| Name | Blackberry |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Rubus fruticosus |
| Native | Native to temperate Europe in the Northern Hemisphere. |
| Common/English Name | Noxious Blackberry, Blackberries, Wild Blackberry, Blackberry, Bramble, Thornless Blackberries, European Blackberry, Shrubby Blackberry, Bramble Berry, Cultivated Blackberries Common Blackberry, Dewberry. |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic : Tût Shawkî, ‘Ullayq Portuguese : Amora , Amora Silvestre Esperanto : Rubuso; Chinese : Ou Zhou Hei Mei Slovašcina : Robida Nagubana Gaelic : Dris Czech : Ostružiník Křovitý, Ostružiníky Hungarian : Feketeszeder, Földiszeder, Szeder Dutch : Gewone Braam, Braam, Braam Sort Greek : Vatomuro Vietnamese : Quả Mâm Xôi (Fruit) Slovencina : Ostružina Riasnatá Finnish : Mustavatukka, Karhunvattu Danish : Almindelig Brombær, Brombær German : Brombeere, Brombeeren, Brombeerestrauch Turkish : Alik, Böyürtlen, Böyürtlen Çalısı Polish : Jeżyna Fałdowana, Jerzyna, Jeżyna Icelandic : Brómber Spanish : Zarza, Zarza Común, Zarzamora Hebrew : Petel Shachor Italian : Moro Delle Siepi, Mora Di Bosco Japanese: Seiyou Abu Ichigo Norwegian : Bjørnebær, Bjønnbær, Brandbær India : Kaalii Anchhi, Kaalaa Jaamun ( Hindu ) Swedish : Blomsterbjörnbär, Sötbjörnbär Estonian : Aedmurakas, Kitsemari, Pampel |
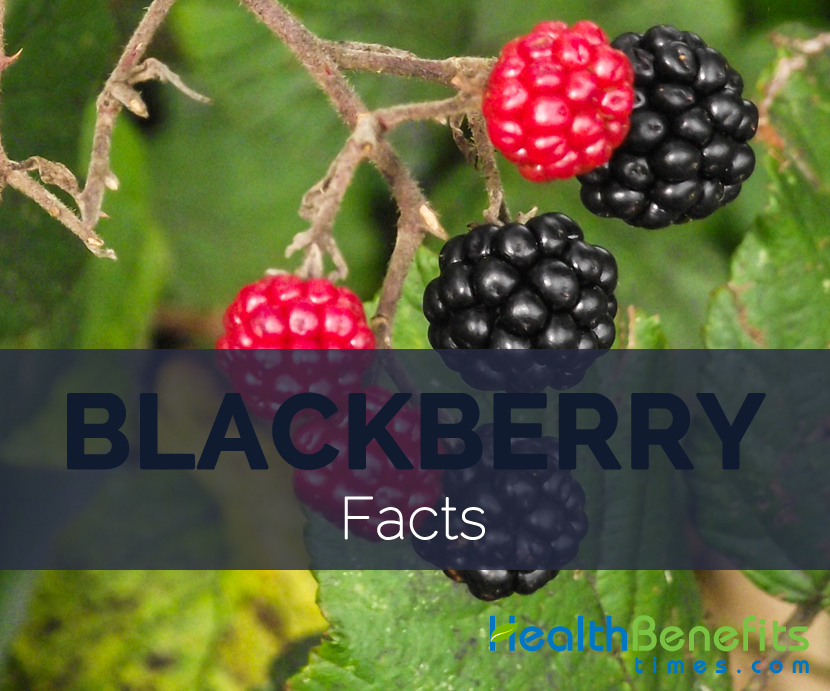
| Description | Blackberry is an eatable fruit produced by many species in the Rubus genus in the Rosaceae family. It is globe-shaped fruit which is green while young and changes to glossy black as they ripen. Due to its sweet taste it is ideal for jams, desserts, snacks, pies. |
| Plant Growth Habit | Perennial, semi-deciduous, prickly or thorn less scrambling, semi-prostrate to almost erect shrub |
| Growing Climate | Sunny (full sun) to part-shaded Position, fruit development better in warm, humid positions protected from wind |
| Soil | Well prepared, well-drained soil enriched with well-rotted manure or compost. |
| Plant Size | 2 m high and with canes to about 7 m long. |
| Root | Perennial root system and are branched, stout, creeping underground, growing vertically to a maximum depth of 1.5 m depending on soil type |
| Stem | Arching, green, reddish or purple, ribbed, angled or concave, with or without hairs and grow up to seven metres long. |
| Leaf | Comprise 3 or 5 ovate leaflets, usually are dark green on the upper surface and with many to no hairs and bears Pickles underneath, leaves have toothed edges |
| Flowering Season | In northern hemisphere, from May to August
In southern hemisphere from November to April |
| Flower | 2–3 cm in diameter with five white or pale pink petals with numerous stamens |
| Fruit shape & size | Globe-shaped, about 2–3.2 mm long, 1.5–2.8 mm wide, 1–1.8 mm thick, made up of approximately twenty to fifty single-seeded drupelets |
| Fruit color | Color green changing to straw yellow, amber, orange-red, red, reddish black, to glossy black as they ripen. |
| Fruit Peel | Smooth and fragile skin |
| Fruit Taste | Wonderful and sweet |
| Seed | Seeds are normally oval, irregularly pitted,coloured light to dark brown, 2.6-3.7 mm long and 1.6-2.5 mm wide. |
| Varieties/Types | Tupi, Jumbo, Chester, Choctaw, Bartin, Oklawaha, Bursa 1, Arapaho,Brazos, Navaho, Thornfree, Chester Thornless, Dirksen Thornless, Ness, Loch Ness, Cherokee, Black Satin,Bursa 3, Apache, Cacanska Bestrna, Chickasaw, Flordagrand, Kiowa, Natchez, Ouachita, Prime-Ark, Bursa 2,Prime-Jan, Prime-Jim, Shawnee, Triple Crown, |
| Season | August-September |
| Major Nutritions | Manganese 0.93 mg(40.43%), Vitamin C 30.2 mg (33.56%), Copper 0.238 mg (26.44%), Vitamin K 28.5 µg (23.75%), Total Dietary Fiber 7.6 g (20%), Vitamin E 1.68 mg (11.20%), Iron 0.89 mg (11.13%), Carbohydrate 13.84 g (10.65%), Vitamin B9 36 µg (9%), Vitamin B5 0.397 mg (7.94%) |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Calories in 1cup (145gm) | 62 |
| Traditional Medicinal Use |
|
| Precautions |
|
| How to Eat |
|
| Other Facts |
|
Comments
comments