The genus name Cerbera is derived from Cerberus, the hell dog from Greek mythology, referring to the poisonous and toxic nature of the seeds. The plant is used locally as an herbal medicine, being mainly harvested from the wild. Medicinal products are sometimes sold in local markets. A very ornamental tree, with beautiful, aromatic flowers that can be produced all year round, and interesting fruits that are used in flower displays, it is sometimes grown in gardens.
Bintaro Facts
| Bintaro Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Bintaro |
| Scientific Name: | Cerbera manghas |
| Origin | India, Sri Lanka, China, Australia, the Malay Archipelago, the Pacific Islands and Madagascar and the Comoros |
| Colors | Initially green turning to red when mature |
| Shapes | Drupe, smooth, ellipsoid or ovoid, 5 to 10 centimeters (2.0 to 3.9 in) long, flattened on one side |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for liver disorders, scabies and prurigo, hemorrhoids, dysuria and ringworm, cardiac disorders, rheumatism and hydrophobia |
| Name | Bintaro |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cerbera manghas |
| Native | India, Sri Lanka, China, Australia, the Malay Archipelago, the Pacific Islands and Madagascar and the Comoros |
| Common Names | Madagascar ordeal-bean, Beach milkwood, Dogbane, Dogbone, Grey milkwood, Pink-eyed cerbera, Reva, Rubbertree, Sea-mango, pong-pong, Pokok Pong Pong, Sea Pong Pong, Buta Buta, Nyan, Pink-eyed Pong Pong Tree, Tanghin Poison, Odollam tree |
| Name in Other Languages | Bengali: Dagor Burma (Myanmar): Kalwa salat Chinese: Hai mang guo (海檬果), hǎi máng guǒ shǔ (海芒果属) English: Madagascar ordeal-bean, Beach milkwood, Dogbane, Dogbone, Grey milkwood, Pink-eyed cerbera, Reva, Rubbertree, Sea-mango, pong-pong Finnish: Madagaskarinsurmanpuu French: Faux manguier, Tanghin Indonesian: Bintaro, bintan, mangga brabu Japanese: Okinawakyouchikutou (オキナワキョウチクトウ), Mifukuragi (ミフクラギ) Javanese: Bintaro Kannada: Chande, Monde Malay: Buta-buta, Pongpong, Bentan, Bintaru, Pokok Bentan Malayalam: Utalam, Chattankaya Malaysia: Bentan, bintaru Marathi: Sukanu Others: Dog-bane, Reva, Madagascar Ordeal Bean, Sea Mango, Pink-eyed Cerbera, Odollam Tree, Jawa Tree, Cerbera, Odallam Philippines: Baraibai Portuguese: Manga-de-água Russian: Tserbera manga (Цербера мангас) Swedish: Klippmangrove Tamil: Kodalma, Kattarali, Kottuma, Caat aralie Thai: Tīnpĕd thrāy (ตีนเป็ดทราย), teenpet lek, teenpet sai, rak khao Vietnamese: Hải guả tủ huờng, muróp sat huờng, muróp xác huờng |
| Plant Growth Habit | Small evergreen tree with round to oval crown |
| Growing Climates | Coastal forests, mangrove areas with freshwater input, rivers or streams, seashore, tidal river banks, in swamp forest, but may also be found in shrubby savanna or in secondary forest edges |
| Soil | Preferably be grown in full light in a fertile, moist but well-drained loam with additional leaf mould |
| Plant Size | 5–25 m tall; trunk to 70 cm in diameter |
| Bark | Grey to dark brown, rough, peeling off in clumps, with large lenticels |
| Wood | Soft, white; glabrous in all parts except for corolla |
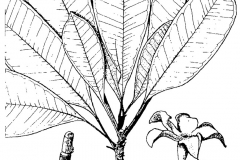
| Leaf | Leaves are lanceolate to oblong-lanceolate about 5–31 cm long, 1–7 cm wide, dark green and glossy, held in dense spirals at the tips of the twigs. Petiole is 1–4.5 cm long |
| Flowering season | April- August |
| Flower | White fragrant, about 5 centimeters across, usually only one open per inflorescence. Sepals are short, pale green, spreading and often recurved, 8–37 mm long and 2–8 mm wide. Corolla tube is slender, greenish, 17–55 mm long |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Drupe, smooth, ellipsoid or ovoid, 5 to 10 centimeters (2.0 to 3.9 in) long, flattened on one side |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to red when mature |
| Seed | Large hard stony pit that contains oily seed |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, latex, fruit |
| Season | July – December |
Plant Description
Bintaro (Sea Mango) is a small evergreen tree with round to oval crown growing 5–25 m tall; trunk to 70 cm in diameter. The plant is found growing in coastal forests, mangrove areas with freshwater input, rivers or streams, seashore, tidal river banks, in swamp forest, but may also be found in shrubby savanna or in secondary forest edges. The plant preferably is grown in full light in a fertile, moist but well-drained loam with additional leaf mold. Bark is grey to dark brown, rough, peeling off in clumps, with large lenticels. Wood is soft, white; glabrous in all parts except for corolla. Leaves are lanceolate to oblong-lanceolate about 5–31 cm long, 1–7 cm wide, dark green and glossy, held in dense spirals at the tips of the twigs. They are narrowed and pointed at both ends, furnished with slender nerves, arranged spirally or fan-like. Leaves are generally smaller than that of the more common Yellow-eyed Pong pong tree (Cerbera odollam). Petiole is 1–4.5 cm long.
