Chinese Knotweed Facts
| Chinese knotweed Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Chinese knotweed |
| Scientific Name: | Polygonum chinense |
| Origin | Bhutan, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, North Korea, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, and Thailand |
| Colors | Bluish black when ripe |
| Shapes | Achene trigonous, 2.8–4 mm long, 2–3 mm diameter |
| Taste | Bitter, sweet, Astringent |
| Health benefits | Alzheimer’s disease, Heart health, Hair growth, Anti-inflammatory properties, Blood enhancement, Liver cleaning, Enhancing athletic performance, Managing sleep disorders, Spiritual sensitivity, |
| Name | Chinese Knotweed |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Persicaria chinensis OR Polygonum chinense |
| Native | Bhutan, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, North Korea, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, and Thailand. In Myanmar found in Ayeyarwady, Bago, Kachin, Mandalay, and Yangon |
| Common Names | Chinese knotweed, red bush, Creeping Smartweed, Common Marsh Buchwheat, rice smartweed, southern smartweed, Climbing knotweed, flowery knotweed, fo-ti, fo-ti-teng, he shou wu, or ho shou wu |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Bitibat sayniin (بطباط صيني) Assamese: Madhu soleng (মধু সোলেংগ), Kelnap Azerbaijani: Polygonum chinense Chinese: Huo tan mu cao (火炭母草), Qīng fàn teng ( 清飯藤), Huǒtàn mǔ ( 火炭母) English: Chinese knotweed, red bush, Creeping Smartweed, Common Marsh Buchwheat, rice smartweed, southern