| Common madder Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Common madder |
| Scientific Name: |
Rubia tinctorum |
| Origin |
Southeastern Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa |
| Colors |
Color varies between red and black |
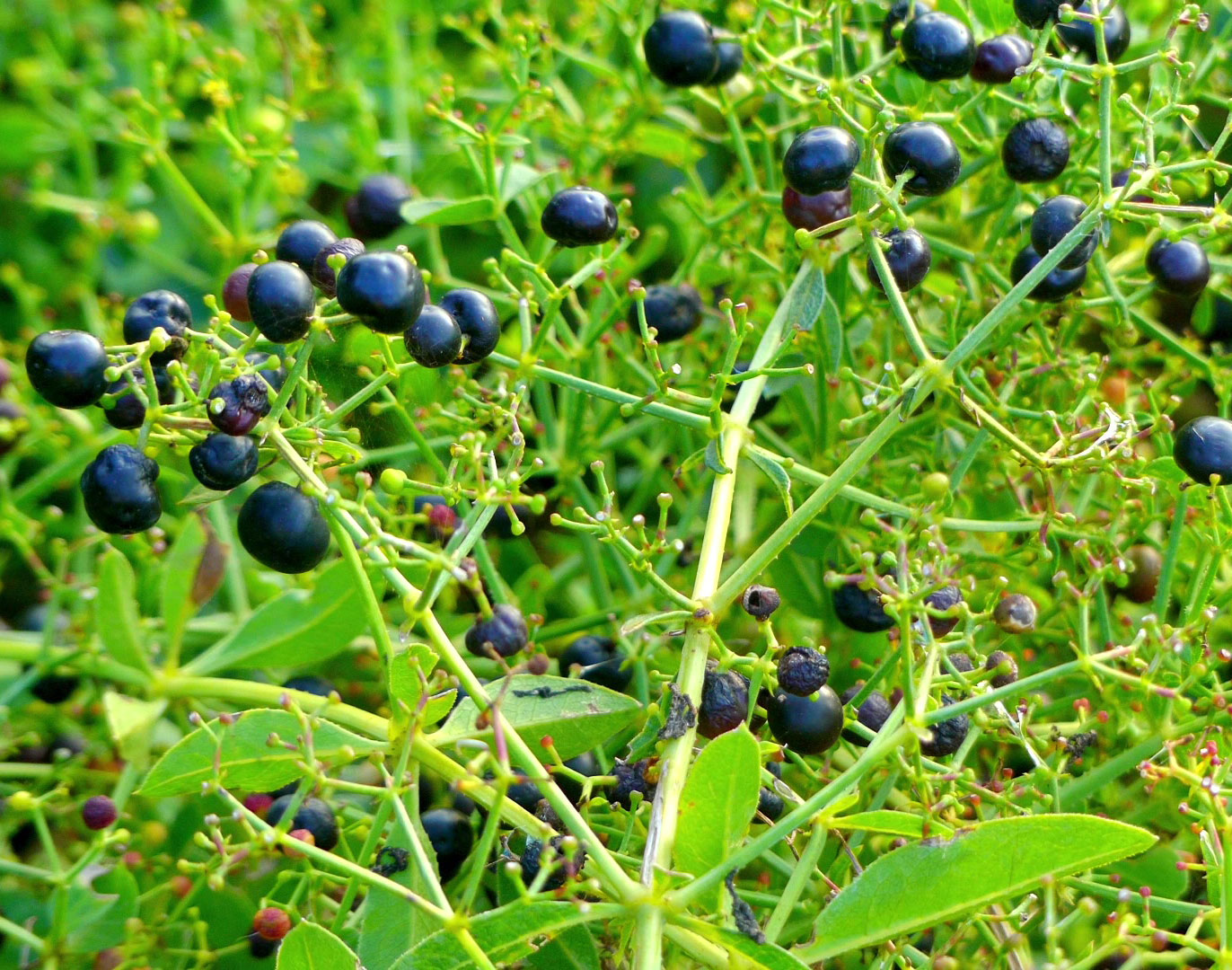
| Shapes |
Small berries that are about 4 mm to 6 mm in diameter |
| Taste |
Bitter |
| Health benefits |
Heals Jaundice, Stops Diarrhea, Halts Bleeding, Helps to Stop Coughs, Increases White Blood Cell Deposits, Good for the Skin, Treats Kidney Stones, Possesses Anti-Inflammatory Properties, Immuno-modulator |
