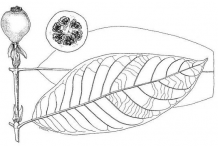
Plant Description
Borojo fruit is a mid-sized, tropical evergreen shrub that grows about 3 to 5m tall. The plant needs high humidity and temperature (an average of at least 25 °C) to thrive, though it can tolerate brief frosts as well as floods. The plant has grey-brown bark and sometimes has two or three smaller trunks as well as one main one.
Flower
Borojo is dioecious (separate male and female plants). Male Borojo plants have clusters of fragrant white flowers. Females have a single white flower at the tips of branches. Only the female plants produce fruits. Masculine flowers in chapters, short calyx, prismatic or conic, generally actinomorphous, sessile, pentamerous and occasionally tetramerous without an ovary or, if it exists, it is rudimentary or non-functional. Feminine flowers are lonely and terminal with two pairs of bracteal stipules and six longer stigmas; inferior ovary, with umbilical calyx at the base, six cavities and many ovules, corolla with six to nine petals, lineal stamen, empty or sterile.
Fruit
The fruit is large about 7 to 12 centimeters in diameter, with a round shape, green in color at the beginning and light brown at maturity and average weight of 740-1000 grams. The pulp represents 88% of the total weight and 12% seeds and shell. The pulp is brown, acid, and very dense (consisting mostly of fructose and glucose). The pulp constituted by mesocarp and the endocarp, with no apparent separation from the shell, weight between 740 and 1 kg. Each fruit has 90 to 640 seeds, and it is considered ripe when it falls to the ground. Borojo has high levels of protein, phosphorus, ascorbic acid, calcium and iron. Borojo is used in the preparation of jam, wine, desserts and traditional medicines with supposed aphrodisiac effects. It is also used by the local communities against hypertension, bronchial diseases and malnutrition.
The fruit cannot be harvested green. At maturity the fruit turns brown, and falls on the ground. Only then the fruit can be harvested and only then, the fruit has all the legendary properties it is known for. The pulp has a relative humidity higher than 60%, indicating that it has high water content in its composition. In dry weight most of the borojo are carbohydrates, dietary fiber, protein, calcium, phosphorus and iron. In traditional medicine the juice of this fruit is used to treat sexual impotence, bronchial affections, Hypertension, cancer, infections and chronic fatigue.
Health benefits of Bojoro
Fruits consists of considerable amount of phosphorus and essential amino acids, as well as other important vitamins and minerals including vitamin C, calcium, and iron. Promoters also claim borojo may help maintain normal levels of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol, as well as normal estrogen production in women. Listed below are few of the health benefits of Bojoro
1. Reduces fatigue after exercise
Due to its large number of carbohydrates, borojo is appropriate for people who have great physical activity, as it can provide the energy needed to recover from training. The main carbohydrate of borojo is fructose, a carbohydrate that has been researched for its effects in sports. Previous research has indicated that fructose decreases fatigue in aerobic and anaerobic sports
2. Strengthens bones, teeth and gums
Calcium is a mineral that is involved in many biological functions essential for life, from its intervention in the process of muscle contraction to blood clotting. It is very important in mineralization and therefore, in strengthening bones, teeth and gums. In addition it favors the adequate clotting of the blood and cardiovascular diseases. This nutrient favors the regulation of heart rate and the transmission of nerve impulses.
3. Keeps you hydrated
Borojó can help you stay hydrated, since more than 80% of its composition is water. However, no food should be a substitute for natural water, as it is very important to maintain our water balance to maintain health.
4. Improves the functioning of the heart, nervous system and digestive system
Borojo consists of considerable amount of Vitamin B1 and it plays an important role in the metabolism of carbohydrates mainly to produce energy. It also participates in the metabolism of fats, proteins and nucleic acids (DNA, RNA). It is essential for normal growth and development and helps maintain the functioning of the heart, nervous and digestive system.
Traditional uses and benefits of Borojo
- It is used by the local communities against hypertension, bronchial diseases and malnutrition.
- Fruit is prized for its tonic and cure-all qualities.
- It is famous in western Colombia for its supposed aphrodisiac properties.
- Borojo can provide support for the bronchial system, and help the metabolism and immune system with healthy cellular regeneration.
- Borojo is also taken by women as well as men as an appetite suppressant and a natural source of energy.
- The presence of Niacin (vitamin B3) makes Borojo potent for treating/fighting diseases like depression, anxiety, arthritis, cancer and most importantly schizophrenia.
- Polyphenols are strong antioxidants that protect cells against free radical damage.
- It is well known to help treat bronchial issues.
- It is said to stabilize blood sugar levels, control arterial hypertension and relieves menstrual discomfort
Culinary Uses
- Borojo is used in the preparation of jam, wine, and desserts.
- Fruit pulp is used to prepare juice, compotes, marmalades, candies and wine.
- In Colombia, the borojo fruit is used as an ingredient in a drink called “jugo de amor” or “love juice” and considered as an aphrodisiac.
Recipe for “Jugo de Amor”
Ingredients
- 1 whole borojo fruit
- 2 liters water
- 1 cup powdered milk
- 1/2 kg sugar
- 2 beaten eggs
- 1 tablespoon vanilla
- 1 teaspoon nutmeg
Directions
- Cut the fruit in half and scoop out the flesh with a spoon.
- Place in blender with a little of the water and blend.
- Dissolve the powdered milk in the remaining water and stir in vanilla, nutmeg, eggs and sugar.
- Add to the blender and process until smooth serve very cold.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Alibertia+patinoi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alibertia_patinoi
http://ez2plant.com/product/__template=iphone/lid=33906363
http://www.valentine.gr/linkOfTheMonth-march2014.php
https://wikivisually.com/wiki/Alibertia_patinoi
https://www.fincalahermosa.com/uploads/5/9/9/5/5995321/borojo_-_info.pdf
Comments
| Borojo Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Borojo |
| Scientific Name: | Alibertia patinoi |
| Origin | Northwest area of Colombia in the Chocó Department and in the Esmeraldas Province of Ecuador |
| Colors | Green when young turning to brown color as they mature |
| Shapes | Large, with a round shape, between 7 to 12 cm in diameter |
| Flesh colors | Chocolate color |
| Taste | Sweet and Sour |
| Health benefits | Improves the functioning of the heart, nervous system and digestive system, Reduces fatigue after exercise, Keeps you hydrated, Strengthens bones, teeth and gums |
| Name | Borojo |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Alibertia patinoi |
| Native | Northwest area of Colombia in the Chocó Department and in the Esmeraldas Province of Ecuador |
| Common Names | Burijo, burojó |
| Name in Other Languages | English: Borojó Spanish: Borojó |
| Plant Growth Habit | Mid-sized, tropical evergreen shrub |
| Growing Climates | Lowland rainforests |
| Plant Size | 3 to 5m |
| Bark | Grey-brown bark |
| Flower | Dioecious plant, meaning there are separate male and female plants. The male plant has clusters of fragrant white flowers whereas the females have a single white flower at the tips of branches. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Large, with a round shape, between 7 to 12 cm in diameter |
| Fruit Color | Green when young turning to brown color as they mature |
| Fruit Weight | 740-1000 grams |
| Flesh color | Chocolate color |
| Seed | Each fruit has 90 to 640 seeds |
| Taste | Sweet and Sour |
| Plant Parts Used | Fruit |
| Available Forms | Juice, jelly, sauce, as a mixer of alcoholic beverages, ice cream, capsules, nutraceuticals and extracts |
| Propagation | Seeds |
| Health Benefits |
|