smartweed French: Empreinte-la-vierge; liane rouge; persicaire de Chine Hindi: Mudanthi, mukkala, oduthan, poovallikod, thiruthanni, thondi, ban ogal, kanjolya, jungali palak (जंगली पालक) Irula: Neerkapachi Japanese: Tsuru soba (ツルソバ) Kannada: Nir kanigalu Khasi: Jaryndem Konkani: Ransisori (रानसिसोरी) Malayalam: Thiruthanni (തിരുതാന്നി), Poovallikodi, Mudanthi, Oduthan, Mudanthi, Thondi, Oduthan, Poovallikodi, Thiruthanni, Mukkala, piripu Manipuri: Angom yensil Marathi: Paral (परल) Mizo: Taham Nepali: Kukur thotne (कुकुर् ठोट्ने) Persian: پرسیکاریا چینی Tamil: Actalaree, Sivappu Kumbakodaali Thai: Phak bang bai (ผักบังใบ), phak phai nam (ผักไผ่น้ำ), phaya dong (พญาดง), Xeụ̄̂xng phĕ dm̂ā (เอื้องเพ็ดม้า), ueang phet ma |
| Plant Growth Habit | Rhizomatous herbaceous twining, perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Grows in wet valleys, grassy slopes, mixed forests, thickets in valleys, brushwood, mountain slopes, open areas, home gardens, abandoned gardens, riverbanks, forest borders, roadsides |
| Plant Size | When not scrambling over other plants or structures, it grows 70 cm to 1 m tall; otherwise it can climb over other vegetation up to 10 m high |
| Tuber | Tubers are reddish-brown in color, wrinkled, and consist of transverse and longitudinal lenticels. |
| Stem | Erect, 70-100 cm tall, ligneous at base, much branched, striate, glabrous or retrorsely hispid and pinkish in color |
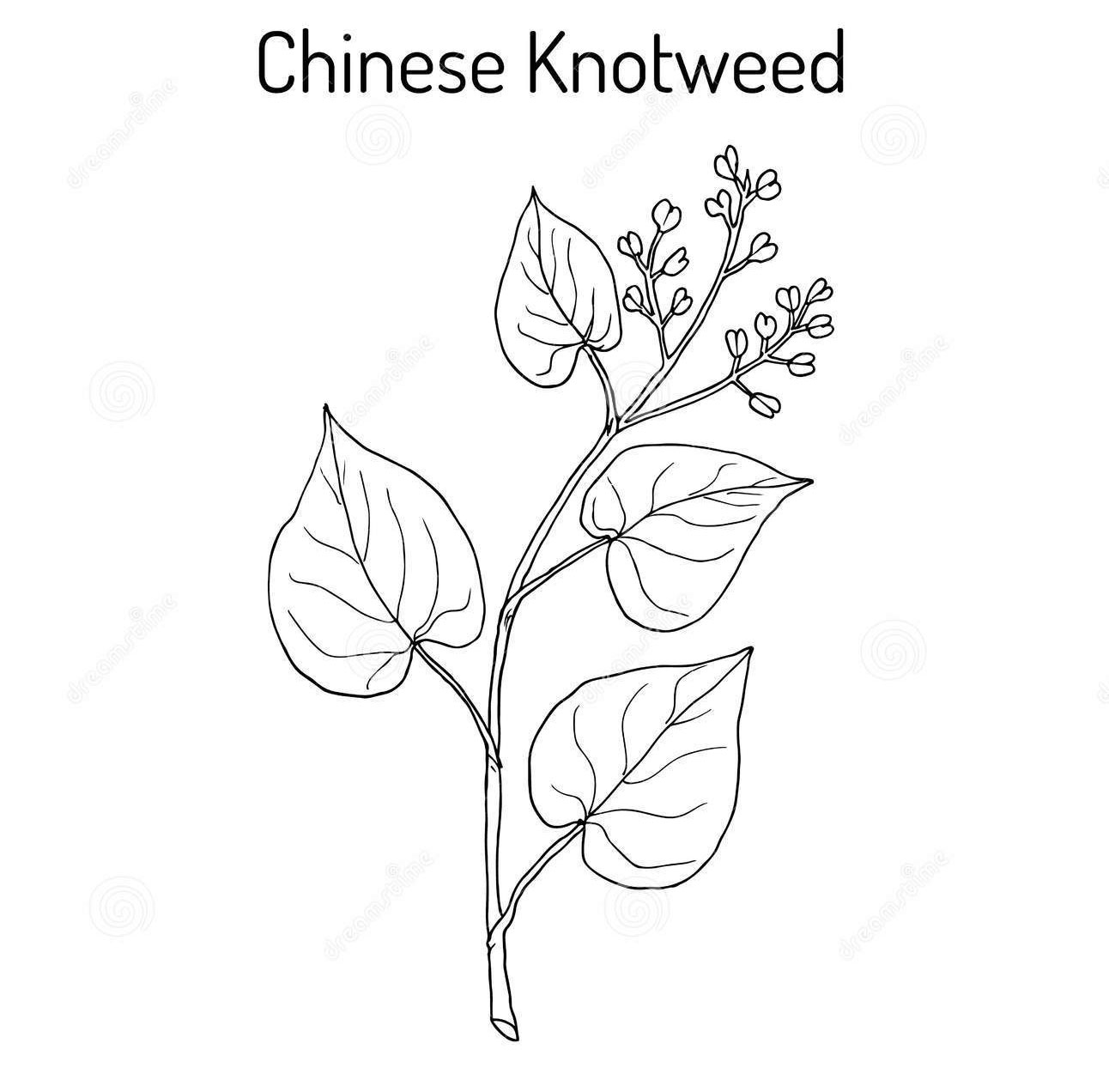
| Leaf | Simple, alternate, ovate- to oblong-shaped entire with an acuminate apex, truncate base, 50–100 mm long and 30–70 mm wide |