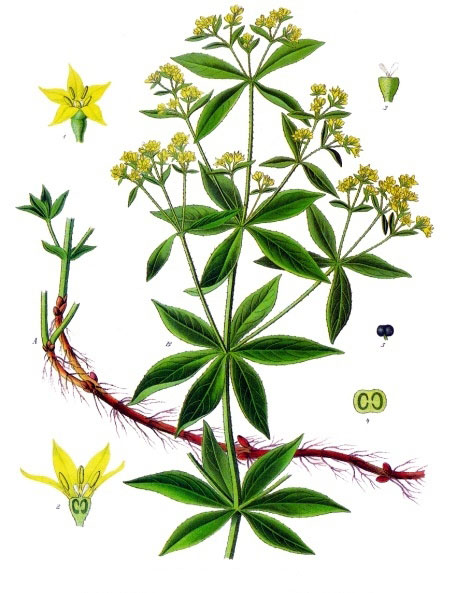
Rubia tinctorum, the common madder or dyer’s madder, is an herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae. The plant is native to Southeastern Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, but was early on introduced to the Central and Northwestern Europe where it became naturalized. Some of the well-known names of the plants are Alizarin, Common madder, Dyer’s madder, European madder, madder and Indian Madder. The name Rubia is from the Latin word ruber meaning red, referring to the red dye from the plant’s roots.
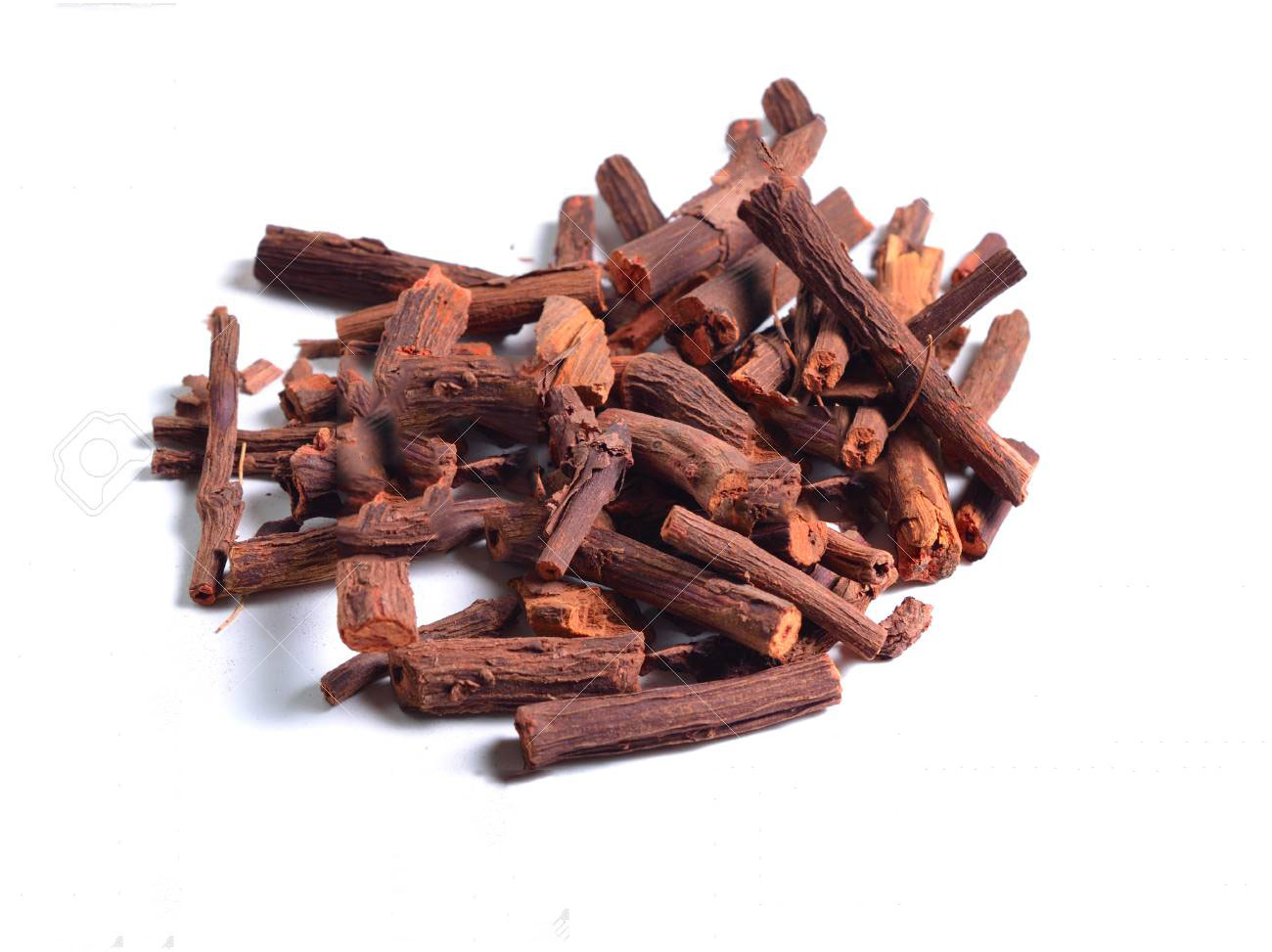
