Melothria pendula is a plant whose name comes from the Greek word Melothron, which means “apple” or “little apple.” The plant’s special name, “pendula,” comes from the way it grows, which is hanging down. This plant is common in the southeast of the United States. It looks like a cucumber that has been grown in a garden. It has small yellow flowers, leaves that look like cucumber leaves and grow in a similar way. When they are still green, the young berries of this plant look a lot like tiny watermelons. Melothria pendula is a useful and versatile plant that can be a great addition to any yard or landscape.
Creeping Cucumber Facts
| Creeping cucumber Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Creeping cucumber |
| Scientific Name: | Melothria Pendula |
| Origin | Mexico, the Caribbean, Central America, and South America |
| Colors | Green or yellow when ripe |
| Shapes | Tiny, smooth, and watermelon-like berry, oblong-elliptic, 10 to 19 millimeters long, about 12 millimeters in diameter |
| Taste | Sweet, cucumber-like taste |
| Health benefits | Anti-inflammatory properties, Antioxidant properties, Digestive health, Immune-boosting, Wound healing, Respiratory Health, Skin Health, Cardiovascular health |
| Name | Creeping cucumber |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Melothria Pendula |
| Native | Mexico, Caribbean, Central America, and South America, but it has since spread to other parts of the world, including parts of East Asia, Africa, and North America |
| Common Names | Creeping Cucumber, Drooping Melonette, Guadeloupe Cucumber, Little Cucumber, Squirting cucumber, Wild cucumber, Small wild cucumber, Meloncito, Diversely-leaved melothria, climbing cucumber, speckled gourd |
| Name in Other Languages | Adi: Yongkoyomi Brazil: Cereja de Purga, Pepininho-do-Mato, Pepiniculo Chinese: Mei zhou ma gua jiao er (美 洲马瓜交儿), páxíng huángguā (爬行黄瓜), Chuí guā guǒ (垂瓜果) Danish: Klatre-agurk Dutch: Klimkomkommer, Guadeloupe-komkommer English: Creeping cucumber, Drooping melonette, Guadeloupe cucumber, Squirting cucumber, Wild cucumber, Small wild cucumber, meloncito Finnish: Köynnöskurkku, Riippaviidakkokurkku French: Melonettes, Mélothrie de la Guadeloupe, Mélothrie pendant, cornichon grimpant, concombre de Guadeloupe, Konkonm pwazon, Melonettes German: Klettergurke, Guadeloupe-Gurke Gujarati: Gometi (ગોમેટી) Hindi: Rengani kheera (रेंगनी खीरा), Amantamul (अमन्तमूल), Tarali (तरली), Ban Kakra (बन काकड़ा) Italian: Cetriolino rampicante, cetriolo di Guadalupa Japanese: Kuwazuikazura (クワズイカズラ), Amerikasuzumeuri (アメリカスズメウリ) Kannada: Karagala Konkani: Goimtini (गोयंटिणी) Korean: Deong-gul oi (덩굴오이) Malayalam: Njerinjampuly (ഞെരിഞമ്പുളി) Mexico: Sandiita, Pepinillo silvestre, Pepinito, Chilacayotito, Tomatito, Esponjuela, Mayil ak, Sandı´a de rato´n, Pentocz, Sandı´a de pa´jaro, Sandı´a chiquita, Sandı´a tzitzi, Sin˜a spuun, Sandı´a tuul, Sandı´a kaan, Sandia xiw, Sandı´a xtulub Manipuri: Lam sabot Marathi: Gometi (गोमेटी) Nepali: Ban kankro (बन कांकरो) Norwegian: Klatreagurk Oriya: Mataka Philippines: Pipinong-gubat Portuguese: Pepino trepador, pepino-de-guadalupe, Melotria pendula, Melancia-pepino, Abobrinha-do-mato, Abóbora-do-mato, Cereja-de-purga, Guardião, Melão-de-beija-flor, Melão-de-morcego, Pepino-bravo, Pipino-silvestre, Tayuya-miúdo Russian: Polzuchiy ogurets (ползучий огурец) Sanskrit: Amlavetasah (अम्ळवेतसः), amlavetasa (अम्लवेतस) Spanish: Pepinillo del Diablo, pepino trepador, Meloncito, Pepinillo silvestre, Pepinito, guajillo, Chilacayotito, Tomatito, Sandia de raton Suriname: Sneki Komkomro, Sneki-komkoro Swedish: Hängmelotgurka, Klättergurka Tamil: Pulivanci (புளிவஞ்சி) Telugu: Adavi donda (అడవి దొండ), tiyyadonda (తియ్యదొండ) |
| Plant Growth Habit | Short lived, slender, twining , herbaceous perennial prostrate or climbing vine |
| Growing Climates | Mixed forests, valleys, moist places, bottom land hardwood forests, along creeks and streams, on moist roadsides, in disturbed areas, understory of forests or along the edges of clearings |
| Soil | Prefers well-draining soils that are rich in organic matter. It can grow in a wide range of soil types, including loam, sandy loam, and clay soils. However, the soil should not be waterlogged, as this can lead to root rot |
| Plant Size | Up to 6 feet in length |
| Root | Fibrous root system that spreads out horizontally along the surface of the soil |
| Stem | Thin, flexible, and twining, allowing it to climb and attach to any available support |
| Bark | Typically light brown in color and may have small cracks or fissures on its surface |