| Flowering season | November-March |
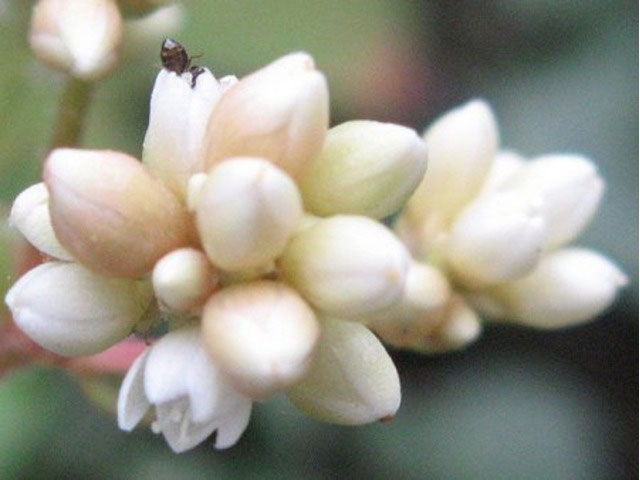
| Flower | Flowers are campanulate, small, white or pinkish in color, 2.0 to 3.5 mm bearing 5 tepals, and 8 stamens with purple tips |
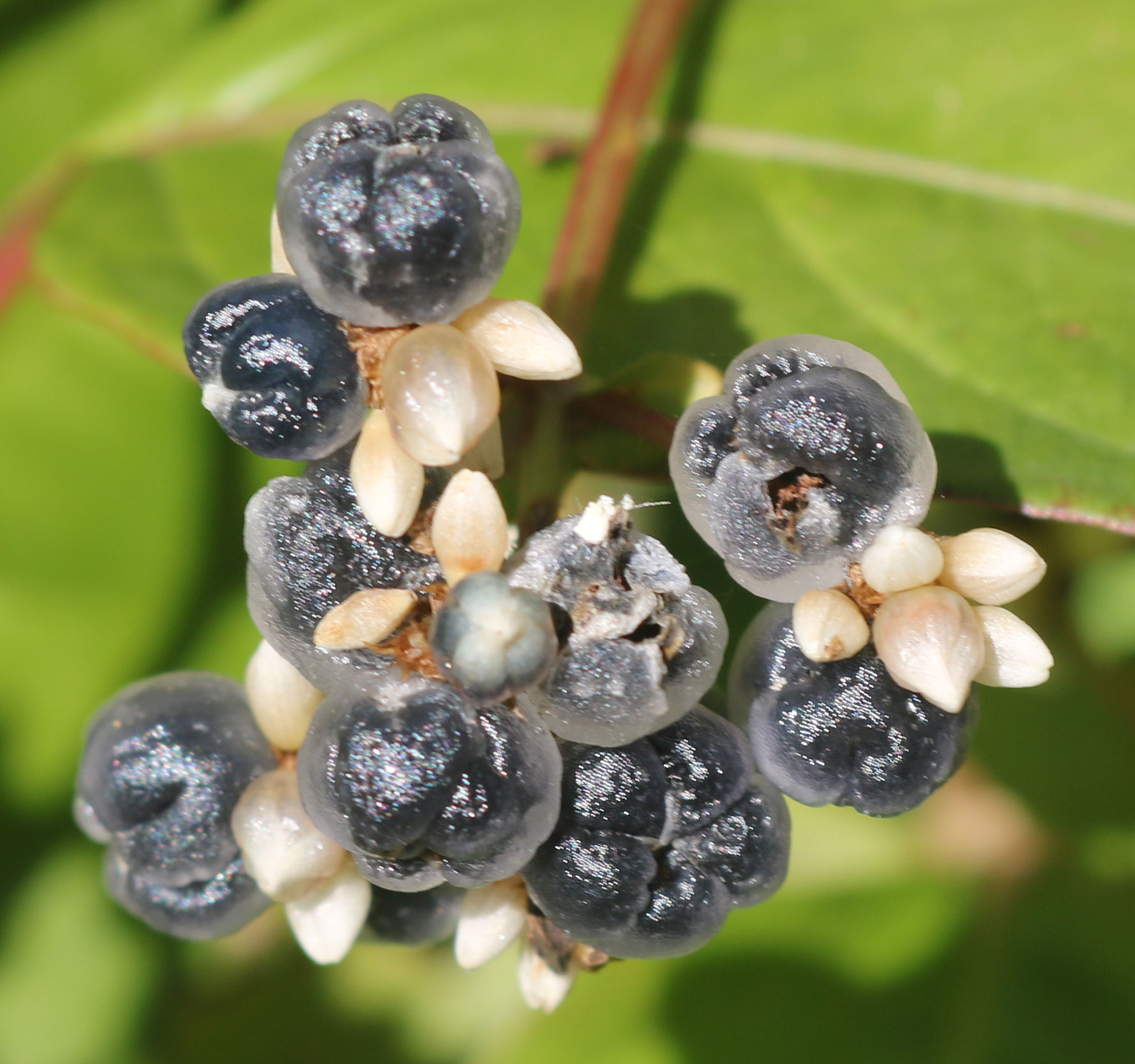
| Fruit Shape & Size | Achene trigonous, 2.8–4 mm long, 2–3 mm diam., black, enclosed by enlarged succulent |
| Fruit Color | Bluish black when ripe |
| Plant Parts Used | Root, stem |
| Seed | Trigonous, small 3 to 4 mm round and black |
| Taste | Bitter, sweet, Astringent |
| Culinbary Uses |
|
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
Chinese knotweed is a rhizomatous herbaceous twining, perennial plant that can grows 70 cm to 1 m tall when not climbing over other plants or structures, and otherwise it can climb over other vegetation up to 10 m high. The plant is found growing in wet valleys, grassy slopes, mixed forests, thickets in valleys, brushwood, mountain slopes, open areas, home gardens, abandoned gardens, riverbanks, forest borders, roadsides and tea- and Cinchona-plantations. The species can tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions including shade, high temperatures, high salinity and drought. Tubers are reddish-brown in color, wrinkled, and consist of transverse and longitudinal lenticels. The stem is cylindrical, full, becoming angular and woody at the base. It is generally glabrous and smooth, often purple in color and has small glandular hairs near the nodes and reddish-purple in color.
