winged, 3-5 mm long, releasing in autumn-winter.
Health Benefits of Cypress
Cypress is part of the Cupressaceae plant family, which is comprised of a wide array of trees native to various parts of the world. Some of the more well-known of these trees is the coastal redwood and giant sequoia. The essential oil that comes from the needles is very well-known and important, but concoctions can also be made from the needles and cones to treat various health issues. Listed below are some of the well-known health benefits of cypress
1. Reduces Inflammation
Cypress when consumed as a tea decoction or applied directly as a topical solution it can reduce inflammation internally and externally. If you suffer from arthritis, gout, or other inflammatory muscle conditions, it can help to relieve the discomfort and pain. Additionally, it can help to soothe the organ systems that may be inflamed by infection or nutrient deficiency, allowing the body to recover more quickly. Salve can also be applied to hemorrhoids to reduce inflammation and eliminate pain.(1)
2. Respiratory Issues
Cypress essential oil is commonly used for aromatherapy in relation to respiratory issues, but a simple tea decoction of the needles can also deliver an effective respiratory remedy if you suffer from asthma, bronchitis, nasal drip, chronic congestion, or any other inflammation of the respiratory tracts. This should only be consumed on a limited basis, as the powerful chemical components of the tea should not be overused. (2)
3. Varicose Veins
Though the exact pathway of this remedy is not completely understood, cypress needles and decoction have been used to eliminate varicose veins for many years. Traditional medicine strongly supports its use, although the modern medical community has not confirmed this particular application.(3)
4. Skin Conditions
Acne is a severe skin condition which affects millions of people around the world, but over the centuries, traditional remedies have become some of the most relied solutions for this widespread problem. Create a salve out of a decoction of needles and carrier oil, can be applied to the skin to prevent bacterial infections (which acne is caused by) and reduce the inflammation and swelling of the sebum glands that can worsen acne. Additionally, these cypress salves are commonly used to speed wound healing and reduce the appearance of scars and blemishes on the skin.(4)
5. Treats Fungal Infections
One of the most popular applications of cypress is as a foot bath. By placing the cones in a hot water bath, many of the beneficial organic compounds of the plant are released into the water, and can considerably boost the health of your feet. Extremities are prime locations for fungal and bacterial infections, and cypress can stop your feet from sweating, which is a major cause of fungal infections like Athlete’s foot. Prevent that condition with cypress foot baths, particularly if you are prone to being on your feet or wearing shoes for extended periods of time. (5)
6. Hair Health
When the decoction is applied to the hair and scalp, it can encourage healthier follicle beds and glands, resulting in stronger, richer hair that is less prone to damage and maintains its rich luster. It can also help to reduce dandruff by preventing the skin from drying out.(6)
Traditional uses and benefits of Cypress
- Cones and young branches are anthelmintic, antipyretic, anti-rheumatic, antiseptic, astringent, balsamic and vaso-constrictive.
- Taken internally, it is used in the treatment of whooping cough, the spitting up of blood, spasmodic coughs, colds, flu and sore throats.
- Applied externally as a lotion or as a diluted essential oil (using an oil such as almond), it astringes varicose veins and hemorrhoids, tightening up the blood vessels.
- Foot bath of the cones is used to cleanse the feet and counter excessive sweating.
- Extracted essential oil should not be taken internally without professional guidance.
- Resin is obtained from the tree by making cuts in the trunk.
- This has a vulnerary action on slow-healing wounds and also encourages whitlows to come to a head.
- An essential oil from the leaves and cones is used in aromatherapy.
- Drug was used externally for head colds, coughs and bronchitis.
- Decoction of the cones and leaves was used in a sitz bath three times a day for one week for hemorrhoids.
- Cones and leaves were used internally as an astringent.
- Externally, the extract of the cypress was incorporated in preparations (ointments and suppositories) and used to treat hemorrhoids, varicose veins and venous circulation disorders.
- The essential oil was used as antiseptic and an antispasmodic for stubborn coughs.
- Cypress was also described as deodorant, and diuretic, to promote venous circulation to the kidneys and bladder area, and to improve bladder tone and as a co-adjuvant in therapy of urinary incontinence and enuresis.
- Cypress is effective in treating Varicocele. Varicocele is the growth of veins in the scrotum. It reduces the swelling and pain in the scrotum.
- It is a good herbal remedy for curing male Infertility. Cypress is useful in enhancing sperm quality and count.
- It provides strength to the nose capillaries and stops nose bleeding. It helps to prevent blood loss and soothes cuts, sores, and wounds.
- It is a good herbal remedy for Menopause and Metrorrhagia.
- It acts as an Astringent and used externally to treat Acne. It makes the skin clear and glowing and removes Pimples, Blackheads, and oily Skin.
- Cypress cleanses the mouth and provides strength to teeth. It prevents Gingivitis and other Tooth Diseases.
- It reduces the excessive sweating and excessive fluids in the body.
- It is antiseptic in nature and prevents the body from Infections. It is a good herbal remedy for urinary tract infections.
- It acts as a hair tonic that nourishes the hair and promotes length. It rinses the scalp and removes excess fat and cures Dandruff.
- Cypress is hepatic in nature and protects the liver against diseases. It maintains the healthy liver and modulates the proper discharge of bile.
- The herb is beneficial for the respiratory system. It increases the effectiveness of the lungs and makes breathing easier. It clears up the Congestion, Cough, and Phlegm from the respiratory tract and lungs.
- It resolves bleeding disorders related to circulation and inflamed veins.
- Make a paste by crushing its leaves and apply on fresh Wounds. This helps in quick welding and stops the flow of blood.
- It keeps a good care of the circulatory system in all aspects
Other Facts
- An infusion of the wood is used in footbaths to combat perspiration of the feet.
- It is cultivated as an ornamental and timber tree.
- Its wood is used for furniture, veneer, door frames, and window frames.
- An essential oil is distilled from the shoots and it is used in perfumery and soap making.
- It is also planted as a windbreak in agricultural areas.
- The tree also has symbolic and social value in Mediterranean areas, and is commonly found in cemeteries.
- The species is very long-lived, with some trees reported to be over 1,000 years old.
- It is also the traditional wood used for Italian harpsichords.
- The wood is suitable for building uses, cabinet making, wardrobes, small carpentry, exterior woodworks (doors, windows, garden furniture, etc.) and ship building since it retains its fragrance, repels moths and is impervious to woodworm.
- It is also used for coffins.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=183456#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/cupressus_sempervirens.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=12665
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Cupressus+sempervirens
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/17105
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=a162
http://www.floracatalana.net/cupressus-sempervirens-l-
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CUSE2
https://www.conifers.org/cu/Cupressus_sempervirens.php
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cupressus_sempervirens
http://iosrphr.org/papers/v6i6V2/H066026676.pdf
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2748781
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CVBSE