| Leaf | Leaves are alternate, petiolate, ovate to cordate in outline, entire to 3-5 lobed, with entire to remotely toothed margins. The surface of the leaf blade is rough pubescent |
| Flowering season | May-August |
| Flower | Small and greenish-yellow, with five petals fused together to form a tube shape. They are borne on long, slender stems that arise from the leaf axils |
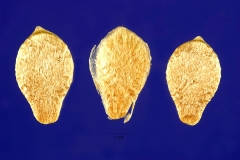
| Fruit Shape & Size | Tiny, green to black, smooth, and watermelon-like berry, oblong-elliptic, 10 to 19 millimeters long, about 12 millimeters in diameter |
| Fruit Color | Green or yellow turning to purplish-black when mature |
| Seeds | Small, oval-shaped, and black. They are about 2-3 mm long and have a hard, shiny outer coat |
| Aroma | Fresh and mildly sweet, with a hint of cucumber and a slightly herbal undertone |
| Taste | Sweet, cucumber-like taste |
| Plant Parts Used | Root, leaf, tendrils, fruit |
| Propagation | By seeds, stem cuttings, or root division |
| Lifespan | One year |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
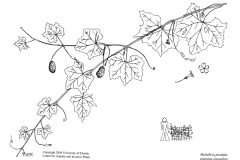
The climbing cucumber is a plant that can grow flat or climb up to 6 feet high. It is a short lived, slender, twining, herbaceous perennial prostrate or climbing vine that grows in mixed forests, valleys, wet areas, bottom land hardwood forests, along creeks and streams, on moist roadsides, in disturbed areas, the understory of forests, or along the edges of clearings. The plant grows best in soils that drain well and have a lot of organic matter. It can grow in loam, sandy loam, and clay soils. But it’s important to keep the dirt from getting too wet, because that can lead to root rot.
Roots
As for the root system of the creeping cucumber, it is a fibrous root system that spreads out horizontally along the surface of the soil. These roots are relatively shallow and do not penetrate deeply into the soil.
Roots of the creeping cucumber play an important role in the plant’s survival and growth. They absorb water and nutrients from the soil and transport them to the rest of the plant. The fibrous nature of the roots allows them to efficiently extract water and nutrients from a large area of soil, which helps the plant to thrive even in nutrient-poor environments.
Stem
The stem is green and cylindrical, with small, triangular leaves that are attached to the stem by long, thin stems called petioles. The stem of creeping cucumber is often used in traditional medicine for its various health benefits. It contains a variety of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, that are believed to support overall health and wellness.
Bark
The bark of creeping cucumber is a thin, fibrous layer that covers the outside of the plant’s stems. The bark of creeping cucumber is typically light brown in color and may have small cracks or fissures on its surface. It is not mostly strong or durable and is easily broken or peeled away from the stem.
Leaves
Leaves of creeping cucumber are simple, alternate, and roughly oval-shaped. They can range from 2-6 cm in length and 1-4 cm in width. The leaves are generally smooth on the upper surface, while the lower surface may have sparse hairs or be slightly hairy. Leaves are dark green color and are slightly succulent in texture. They are often slightly lobed, with a serrated edge. Leaves are attached to the stem by long petioles, which are also slightly hairy.
The leaves of creeping cucumber are important for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants produce energy from sunlight. They also play a role in transpiration, which is the loss of water from the plant through small pores on the leaves called stomata. In traditional medicine, the leaves of creeping cucumber have been used to treat various ailments, such as headaches, fever, and skin irritations. They are believed to have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the medicinal properties of creeping cucumber leaves.
Flowers
Flowers of creeping cucumber are small and greenish-yellow, with five petals fused together to form a tube shape. They are borne on long, slender stems that arise from the leaf axils, which are the areas where the leaves attach to the stem.
The flowers are unisexual, meaning that they have either male or female reproductive parts, but not both. The male flowers are borne in clusters and have a single stamen that produces pollen. The female flowers are solitary or in small clusters and have a pistil with a stigma for receiving pollen. The flowers of creeping cucumber are pollinated by insects, particularly bees.