Leaves
The leaves are simple, alternate, with petioles 0.5 to 2 cm, often winged on the upper side. At the base of the petiole, there are 2 rounded clasping auricles. The ocrea is 1 to 2 cm long, obliquely truncated at the top, membranous, glabrous with some small glandular hairs. The lamina is oval to elliptical, 3.5 to 10 cm long and 2.5 to 6 cm wide, acuminate at the top, truncated or wide angled at the base. The margin is entire, sometimes wavy. Both sides are smooth, sometimes with loose hairs on the underside. The venation is marked, consisting of many parallel arched ribs. Upper surface of leaf with an inverted “V” shaped spot. The leaf blade is green, often with a darker spot in the center.
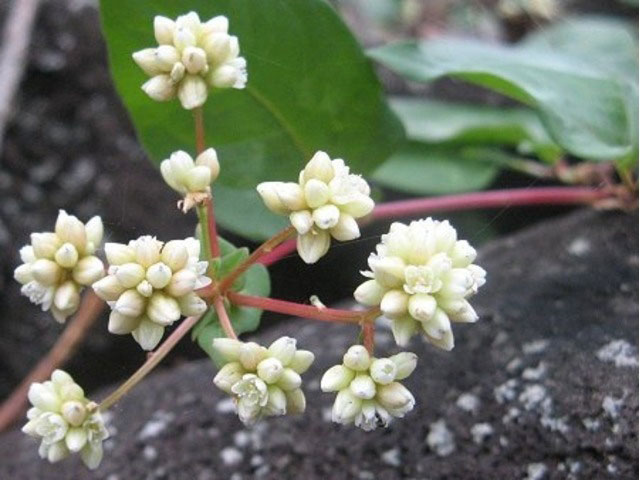
Inflorescence
The inflorescence is a loose terminal panicle, bearing at the ends of the branches small glomerules of white or pink flowers, 3 to 8 mm in diameter. The stems, 2 to 3 cm long, are covered with short glandular yellowish hairs.
Flower
The flowers are held by a short pedicel at the base of which is a foliaceous, oval, sessile bract. The flowers are campanulate, small, white or pinkish in color, 2.0 to 3.5 mm bearing 5 tepals, and 8 stamens with purple tips. Flowering normally takes between November-March.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by achene trigonous, 2.8–4 mm long and 2–3 mm diameter, bluish black, enclosed by enlarged succulent, blue-black persistent perianth. The seeds are trigonous (triangular in cross-section), small 3 to 4 mm round and black.