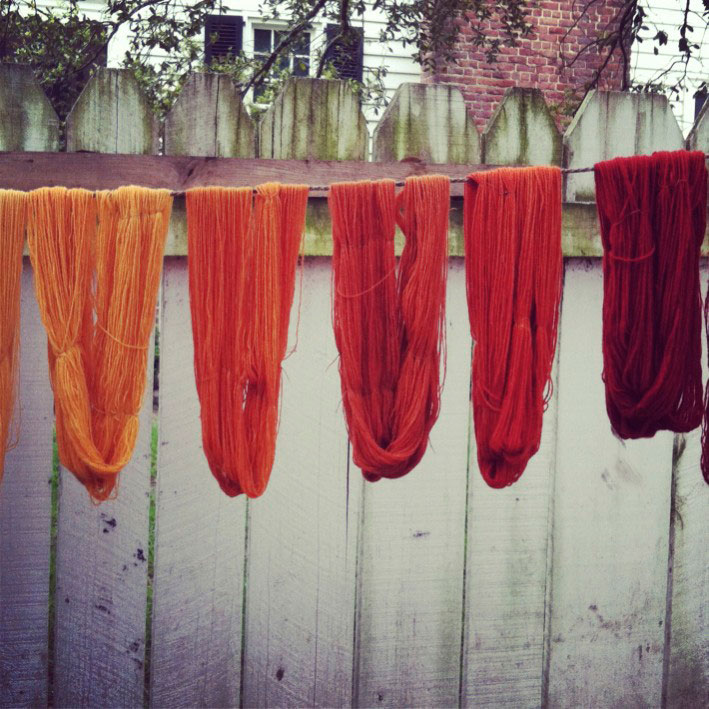
Madder makes a permanent red dye called Turkey red that has been used traditionally to color Turkish fezzes, soldiers’ uniforms, and hunting jackets. Madder root is a natural source of red, pink, orange, apricot, lilac, purple, brown, and black shades of dye, ink, and paint. The plant was originally exported from Turkey for cultivation in the main textile centers of Northern Europe. In 1868, alizarin, the main pigment in madder root, was synthesized from coal tar, thus reducing market demand for the natural material. Madder is still used as a red dye in textiles.
