African scarlet eggplant, Azoko, Ethiopian eggplant, Garden egg, Gilo, Golden apple, Kumba, Love apple, Mock tomato, Ruffed tomato, bitter tomato, chinese scarlet eggplant, ethiopian eggplant, ethiopian nightshade, garden eggs, mock plant, mock tomato, scarlet eggplant, silverleaf nightshade and tomato-fruit eggplant are some of the popular common names of the plant. These names are a result of its varied morphology, with ripe fruit often looking like a cross between an eggplant and a tomato, which are also from Solanum. In fact, the Ethiopian eggplant was so much confused with the ordinary eggplant that this was considered by some a variety violaceum of S. aethiopicum.
Bitter Tomato Facts
| Bitter tomato Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Bitter tomato |
| Scientific Name: | Solanum aethiopicum |
| Origin | Tropical Africa and South America; specifically Brazil |
| Colors | Green or white turning to red or orange as they mature |
| Shapes | Globose to oblate, ellipsoid, ovoid or fusiform berry. They are 5–15 cm across and 2–12 cm long, smooth to furrowed |
| Flesh colors | White |
| Name | Bitter Tomato |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Solanum aethiopicum |
| Native | Wild tropical Africa and South America; specifically Brazil. However, this species is less domesticated in south France and Italy. Recently, the plant species has spread to sub-Saharan Africa and other parts of South America. |
| Common Names | African scarlet eggplant, Azoko, Ethiopian eggplant, Garden egg, Gilo, Golden apple, Impwa, Kumba, Losuke, Love apple, Mock tomato, Ruffed tomato, bitter tomato, chinese scarlet eggplant, ethiopian eggplant, ethiopian nightshade, garden eggs, gilo, granadillo, jilo, kumba, röd aubergin, scarlet eggplant, shum, silverleaf nightshade, tomato-fruit eggplant, tutía enano, African Bitter Pea-Aubergine, African Eggplant, Dayak Eggplant, Jamaican Bitter Balls, Sarawak Wild Eggplant, Shum, Terung Sarawak, Wild Pea-Aubergine, Wild African Aubergine |
| Name in Other Languages | Amharic: Bmy Angola : Tungo Arabic: حدق أثيوبي Brazil : Jagatú Tunga, Jiló: Benin : Aubergine indigene, tomate amère, gboman, assoukoussé Catalan: Fals tomàquet Central African Republic : Sasa Chinese: Xiao gu qie, Xiao ku fan qie Congo : Ngbagu Danish: Kinesisk aubergine, Æthiopisk ægplante English: African bitter pea-aubergine, African eggplant, Bitter tomato, Ethiopian eggplant, Garden egg, Jamaican bitter balls, Mock tomato, Scarlet eggplant, Tomato-fruited eggplant, Wild pea-aubergine, Wild African aubergine, Chinese scarlet eggplant, Gilo, Ethiopian nightshade, Kumba, Shum Ethiopia : Bmy French: Aubergine africaine, Aubergine amère, Aubergine écarlate, Petite bringelle maronne, Tomate amère, Africaine, Aubergine indigene, Djakattou, Petite Bringelle Maronne German: Äthiopische Eierfrucht Lingala: Mosangó Malaysia : Dayak Eggplant, Sarawak Wild Eggplant, Sour Brinjal, Terong Asam, Terong Iban, Terong Sarawak, Terung Dayak, Terung Dayak Sarawak, Terung Asam Manipuri: ꯈꯥꯃꯦꯟ ꯑꯈꯥꯕꯥ Khamen Akhaba Nigeria : Osun Portuguese: Jiló, Jagatú tunga, Gilo, Jiloeiro Senegal : Dyahat Swahili: Ngogwe, Nyanya chungu Swedish: Röd aubergin Thai: Mak̄heụ̄x k̄hm (มะเขือขม) Uganda : Ekitulatula, nakatti Unidentified: Nakati |
| Plant Growth Habit | Perennial or annual deciduous shrub |
| Growing Climates | Cultivated in woodland and wooded grassland zones |
| Soil | Fairly deep and well-drained soils |
| Plant Size | Up to 200 cm tall |
| Root | Root system extending both vertically and laterally |
| Stem | Glabrous to stellate-pubescent with trichomes porrect, translucent or orange translucent, sessile or shortly stalked |
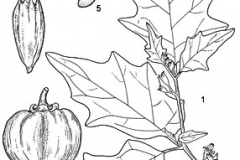
| Leaf | Leaf blades are yellowish green to dark red-brown or almost black, 2–3 times longer than wide, broadly ovate, 6–30 cm long and 4–21 cm wide, base cuneate to rounded, often unequal or oblique, margin sub entire to weakly lobed |
| Flowering season | July to September |
| Flower | Flowers are 5-merous. Flower-stalk is 5-12 mm, with prickles 0.2-2 mm. Calyx is bell-shaped; sepals are slightly unequal, ovate to ovate-lance shaped, 5-7 long and 3-4 mm wide. Flower is white or slightly purplish, star-shaped or star-shaped-rotate, 1.5-2.5 cm in diameter |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Globose to oblate, ellipsoid, ovoid or fusiform berry. They are 5–15 cm across and 2–12 cm long, smooth to furrowed, superficially resembling a tomato, often longitudinally 4-6-grooved |
| Fruit Color | Green or white turning to red or orange as they mature |
| Flesh Color | White |
| Fruit skin | Thin waxy |
| Seed | Lenticular to reniform, flattened, kidney shaped about 2–5 mm in diameter, pale brown or yellow |
| Season | August to October |
Plant Description
Bitter tomato is a perennial or annual deciduous shrub that normally grows up to 200 cm tall. The plant is cultivated in woodland and wooded grassland zones. The plant prefers fairly deep and well-drained soils. It does well on annual daytime temperatures ranging from 200c-300c. Sometimes it can tolerate from as low as 100c and high up to 400c. Annual rainfall ranges from 1200mm to 1600mm. The plant has root system that extends both vertically and laterally. Young stems are glabrous to stellate-pubescent with trichomes porrect, translucent or orange translucent, sessile or shortly stalked, stalks up to 0.1 mm, rays 0.15–0.3 mm, midpoints shorter than rays.