Health benefits of Chinese Knotweed
Chinese knotweed is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine that is used quite commonly to deal with several health problems and achieve endurance. Even after its widespread usage, there have been some unpleasant reports related with it. Read on to know more about the health benefits that can be obtained by using Chinese knotweed in your regular lifestyle
1. Alzheimer’s disease
Chinese Knotweed is considered quite beneficial for people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, as Chinese Knotweed can improve the fluidity of mitochondria membrane in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Research carried out on Alzheimer’s disease model group, control group and treatment group concluded that Chinese Knotweed may probably benefit people at risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
2. Heart health
Chinese knotweed is extremely beneficial to your heart because it consists of lectins which attach to carbohydrates in the cells of the body. Lectins help in decreasing the buildup of plaque in blood vessels which can result in cardiovascular conditions. Additionally, Chinese knotweed lower cholesterol levels and decrease the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions as well as maintaining the elasticity of arteries which carries the risk of heart attack.
3. Hair growth
Chinese knotweed has long been recognized as the perfect hair growth and rejuvenation tonic. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, our hair reveals the state of your liver, kidneys and blood. Research in the US National Library of Medicine concluded that the herb consists of Radix Polygoni Multiflori (RPM) which has hypolipidemic effects. Mostly, hypolipidemic agents help to reduce the concentrations of lipids or fats in the blood which improve the essence of blood and enhance nourishment to the liver as well as kidneys. Hypolipidemic agents are known to revitalize hair and strengthen bones.
4. Anti-inflammatory properties
Chinese knotweed has been shown to help in preventing pro-inflammatory pathways and controlling diseases related to inflammation due to its bioactive constituents. Research found that patients who took a daily dose of 250 mg of the tonic orally showed significant improvement of the condition compared to patients who received a placebo. Thus it is concluded that the bioactive constituents of the herb consists of anti-inflammatory agents that helps to combat free radicals.
5. Blood enhancement
Chinese knotweed consists of good amount of iron compared to the highly praised Goji berries. Iron is critical for the making of red blood cells in the body. Additionally, the herb is packed with lecithin which makes up nerve tissue and is supposed to boost membranes of red blood cells.
The herb has been shown to protect against excessive clumping of blood platelet and boost blood flow. While blood clumping is important for forming scabs on injury sites, excessive clots inside blood vessels results in strokes or heart attacks.
6. Liver cleaning
Chinese knotweed root extract is extremely beneficial in helping the liver to clean up blood by preventing accumulation of liver fat. Lipid peroxidation usually happens when cell membranes experience reduced electrons taken away by free radicals or oxidation. When the liver is functioning optimally, it is greatly effective in getting rid of toxins from the blood.
7. Enhancing athletic performance
Chinese knotweed is known to support muscle growth and tissue recovery making it ideal for weightlifters and bodybuilders. While there is not sufficient clinical evidence to show how the herb helps in increasing muscle strength and size, Chinese knotweed constituents are known to induce vasodilation.
8. Managing sleep disorders
Sleeplessness or insomnia is a disorder where people are unable to fall asleep or stay asleep to enjoy the full effects of a good night’s sleep. Common ways of combating sleep disorders involve targeting melatonin receptors, GABA receptors and serotonic receptors using pharmaceutical products. Unfortunately, pharmaceutical products come with undesired effects including tolerance and dependence.
9. Spiritual sensitivity
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, spiritual sensitivity is important for people who want to expand their knowledge and experiences. Chinese knotweed is known to stimulate intuitiveness and promote spiritual sensitivity which opens people to deeper awareness and spirituality. People who use the herb regularly often notice an increase in creativity, guidance and inspiration.
Traditional Uses and benefits of Chinese knotweed
- Chinese knotweed is used in traditional Asian medicine.
- It is used as an herbal medicine to treat stomach-ache, eczema, and eye disease, and as a depurative herb in Malaysia.
- Decoction is used for dysentery, gastroenteritis, bloody stool, indigestion, hepatitis, tonsillitis, and laryngo-pharyngitis.
- Poultice of dried material are used for furuncle and abscesses.
- Decoction is used as external wash for dermatitis, eczema, pruritus.
- Poultice or decoction is used as external wash used for sprains, bruises, poisonous snake bites.
- It is used to treat ulcers, eczema, stomach aches and various inflammatory diseases in traditional Chinese medicine.
- It is also used to treat worms and scorpion bites.
- In Nepal, veterinary use it as diuretic.
- The plant is antiscorbutic, tonic, vulnerary.
- Decoction of the plant is used as a depurative.
- Externally, the decoction is used to treat eczema of the ears.