Plant Description
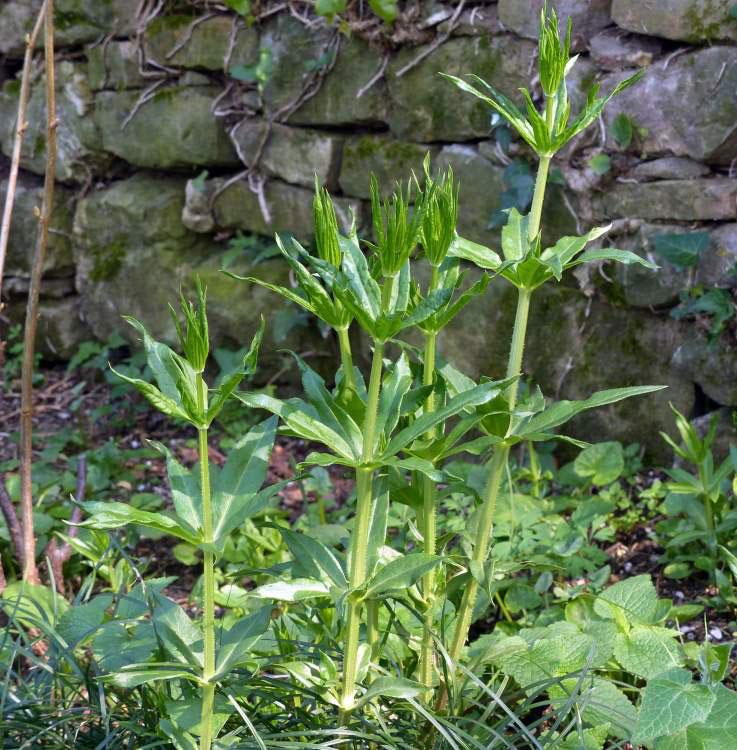
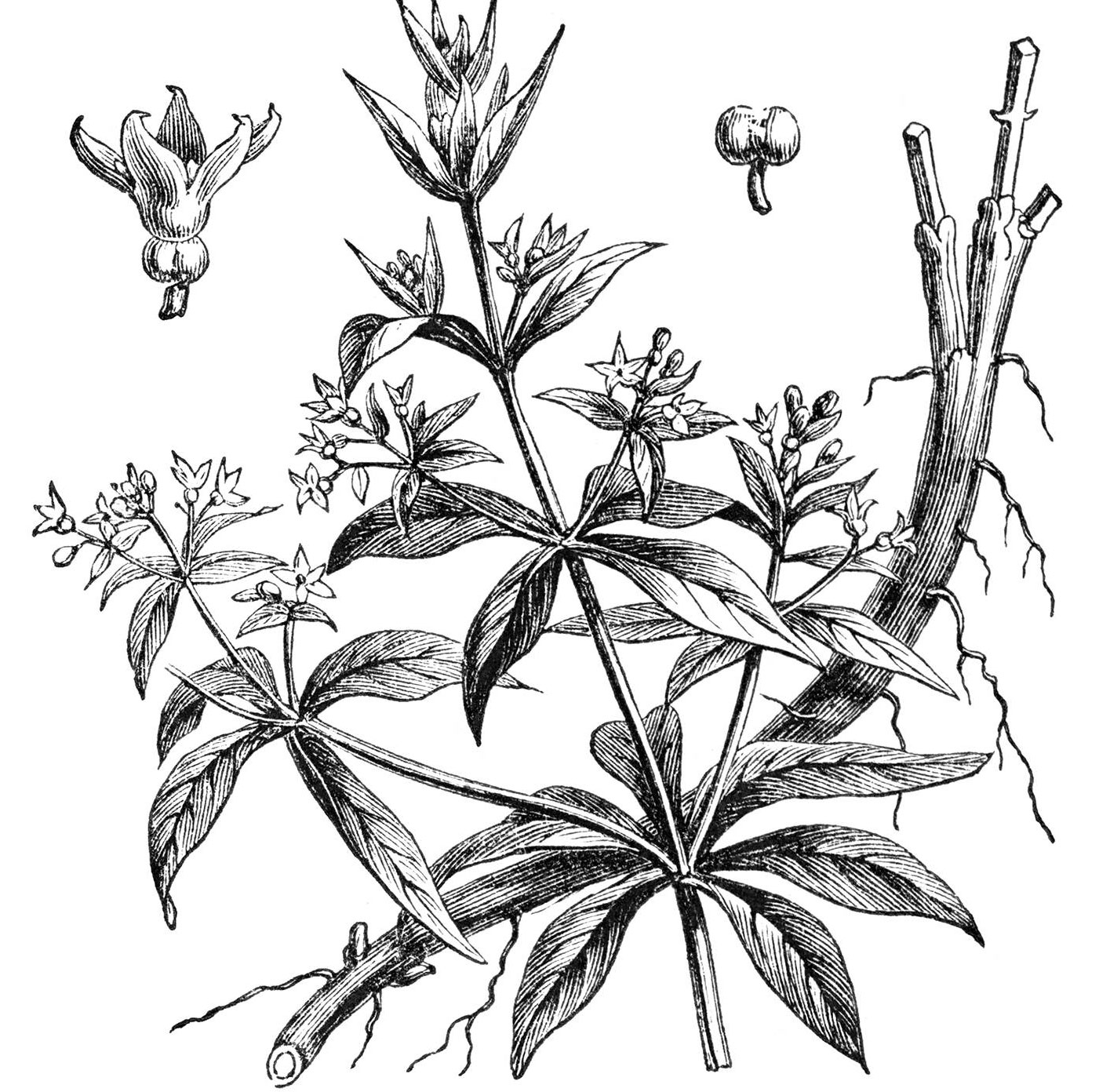
Common madder is a perennial climbing plant that grows up to 1.5 m tall. The plant is found growing in neglected ground, hedgerows and among rubble. The plant thrives in well-drained loamy soil in full sun or semi-shade. Root are quite elongated and may measure up to more than a meter in length and be about 12 mm thick. Stems are several in numbers, herbaceous, diffuse, brittle, branched, tetragonal, and very rough, with sharp hooks.