Leaves
The branches and leaves can be with or without prickles and stellate hairs. Leaf blades are yellowish green to dark red-brown or almost black, 2–3 times longer than wide, broadly ovate, 6–30 cm long and 4–21 cm wide, base cuneate to rounded, often unequal or oblique, margin sub entire to weakly lobed. The upper leaves are smaller, narrower, and less lobed and often sub opposite. The lobes are up to 3 on each side, up to 1.5 cm long, broadly rounded (acute) and extending up to 1/4 of the distance to the mid vein, apex acute; glabrous to stellate-pubescent. Rays are 0.2–0.35 mm long, midpoints shorter than rays, adaxially with thick stalks and reduced rays and midpoints, often with minute simple hairs. Petiole is 1–4 cm long, 1/4–1/3 of the leaf length.
Flowers
Flowers are borne in few flowered, racemose clusters. Flower-cluster-stalk is about 1-1.5 cm long. Flowers are 5-merous. Flower-stalk is 5-12 mm, with prickles 0.2-2 mm. Calyx is bell-shaped; sepals are slightly unequal, ovate to ovate-lance shaped, 5-7 long and 3-4 mm wide. Flower is white or slightly purplish, star-shaped or star-shaped-rotate, 1.5-2.5 cm in diameter. Limb is about 6.5 mm. Filaments are 0.5-1 mm long and hairless. Anthers are lance shaped-elliptic, 4-5 mm long and 0.7-1 mm wide, notched at tip and base. Ovary is 4-8-locular. Style is 5.7-7.5 mm long. Flowering normally takes place in between July to September. Flowering starts between 40 days to 100 days after seeds broadcast.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by globose to oblate, ellipsoid, ovoid or fusiform berry. They are 5–15 cm across and 2–12 cm long, smooth to furrowed, superficially resembling a tomato, often longitudinally 4-6-grooved. Immature fruits are green or white turning to red or orange as they mature and are many-seeded. Seeds are lenticular to reniform, flattened, kidney shaped about 2–5 mm in diameter, pale brown or yellow. It is a popular vegetable in north-east India. One plant can produce up to 8 kg of fruits with varied cultivation conditions. Fruits produced resemble hens’ egg.
Origin/Distribution
Solanum aethiopicum, one of the leading vegetables in tropical Africa was reported to have been domesticated from the wild Solanum anguivi Lam., via the semi-domesticated Solanum distichum Schumach. & Thonn. Both these ancestral species occur throughout tropical Africa, Solanum anguivi in disturbed vegetation and Solanum distichum in gardens. Solanum aethiopicum is grown throughout tropical Africa and South America (mainly Brazil), and occasionally elsewhere, e.g. in southernmost France and Italy and in Southeast Asia.
Traditional uses and benefits of Bitter Tomato
- Fruits of bitter cultivars are used as medicine in many African countries.
- Roots and fruits are used to treat colic and high blood pressure.
- Leaf juice as a sedative is used to treat uterine complaints.
- An alcoholic extract of leaves as a sedative, anti-emetic are used to treat tetanus after abortion.
- Macerated fruits are used as an enema.
- Alkaloids are also extracted from the leaves used as an anti-inflammatory agent.
- Hot leaf infusion is taken to treat diabetes mellitus in Nigeria.
- Leaf infusion is also taken to treat intestinal worms in southern Uganda.
Culinary Uses
- Fruit can be cooked when fully ripe.
- It can be used like aubergine as a vegetable or as a flavoring for other foods.
- Very young leaves are said to be edible when cooked though they are bitter.
- Leaves of Solanum aethiopicum are eaten as a leaf vegetable and are actually more nutritious than the fruit.
- Immature fruits of Solanum aethiopicum are used as cooked vegetables in stews, and sometimes eaten raw.
- Leaves and shoots are used as a cooked vegetable.
- Young shoots are stripped of their numerous flowers and buds, and then finely cut for use in soups.
- The fruits are sour with a pleasant aroma and are used raw or cooked in stews, soups, sauces or relish.
- It is cooked with fish, made into kerabu (spicy salad) or cooked in coconut milk.
Other Facts
- Solanum aethiopicum is used occasionally as an ornamental in Asia.
- In Nigeria, Igbo people use it as a substitute for kolanut especially for those who do not want to chew kolanut.
- It is sometimes used to make a tomato based sauce which can be used to eat yam.
- Igbo people in south-eastern Nigeria traditionally welcome visitors into the family house by offering fruits.
- Solanum aethiopicum is occasionally cultivated as an ornamental.
- Some cultivars are occasionally used as a rootstock for tomato and eggplant.
- One plant may produce from 500 g to about 8 kg of fruits, depending on the cultivar and growing conditions.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=505828#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=100448
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Solanum+aethiopicum
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SOAE2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solanum_aethiopicum
http://wgb.cimmyt.org/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=100448
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/50505
https://www.prota4u.org/database/protav8.asp?g=pe&p=Solanum+aethiopicum+L
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/tro-29600093
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Bitter%20Tomato.html
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Solanum+aethiopicum
https://thewesternghats.in/species/show/245034