- Juice of the plant is used in the treatment of eye diseases.
- Poultice is applied to the abdomen as a treatment for stomach-ache.
- Chinese Knotweed is used in Chinese Medicine system for increasing longevity, providing strength, restoring hair color and solving the problem of erectile dysfunction and vaginal discharge.
- Chinese Knotweed is used with black beans for preventing heart diseases. The combination is used for preventing the formation of plaque in the vessels. Plaque formation is the root cause of Heart diseases.
- Lectins attach to carbohydrates in the body and block the accumulation of fat in the blood.
- It helps in reducing the levels of cholesterol in the blood.
- It is a good herbal remedy for boosting the production of Red Blood Cells and curing Anemia.
- It improves blood circulation in the body and cures the problem of Erectile Dysfunction in men and cures infertility in women
- It acts as a nutritive tonic for hair and treats Baldness. It promotes hair growth and solves the problem of gray hair.
- It provides nourishment to the nerves and treats Nerve Disorders.
- It is helpful in curing Alzheimer’s disease.
- It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions that help in reducing inflammation.
- Chinese Knotweed has been recommended for people with cardiovascular disorders.
- It keeps a good care of your heart and increases its efficiency.
- It is an immunity booster and increases the ability of the immune system to fight against infections.
- It has antimicrobial property that prevents the microbial growth in the body.
- It is recommended for diabetic patients as it tones the overall health of Spleen. It improves the functioning of the spleen and lowers the levels of blood sugar.
- The Laxative action helps in curing Constipation.
- Chinese knotweed has a reputation as an herb that could be helpful to increase fertility naturally in males and as an herbal impotence remedy.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Chinese knotweed
- Anxiety: Take half a teaspoon of dried powdered Chinese Knotweed. Boil in half a cup of water. Consume it.
- Debility: Ginseng Korean, Polygonatum, Chinese Knotweed, Dong Quai, Schisandra, Wild Yam, Chinese Licorice, Goji Berry, White Peony, Hoelen, Eucommia, Glehnia, Cornus Officinalis, Citron, Paeonia Suffruticosa, Red Sage and Bupleurum in conjunction are beneficial for Energy, Stamina and improve overall feeling of well-being. OR You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule per day.
- Liver and Kidney Tonic: Chinese Knotweed, Dong Quai, Polygonatum, Rehmannia , Ligusticum Wallichii, Angelica Dahurica, Allspice, Clove and Citron in conjunction are beneficial for Liver and Kidney nourishment. OR You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule per day.
- Reproductive Problems of Males: Ginseng Korean, Astragalus, Dong Quai, Rehmannia, Cuscuta Chinensis, Goji Berry, Fennel, Zanthoxylum Piperitum, Morinda Officinalis, Cornus Officinalis, Polyporus Umbellatus, Psoralea, Achyranthes Aspera, Yam Rhizome, Horny Goat Weed, Eucommia, Cinnamon, Paeonia Suffruticosa, Raspberry, Chinese Knotweed, Anemarrhena, Atractylodes Macrocephala, Water Plantain, Senega, White Peony, Anemone Chinensis and Honey in conjunction are beneficial for Reproductive Problems of Males and act as a powerful kidney tonic. OR You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule 3 times a day.
Precautions
- Excessive use may cause liver toxicity.
- Avoid use during Pregnancy, Breast feeding.
- It may cause diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, stomach pain, jaundice, hepatitis and numbness in the arms/legs.
- Consultation with Healthcare Professional is must before use.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=823783#null
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=POCH6
https://www.aphis.usda.gov/plant_health/plant_pest_info/weeds/downloads/wra/Persicaria_chinensis_WRA.pdf
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/118915
https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1106856
http://caws.org.nz/old-site/awc/2018/awc201812511.pdf
http://www.stuartxchange.org/Daynon
https://biodiversity.bt/species/show/1745
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Persicaria+chinensis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Persicaria_chinensis#:~:text=Persicaria%20chinensis%20(synonym%20Polygonum%20chinense,species%20from%20the%20family%20Polygonaceae.
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/tro-50133756
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/266372
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Chinese%20Knotweed.html
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/POLCH
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/251881
https://bie.ala.org.au/species/NZOR-6-68380