The name Chameleon plant (or chameleon herb) should be used only for the beautifully colored variety which is most common as an ornamental in the West, and whose triple-hued leaves (yellow, red, green) remember to the proverbial color-shifting chameleon. The English names fishwortand heartleaf refer, with some exaggeration, to the plant’s strong odor and to the heart-shaped leaves, respectively.
It is normally grown as a leaf vegetable, mostly in Vietnam, and is used as a fresh herbal garnish. Leaf has an unusual taste that is often defined as ‘fishy’ (earning it the nickname “fish mint”), so it is not appreciated as universally as basil, mint, or other more commonly used herbs. In NE India, mainly Meghalaya, it is locally known as ja mardoh and used in salads or cooked with other vegetables. In Manipur, it is known as toningkok and used as garnish over eromba and singju, ethnic side dishes. In Assam it is called Masunduri and popular mostly among the tribes. It is taken raw as salad and cooked along with fish as fish curry. Chameleon Plant is found in the Himalayas at altitudes up to 2500 m.
Plant Description
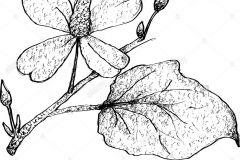
Chameleon Plant is a medium-sized herbaceous, rhizomatous, perennial ground cover plant that grows about 0.6–1 meter (2.0–3.3 ft.) tall and spreading up to 1 meter (3.3 ft.) wide. The plant is found growing in stream sides, forests, wet meadows, slopes, thicket, field margins, trail sides, roadsides, and ditch banks, near sea level, lakes, urban areas, water courses and ravines. Soil having a reasonable amount of moisture content is best for the growth of these plants. Wet soil that is subjected to a partial amount of sunlight could also work wonders for the plant’s growth. It is primarily grown as a ground cover in moist to wet areas, including aquatic margins. The proximal part of the stem is trailing and produces adventitious roots, while the distal part of the stem grows vertically. Stems are green or sometimes purplish red, and either smooth or pubescent on the nodes.
Leaves
Leaves are heart shaped up to 75 mm long and almost as wide. The leaves are comprised of a mixture of colors from green through yellow to red, the brighter colors being more prominent when grown in full sunlight. The leaves are opposite along thin erect stems which arise from slender rhizomes. Foliage is aromatic when bruised.
Flowers & Fruits
Flowers are small, greenish-yellow crowded into a short terminal spike around 2–3 cm (0.79–1.18 in) long, with four to six large white, petal-like bracts at the base. The stamens usually degenerate. Flowering normally takes place from April-June. Fertile flowers are followed by dehiscent dry fruit (Capsule). Fruits are apomictic, i.e. they develop seeds without being fertilized.
Health Benefits of Chameleon Plant
Researchers have observed the biological behavior of Chameleon Plant and extensive research has discovered surprising revelations about its relation to human health.
1. Cure for Environmental Sensitivities
When you’re allergic to a substance, your body produces histamine, a compound that initiates an immune response. Research demonstrates that Chameleon Plant has inhibitory effects on histamine release, possibly blocking it and reducing its effects. Researchers have even estimated Chameleon Plant‘s effects against allergies and asthma, issues partly characterized by excessive release of histamine.
2. Powerful Antioxidant
Chameleon Plant consists of polyphenols, potent compounds high in antioxidant activity that battle free radicals. Free radicals have a free, unpaired electron and are often unstable. They damage other compounds, cells, and DNA and research has linked free radicals to aging, cancer, and many other ills. Chameleon Plant has been billed as an excellent free radical scavenger and helps neutralize circulating free radicals.
3. Protection against Harmful Organisms
Antibacterial is a buzzword that sounds good, right? Well, not so fast; not all bacteria are bad. In fact you need a balance of bacteria in your digestive system as good bacteria supports digestion, and that’s only one application. Recent article has shown that Chameleon Plant encourages intestinal balance by discouraging harmful bacteria from thriving in the digestive system.
