| Name | Camu camu |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Myrciaria dubia |
| Native | South American Rainforest in Peru and Brazil, also available in Columbia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and Brazil. |
| Common/English Name | Camu-Camu, Rumberry, Guavaberry, Cacari, Zamu Camu Berry |
| Name in Other Languages | Brazil : Camu-Camu, Arazá De Agua; Columbia : Guayabo; Peru : Camu-Camu, Camo-Camo; Spanish : Camo Camo, Guapuro Blanco; Venezeula : Guayabato, Guaiabito |
| Plant Growth Habit | Bushy, low-growing shrub |
| Growing Climate | Hot, damp tropical |
| Soil | Well-drained |
| Plant Size | 1-3 m |
| Bark | Thin, pale to bronzy-brown |
| Stem | Smooth |
| Leaf | Evergreen, ovate or elliptic, length: 5 cm-12 cm, width: 2cm-4.5 cm |
| Edible parts of the plants | Juice is made by adding water, honey or sugar. It is also preserved in the form of jams, jellies, ice creams, drinks, liqueurs, pickles and wines. The juice is also sold as a carbonated drink and exported to use in Vitamin C tablets to the USA and other international markets. |
| Flowering Season | Dry |
| Flower | White, fragrant |
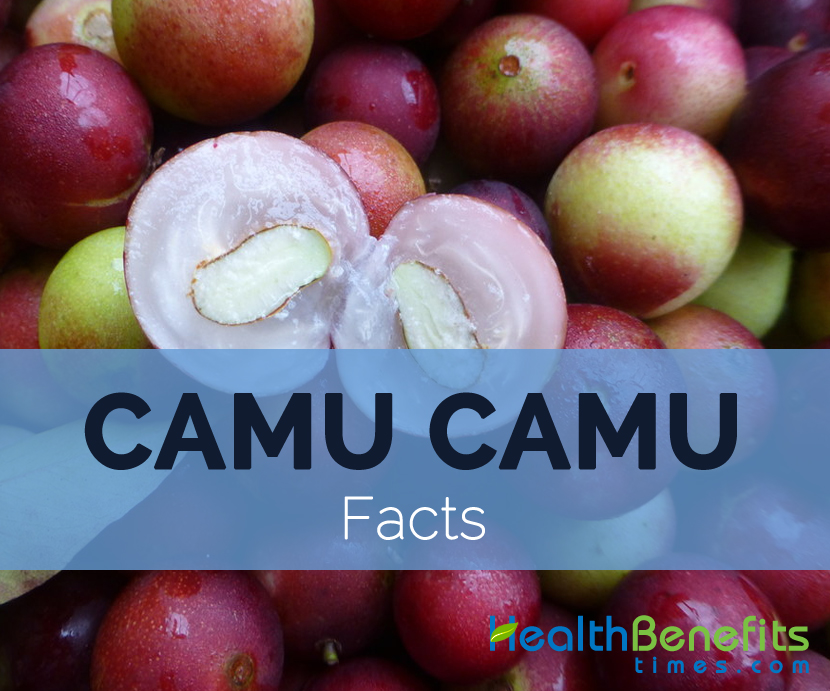
| Fruit shape & size | Cherry, Diameter: 1.0–3.2 cm, Size:2-4 cm |
| Fruit color | Reddish-brown or purple-black |
| Flesh color | White |
| Fruit peel | Thin and shiny |
| Flavor/aroma | Tart |
| Fruit Taste | Sour |
| Seed | 2–3, large |
| Fruit Season | Rainy |
| Major Nutritions | Carbohydrate 4.7 g (3.62%) Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) 0.04 mg (3.08%) Magnesium, Mg 12.38 mg (2.95%) Calcium, Ca 27 mg (2.70%) Phosphorus, P 17 mg (2.43%) Vitamin A 14.2 µg (2.03%) Total dietary Fiber 0.6 g (1.58%) Protein 0.5 g (1.00%) Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) 0.01 mg (0.83%) Sodium, Na 11.13 mg (0.74%) |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Calories in 1cup (100 gm) | 17 Kcal |
| Traditional uses |
|
| Precautions |
|
| How to Eat |
|
| Other Facts |
|
Camu Camu (Myrciaria dubia)Scientific Classification
| Scientific name | Myrciaria dubia |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Order | Myrtales |
| Family | Myrtaceae |
| Genus | Myrciaria |
| Species | Myrciaria dubia |
| Division | Magnoliophyta |
| Class | Magnoliopsida |
Comments
comments