Fruits
If you want to add something different and cool to your fruit bowl, the creeping cucumber is the way to go. These small, round fruits are also called Guadeloupe cucumbers or mouse melons. They are very tasty. The fact that they look like tiny watermelons with green lines on a pale green background is enough to get your attention. But what will keep you coming back for more is the thin, edible skin, juicy, crisp meat, and slightly sour, yet refreshing taste. These fruits are only an inch long, so they are great for snacking on their own or adding to salads and drinks. When they are not ripe, they look like little watermelons and taste like cucumbers. Don’t eat them when they are ripe, when they look like black olives. Give the creeping cucumber a try and enjoy the unique taste of this small food.
Creeping cucumbers are not only tasty and cool, but they are also very healthy. These small fruits are a great source of minerals like potassium and magnesium, as well as the vitamins C and K. They are also low in calories and high in fiber, which makes them a healthy choice for a lunch. In many parts of the world, people eat creeping cucumbers as a food and use them in different dishes. Like gherkins, you can eat them raw in salads or pickle them in vinegar or sauce. They are often used in salsas and stews and soups in Mexico and other Latin American countries. It’s important to keep in mind that the growing cucumber fruit should only be eaten when it looks like a small, light-green watermelon. When the fruit is fully ripe and goes dark purple or black, it can cause diarrhea and shouldn’t be eaten. So, if you want a healthy and tasty snack, give the growing cucumber a try. Just make sure to eat it when it’s ready.
Seeds
Seeds are small, oval-shaped, and black. They are about 2-3 mm long and have a hard, shiny outer coat.
Health benefits of Creeping cucumber
Melothria pendula, also known as Guadeloupe cucumber, is a tropical plant that has a long history of use in traditional medicine for various health conditions. Here is some potential health benefits associated with Creeping cucumber
1. Anti-inflammatory properties
Creeping cucumber has been used to treat inflammation and pain due to its anti-inflammatory properties. It is believed to contain compounds that can reduce inflammation and swelling, making it useful in treating conditions such as arthritis and gout.
2. Antioxidant properties
Creeping cucumber contains antioxidants that help to protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants can help to prevent or slow down the development of various diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Digestive health
The fruits of creeping cucumber have a cooling effect on the digestive system and are traditionally used to relieve constipation, bloating, and indigestion.
4. Immune-boosting
Creeping cucumber is believed to have immune-boosting properties that can help to strengthen the body’s defenses against infection and disease.
5. Wound healing
The plant has been used topically to promote wound healing and prevent infections.
6. Respiratory Health
Creeping cucumber has been used traditionally to treat respiratory conditions such as coughs, colds, and asthma. It is believed to have expectorant and bronchodilator properties that can help to clear the airways and improve breathing.
7. Skin Health
Creeping cucumber has been traditionally used to treat skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. It is believed to have a cooling and soothing effect on the skin, helping to reduce inflammation and irritation.
8. Cardiovascular health
Creeping cucumber may have potential cardiovascular benefits, as it has been shown to lower blood pressure in some studies.
Traditional uses and benefits of creeping cucumber
- The use of creeping cucumber in traditional medicine dates back a long time.
- The fruit is thought to possess diuretic qualities and is used in the treatment of urinary tract infections and kidney stones.
- Foliage and stems are utilized for the treatment of skin irritations and insect bites.
- Plant has also been used in traditional medicine for the remedy of different conditions such as fever, headaches, and skin ailments.
- It has been utilized for the treatment of digestive problems such as constipation, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
- It has a positive impact on the health of the digestive system, by supporting proper digestion and helping to control bowel movements.
- Fruits are used in traditional medicine to manage diverse health issues, like diabetes, hypertension, and digestive disorders.
- It is believed to reduce inflammation and act as antioxidants, which can potentially enhance the immune system and contribute to better overall health.
- In Mexico, a fruit infusion is used to treat anemia, and fruits that have been cooked are used to treat heart disease.
- The aerial parts of the plant are infused and taken as a treatment for diabetes due to their hypoglycemic effect.
- The infusion is also used as a remedy for gastritis, calculus, and sores.
- The leaves are decocted and used to wash wounds and burns.
- The fresh plant is crushed and used for snake bites, as well as topically applied to treat rash and hemorrhoids.
- In Suriname, an infusion of tendrils is consumed as a remedy for over acidity in the stomach. It is also given to children.
- In Brazil, the fruit is used as a purgative.
- In Mexico, a plant infusion is used for diabetes.
- It is used as a tonic for anemia.
- For heart problems, boiled fruits are used.
- When the fresh plant is crushed, it can be used to treat snake bites, rashes, and sores.
- In Yucatan, a tea made from the whole plant is used to treat gastritis, kidney stones, and sores.
- Freshly picked and crushed roots can be put on the skin to help with rashes and hemorrhoids.