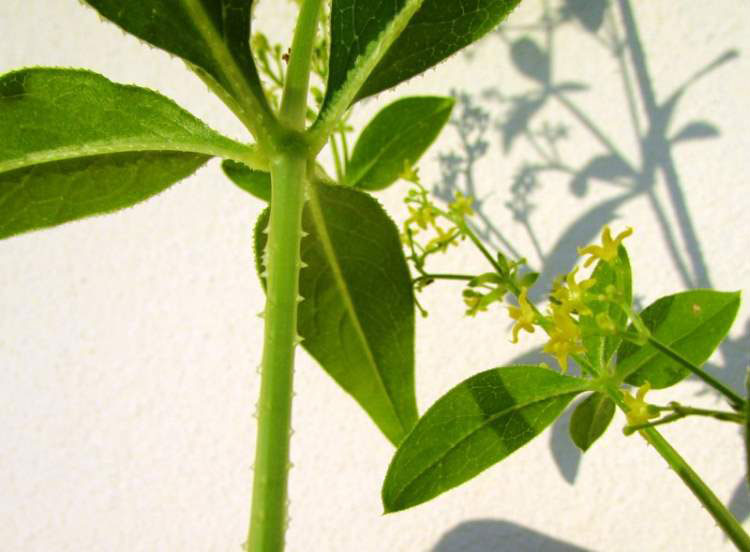
Leaves
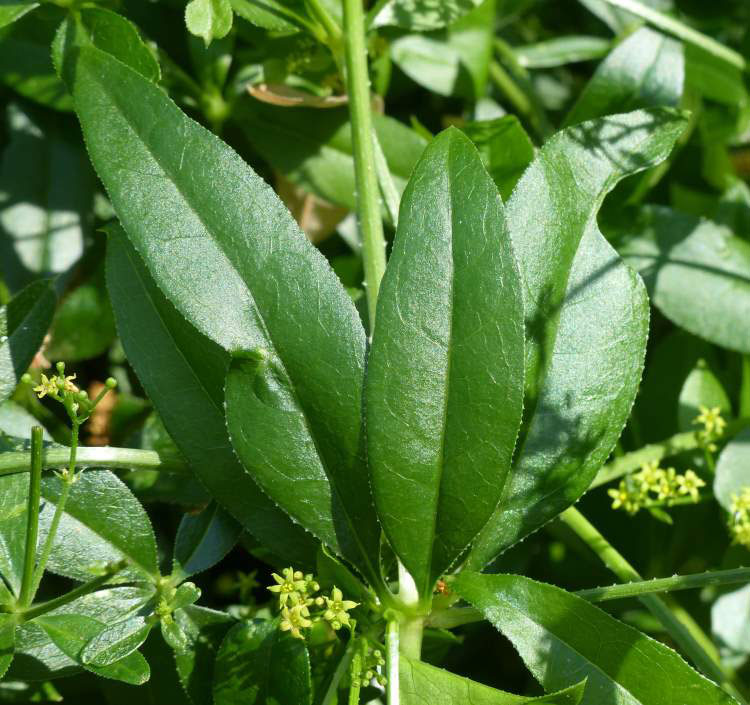
The leaves of this plant are evergreen and grow up to 5-10 cm long and 2 – 3 cm width. About four to seven leaves emerge in whorls on the main or central stem and each of them have a shape similar to the stars. Leaves and stems have tiny hooks with the help of which the plant adheres to erect structures and climbs upwards.