Flower
Flowers are white fragrant, about 5 centimeters across, usually only one open per inflorescence. Sepals are short, pale green, spreading and often recurved, 8–37 mm long and 2–8 mm wide. Corolla tube is slender, greenish, 17–55 mm long; lobes white, often pinkish outside, obliquely elliptic to obovate, 14–30 mm long, 9–18 mm wide with 5 white or yellow lanate scales 1.5–3 mm long in the center, pubescent at the mouth and inside the tube. They have five stamens and the ovary is positioned above the other flower parts. Anthers are subglobose, 1.5–3 mm long. The center of the flower is initially orange-pink, but becomes red to purple with age. Several flowers are arranged together in terminal inflorescences known as cymes. The flowers appear at the tips of the twigs. Flowering normally takes place in between April- August. All parts of the flower contain latex.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by a drupe, smooth, ellipsoid or ovoid, 5 to 10 centimeters (2.0 to 3.9 in) long, flattened on one side, initially green turning to red when mature. The outer part of the fruit is fleshy, while the inner part is fibrous. It is classified as a drupe, because it holds a hard stony pit that contains oily seed.
Traditional uses and benefits of Bintaro
- Milky sap and leaves are emetic and purgative.
- Fruit combined with Datura is used for hydrophobia.
- Red fruit, when fresh are rubbed on legs for rheumatism.
- Latex is rubifacient on the skin.
- Fruit kernel is used as abortifacient.
- Oil can be rubbed on skin to cure itches.
- In Java, along with heating oils, rubbed on skin as rubifacient to cure colds.
- The oil is applied to hair as an insecticide in Burma.
- Some individuals in Samoa use the fruit as a laxative and a component of medicines that are applied externally.
- Roots and bark can also be used to make a laxative.
- Seeds are used in traditional medicine in Madagascar to treat cardiac disorders.
- The seeds are used to treat scabies and itch in tropical Asia.
- Bark is used as a laxative and antipyretic and in the treatment of dysuria and ringworm.
- Flowers are used to treat hemorrhoids and the root bark and leaves to prepare purgative.
- Seed oil in plasters applied to the skin is effective for scabies and prurigo, applied to hair kills head-lice.
- The glycosides extracted from the seeds are active on hearty failure.
- Scraped root is used to treat liver disorders.
- Decoction of the inner bark is drunk with cold water as an abortifacient.
Other Facts
- Seeds were used in sentence rituals to poison kings and queens in Madagascar.
- Soft wood produces a fine charcoal, which the Siamese used in 1778 for gunpowder.
- In Penang, oil of seeds used as an illuminant.
- Sap is mixed with “ipoh” to produce a poison in Benua.
- It is used as fish poison in small streams in Philippines.
- All parts of the plant exude white, milky latex when cut.
- It can also be used for carvings and furniture.
- Oil extracted from the seeds can be used to make candles.
- Wood is occasionally used in tropical Asia for moldings, interior trim, fruit cases, core veneer, matches, shuttering, clogs, plain furniture, and carvings and also for charcoal.
- It is planted as an ornamental plant.
- In Sri Lanka this wood is used for making masks particularly because it is a lighter wood.
- Fruit was reportedly eaten to commit suicide in the Marquesas Islands.
- In Hawaii Cerbera manghas is called suicide apple.
Precautions
- Seeds are toxic.
- Green fruit used to kill dogs.
- Latex causes blindness.
- Fruit kernel is an irritant poison, which may cause vomiting, purging, collapse and death.
- Plant with its cardiac glycoside content has cause of suicidal or homicidal deaths.
- Leaves and the fruits consist of the potent cardiac glycoside cerberin, which is extremely poisonous if ingested.
- Since all parts of bintaro tree is poisonous, don’t burn the woods, leaves or the fruits because the toxins could be spread by the smokes.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=893828#null
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/12177
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CEMA20
http://www.stuartxchange.org/Baraibai
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/KBRMA
https://en.hortipedia.com/Cerbera_manghas
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-37166
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cerbera_manghas
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Sea%20Mango.html
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Cerbera_manghas_(PROSEA)
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Cerbera+manghas