- It has a long history of being used as a digestive aid to ease stomach problems like indigestion, bloating, and constipation.
- It has been applied externally to help relieve pain and inflammation that is related to injuries such as bruises and sprains.
- This substance has a traditional use in easing respiratory issues such as coughs, bronchitis, and asthma.
- This substance is utilized for treating various medical conditions, such as arthritis, skin rashes, and respiratory illnesses.
- The Creeping Cucumber plant has a history of traditional use in the treatment of diseases related to the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and vascular systems.
- Certain traditional healers use the bark of this plant to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- It is also believed to have diuretic properties and can be utilized in the treatment of urinary tract infections.
- Seeds of this plant are used in traditional medicine to treat various health problems, such as digestive problems and inflammation.
Culinary Uses
Creeping cucumber is a type of squash that is commonly used in Mexican cuisine. Although it is frequently used in savory dishes, it can also be used in sweet dishes like desserts. Here are some culinary uses of creeping cucumber:
- Stews and soups: In Mexican cuisine, creeping cucumber is frequently added to stews and soups. Its mild flavor and nutritious properties make it an excellent ingredient for enhancing the texture and flavor of dishes.
- Candied Creeping Cucumber: Creeping cucumber can be candied and utilized as a sweet topping or filling for pastries and desserts. To candy creeping cucumber, it is usually peeled, diced, and cooked in sugar syrup until it turns translucent.
- Creeping Cucumber Jam: By boiling it with sugar and lemon juice, creeping cucumber can be transformed into a jam. The resulting jam can be utilized as a spread on bread or as a topping for yogurt or ice cream.
- Creeping Cucumber Salsa: Creeping cucumber can be chopped into small pieces and mixed with other vegetables and herbs to create a delicious and refreshing salsa. It is commonly paired with tomatoes, onions, cilantro, and lime juice.
- Creeping Cucumber Salad: Thinly sliced Creeping cucumber can be added to salads, where it is typically paired with other vegetables like tomatoes, onions, and avocado. The salad is then dressed with a simple vinaigrette.
Other Facts
- Creeping cucumber can be a valuable and beneficial addition to any landscape.
- Due to its fast-growing and trailing characteristics, it is an ideal plant for use in hanging baskets and as a ground cover.
- The plant is also occasionally utilized as a ground cover because it has a fast-spreading growth habit and can aid in erosion control.
- In certain regions, creeping cucumber is viewed as an invasive species since it can grow rapidly and overpower native plants.
- Creeping cucumber is a versatile and beneficial plant that has a range of potential uses, both practical and aesthetic.
- The plant is also recognized by the names “Guadeloupe cucumber” and “Squirting cucumber” due to the appearance and texture of its fruit.
- The creeping cucumbers are commonly regarded as a symbol of fertility, healing, and purity.
- One of the primary pieces of information about this vine that people tend to remember is that it should only be eaten when it’s green, not when it has turned purple or black.
- Its aroma is subtle and pleasing, making it a popular choice for aromatherapy and as a natural air freshener.
- Creeping cucumber seeds can remain viable for up to 5 years if they are stored correctly.
Precautions
There are a few precautions to keep in mind when handling or consuming this plant:
- Toxicity: Although not commonly regarded as a poisonous plant, the creeping cucumber does contain cucurbitacin which can lead to stomach discomfort and be harmful in large quantities. It is generally advised to consume only small amounts of the fruit and to refrain from eating any other part of the plant.
- Skin irritation: Certain individuals may encounter skin irritation or an allergic reaction when handling the creeping cucumber plant. It is advisable to wear gloves and long sleeves while working with the plant to prevent skin contact.
- Invasive potential: The creeping cucumber is a rapid-growing and highly productive plant that has the potential to rapidly overtake an area. In certain regions, it is classified as an invasive species and should be planted with caution, or avoided entirely in areas where it could potentially cause harm to the indigenous flora and fauna.
- Companion planting: Despite being a beneficial and visually appealing plant in a garden environment, it is critical to recognize that the creeping cucumber belongs to the cucurbit family. Therefore, it should not be planted close to other cucurbits, including cucumbers, melons, or squash, to prevent the transmission of diseases.
Control
Cultural Control
The creeping cucumber can be managed using cultural practices like hand weeding and mulching. However, it is necessary to eliminate the whole plant, including the roots, to prevent regrowth.
Chemical Control
If cultural methods are insufficient, chemical control techniques may be employed. Herbicides, including glyphosate, can be effective in managing the creeping cucumber. It is critical to adhere to the label instructions and take caution when applying herbicides.
Biological Control
At present, there are no known biological control techniques available for managing creeping cucumber.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=22339#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=301051
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/MEEPE
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2373217
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melothria_pendula
http://www.stuartxchange.com/Pipinong-gubat
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Creeping%20Cucumber.html
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=MEPE3