Flower and fruit
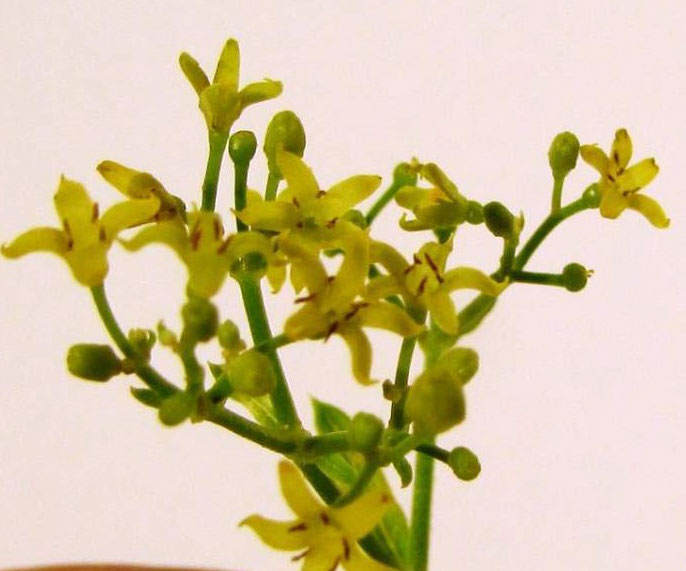
Flowers of madder are very small and measure about 3 – 5 mm in diameter. Each flower has five yellow hued petals and they bloom between June and August. Fertile flowers give rise to small berries whose color varies between red and black. Each berry is about 4 mm to 6 mm in diameter.
Health Benefits of Madder Root
Let’s take a closer look at the many health benefits of madder root.
1. Heals Jaundice
Madder root has the ability to treat jaundice. Jaundice means excess bilirubin in the blood and results in a discoloration of mucous membranes, the skin as well as the white parts of eyeballs into yellow.
The symptoms experienced by people with jaundice include dark urine, light-colored stools, mild rashes, yellow discoloration of the white part of eyeballs, skin, and mucous membranes. Jaundice can occur mostly due to liver-related diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, thalassemia, and malaria.
2. Halts Bleeding
Madder root halts bleeding, whether it is internal or external. In cases of internal bleeding like nosebleeds, the root can be of immense help. Also, in terms of external bleeding, the herb can cure severe skin wounds by making them dry fast. For centuries, Madder root has been used to stop internal bleeding and nosebleeds.
3. Increases White Blood Cell Deposits
Madder root increases the deposits of white blood cells or leukocytes. It also helps to treat leucopenia, which is a shortage in the number of white blood cells present in the blood system, making the people at the risk of many infections.
4. Treats Kidney Stones
Madder root helps to deal with urolithiasis also known as kidney stones. In fact, the herb is also effective for treating other forms of bladder diseases. Madder root consists of good amount of ruberythric acid, which helps to tone down magnesium and calcium as well as the formation of bladder stones in the long run. Additionally, madder root is an amazing antispasmodic agent that accelerates the easy passage of kidney stones through the urinary system.
5. Possesses Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Madder root is a powerful anti-inflammatory that is effective in the treatment of inflammatory conditions related with arthritis or other forms of joint pains. We all know how important it is for inflammation to be stopped because it usually indicates the early stage of most diseases. And so, if inflammation is not stopped early, then the chances of one falling really ill is very high.
Madder root has proven to be a good anti-inflammatory agent that helps with treating arthritis, joint pain, swelling, redness as well as pain in general. Like we said before, inflammation is the first sign of a disease and should be stopped before we become really sick.
6. Immuno-modulator
An immunomodulator is a chemical agent that changes and adjusts the response or activity of the immune system. Immunomodulators like madder root are effective in preventing autoimmune diseases and inflammations.
7. Helps to Stop Coughs
Madder root helps to stop coughs as it is a natural expectorant that reacts very fast. An expectorant is a medicine that helps to encourage the release of sputum by the air passages. And just in case you didn’t know, sputum is actually a mixture of saliva and mucus formed in the respiratory tract, such as phlegm. This is why expectorants like madder root are very effective in the treatment of coughs.
8. Good for the Skin
Madder root is considered very effective for healing acne, skin rashes, boils, skin irritations, and other conditions of the skin. It can be applied topically to the affected area when made into a paste.