4. Immune System Support
Research has shown that Chameleon Plant may help support the immune system by stimulating the production of lymphocytes, white blood cells that are crucial for the body’s natural defense system. These white blood cells are occasionally referred to as natural killer cells, and a plethora of research has found that these cells are important for promoting good health. Chameleon Plant, in this case, should be seen as just a natural component in an overall healthy lifestyle. Exercise, a vegetarian diet, and plenty of sunshine and sleep are also instrumental for supporting immune system function.
5. Diabetes
A research result by Kumar et al., (2014) recommends that Houttuynia cordata consists of anti-diabetic properties. This plant is presently being experimented and examined in order to determine its pharmacological abilities in regulating blood sugar level in human beings.
6. Weight Management
Studies reveal that Houttuynia cordata consists of anti-obesity properties thus can be frequently eaten to shed excess weight.
7. Herpes
Houttuynia cordata can be given to patients suffering from herpes virus since the plant contains properties that are capable of inhibiting pseudo rabies herpes virus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pBBZdJCWWmw
Traditional uses and benefits of Chameleon Plant
- Whole plant is antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-phlogistic, antiviral, depurative, diuretic, emmenagogue, febrifuge, hypoglycemic, laxative and ophthalmic.
- Decoction is used internally in the treatment of many ailments including cancer, coughs, dysentery, enteritis and fever.
- Its use is said to strengthen the immune system.
- Externally, it is used in the treatment of snake bites and skin disorders.
- Leaves and stems are collected during the growing season and used fresh in decoction.
- Leaf juice is antidote and astringent.
- Root extract is diuretic.
- Root is also said to be used in medicinal preparations for certain diseases of women.
- Rhizomes produce a sterol, resembling sitosterol, which encourages the secretion of antibiotic substances from a gram-positive spore-forming bacillus.
- An active substance, effective in the treatment of stomach ulcers, has been extracted from the plant.
- Leaf-extract is used in dysentery; rhizome is used in stomach ulcers.
- Boiled extract of rhizomes is taken for muscular pains due to over strain.
- It is a remedy for colds, indigestion, urinary and liver problems.
- Root is used as diuretic and leaves for measles and dysentery.
- It is used as a treatment of upper and lower respiratory tract infections.
Culinary Uses
- Tender young shoots and leaves are consumed raw or cooked as a pot-herb.
- Leaves and young shoots are harvested in the spring when about 8 cm long.
- Leaves have a delicious orange-like smell and make a marvelous flavoring in salads.
- In the spring and summer it has a very acceptable flavor, but by autumn a distinct bitterness has crept in.
- Root can be consumed after cooking.
- It is commonly grown as a leaf vegetable, and is used as a fresh herbal garnish.
- Leaf has an unusual taste that is often described as ‘fishy’ (earning it the nickname “fish mint”), so it is not enjoyed as universally as basil, mint, or other more commonly used herbs.
- It is commonly used in salads or cooked with other vegetables and as a garnish over ethnic side dishes in Northeastern India.
- Tender roots can also be ground into chutneys along with dry fish, chilies, and tamarind.
- It is taken raw as salad and cooked along with fish as fish curry.
- Its dried leaves may be used as a tea in Korea and Japan.
- In several southwestern provinces of China like Guizhou, Sichuan and Yunnah, the roots of this plant is consumed as a root vegetable.