To make the paste more effective, simply mix about 100 grams of madder root powder with around 50 grams each of sandalwood, turmeric, and orange peel. Apply the paste on the skin and allow it to get dry before washing it off.
9. Stops Diarrhea
According to researches, animals that are fed with madder root usually get healed faster of diarrhea. As you already know, diarrhea is a frequent need to empty the bowels, and the stool is typically loose and watery. While diarrhea may automatically heal after some days, it is still an uncomfortable experience for its sufferers. However, studies suggest that madder root can effectively heal diarrhea and quickly too.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=11PrzOOs_OM
Traditional uses and benefits of Common Madder
- Root is aperient, astringent, cholagogue, diuretic and emmenogogue.
- It is taken internally in the treatment of kidney and bladder stones.
- Root is seldom used in herbal medicine but is said to be effective in the treatment of amenorrhea, dropsy and jaundice.
- Roots are harvested in the autumn from plants that are at least 3 years old.
- When taken internally the root imparts a red color to the milk, urine and bones, especially the bones of young animals, and it is used in osteopathic investigations.
- Madder has been reputed as effectual in amenorrhea, dropsy and jaundice.
- People use madder root orally for treating menstrual disorders, jaundice, blood disorders, wounds, paralysis, spleen disorders, urinary tract infections, and sciatica, as well as preventing and dissolving kidney stones.
- Madder root is also applied to the skin for certain skin issues.
- Hippocrates used the herb as an expectorant remedy and against various gynecological diseases.
- It was listed as an astringent and diuretic agent as a remedy for anemia.
- Pliny (23-79 AD) used madder as a cure for jaundice.
- Madder is perhaps best known for its application in powder or extract form to treat kidney and bladder disorders.
- Some clinical studies have been made with positive results on the herb’s ability to dissolving kidney and bladder stones.
- Herbal tea of the leaves and stems were used to treat constipation.
- Madder was used traditionally as a topical remedy for sciatica.
- Tincture made from the fresh roots was used for delayed or missed menstrual periods, disorders of the spleen and various other ailments.
- Herbalists boiled the root in wine and added sugar or honey for taste and gave it to the patient.
- To treat spleen swelling, the madder seed is drunk along with honey and vinegar.
- Leaves as well as the stem of madder are useful in treating delayed menstruation.
- Leaves and roots of the plant are crushed and applied to freckles as well as skin blemishes to cure these conditions.
- It helps to diminish the size of kidney stones that have formed from before.
Other facts
- A very good quality red dye is obtained from the roots.
- Some reports say that 2 year old roots are used in the spring and autumn whilst others say that 3 year old roots are used.
- Roots can be dried for later use.
- The dye can also be extracted from the leaves.
- This dye is also used medicinally.
- Leaves and stem are prickly, the whorls of leaves having spines along the midrib on the underside.
- This feature enables them to be used for polishing metalwork.
- Herb is used as fodder for animals.
- Red-colored rhizomes and roots are the source of red dyes known as rose madder and Turkey red.
- People in France, also used the residue of the plant to make a spirit.
Dosing
Appropriate dose of madder root for a person depends on certain factors such as the user’s health, age, and several other conditions. Currently, there is not enough scientific information on the right range of doses for madder root. But remember that herbal products are not necessarily safe and dosages can be essential. Always check with your doctor before using madder root.
Precautions
- The plant has the potential to cause cancers, particularly liver and kidney.
- From the information currently available it is not recommended as an herbal medicine.
- It is advisable for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and young children to avoid the use of madder root.
- Madder root is likely to be unsafe when consumed by mouth, because the chemicals it contains may lead to cancer.
- There are also concerns that the herb may also result in body fluids, including urine, saliva, urine, tears, sweat, or even breast milk to become red.
- Madder root should be used only under the supervision of a medical practitioner.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=35145#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/59686/
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Rubia+tinctorum
https://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/m/madder02.html
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=RUTI2
https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q163641
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-180430
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/RBITI
http://www.catalogueoflife.org/col/details/species/id/ee6c22fda9d418956146f01718d3f08a
http://www.tn-grin.nat.tn/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=32244
http://luirig.altervista.org/flora/taxa/index1.php?scientific-name=rubia+tinctorum
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rubia_tinctorum
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/46893
Comments
comments