- Leaves of the plant is loved and relished in pakoras and salads in places like Manipur.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=506518#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/73839/
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/houttuynia_cordata.htm
https://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?latinname=Houttuynia+cordata
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=a638
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=HOCO3
http://issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=854&fr=1&sts=&%20ang=EN&ver=print&prtflag=false
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2853867
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Chameleon%20Plant.html
https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Houttuynia+cordata
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Houttuynia_cordata
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/230009
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/HOTCO
Comments
| Chameleon Plant Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Chameleon Plant |
| Scientific Name: | Chameleon Plant |
| Origin | Southern China, Korea, Japan, and Southeast Asia |
| Shapes | Dehiscent dry fruit (Capsule) that are apomictic |
| Taste | Fishy minty taste |
| Health benefits | Cure for Environmental Sensitivities, Powerful Antioxidant, Protection against Harmful Organisms, Immune System Support, Diabetes, Weight Management and Herpes |
| Name | Chameleon Plant |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Houttuynia cordata |
| Native | Southern China, Korea, Japan, and Southeast Asia |
| Common Names | Chinese lizard tail, Fish mint, Fish plant, Fishwort, Heartleaf , Himalayan spinach, Lizard’s tail, Edible houttuynia, Heartleaf houttuynia, Vietnamese fish plant, White chaplu, Wild houttuynia, Chameleon, Chameleon plant, fishwort, houttuynia |
| Name in Other Languages | Assamese: Musundari, Aich, Mosondoi, Masundari, Mosundori, Mochondori Cambodia: Chii yaab kaa Chinese: Chòu cài aa (臭菜), gǒu tiē ěr(狗貼耳), jí cài (蕺菜), zhé ěr gēn (折耳根), shí yào (十藥), Yú xīng cǎo (魚腥草), Chou cai, Gou tie er, Tsi cai Danish: Houttuynia Dutch: Houttuynia, Moerasanemoon English: Chinese lizard tail, Fish mint, Fish plant, Fishwort, Heartleaf , Himalayan spinach, Lizard’s tail, Edible houttuynia, Heartleaf houttuynia, Vietnamese fish plant, White chaplu, Wild houttuynia, Chameleon, Chameleon plant, fishwort, houttuynia French: Hottonie, Houttuynie, Plante caméléon German: Buntblatt, Chinesischer Eidechsenschwanz, Houttuynie, Chamäleonpflanze Hindi: Simdalu Indonesia: Jukut hanyir Japanese: Dokudami Khasi: Ja mardoh Korean: Yagmomil (약모밀) Laotian: Phak, khav thong(ຄາວທອງ), phak khav thong (ຜັກຄາວທອງ), Khautong Manipuri: ꯇꯣꯛꯅꯤꯡꯈꯣꯛ Tokningkhok, তুনিংকোক, ꯇꯨꯅꯤꯡꯀꯣꯛ, Tuning Kok Nepalese: Gandhe (गन्धे), Gaane (गाने), Ganaaune Jhaar (गनाउने झार) Polish: Pstrolistka sercowata Portuguese: Dokudami Russian: Xauttyuyniya serdtsevidnaya (Xауттюйния сердцевидная), Хоуттуиния Slovenian: Hutujnija Swedish: Hoyttynia, Ödleblad Thai: Phak kan tong (ผักก้านตอง), Phak khao tong (ผักคาวทอง), Phlu kae (พลูแก) , Khāw thxng (คาวทอง), Phlūkhāw (พลูคาว), Cowtong, Kaotong, Plu khao, Pluu-kao Vietnamese: Diếp cá, Giấp cá, Ngư tinh thảo, Rau dap ca, Vap ca |
| Plant Growth Habit | Medium-sized herbaceous, rhizomatous, perennial ground cover plant |
| Growing Climates | Stream sides, forests, wet meadows, slopes, thicket and field margins, trail sides, roadsides, ditch banks; near sea level, lakes, urban areas, water courses and ravines |
| Soil | Soil having a reasonable amount of moisture content is best for the growth of these plants. Wet soil that is subjected to a partial amount of sunlight could also work wonders for the plant’s growth |
| Plant Size | Growing about 0.6–1 meter (2.0–3.3 ft.), spreading up to 1 meter (3.3 ft.) |
| Stem | Stems are green or sometimes purplish red, and either smooth or pubescent on the nodes |
| Leaf | Heart shaped leaves up to 75 mm long and almost as wide. The leaves are comprised of a mixture of colors from green through yellow to red, the brighter colors being more prominent when grown in full sunlight. |
| Flowering season | April-June |
| Flower | Flowers are small, crowded into a short spike around 2 cm long, with four white, petal-like bracts at the base. The stamens usually degenerate |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Dehiscent dry fruit (Capsule) are apomictic, i.e. they develop seeds without being fertilized |
| Propagation | By seed and rhizomes |
| Flavor/Aroma | Delicious orange-like smell |
| Taste | Fishy minty taste |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, stems, and roots |
| Season | July-August |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Other Facts |
|