Herbs like Safflower, Pomegranate, Ginseng, and Turmeric help reduce age spots. Their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties combat oxidative stress, inhibit melanin, and boost collagen, offering natural, safer alternatives to managing age spots and overall skin health compared to conventional medications.
 Age spots, also known as solar lentigines or lentigo senilis, are light brown to black pigmented lesions that typically develop on chronically sun-exposed skin. These spots are strongly associated with chronic sun exposure and photodamage, and they carry an increased risk for skin cancer. Pathologically, age spots are characterized by the aggregation of basal cells containing lipofuscin bodies, which are indicative of cellular aging. The accumulation of these aged cells leads to the formation of flat spots that can become protruding over time due to the successive deaths of lipofuscin-containing cells and the encapsulation of these cells by fibrotic membranes. The development of age spots involves complex processes including the increased proliferation of basal keratinocytes and the decreased turnover of suprabasal keratinocytes, which disrupts the normal processing of melanin and leads to the exaggerated formation of rete ridges in the epidermis.
Age spots, also known as solar lentigines or lentigo senilis, are light brown to black pigmented lesions that typically develop on chronically sun-exposed skin. These spots are strongly associated with chronic sun exposure and photodamage, and they carry an increased risk for skin cancer. Pathologically, age spots are characterized by the aggregation of basal cells containing lipofuscin bodies, which are indicative of cellular aging. The accumulation of these aged cells leads to the formation of flat spots that can become protruding over time due to the successive deaths of lipofuscin-containing cells and the encapsulation of these cells by fibrotic membranes. The development of age spots involves complex processes including the increased proliferation of basal keratinocytes and the decreased turnover of suprabasal keratinocytes, which disrupts the normal processing of melanin and leads to the exaggerated formation of rete ridges in the epidermis.
Infrared Thermometer
Types of Age Spots
Age spots, often seen as small, dark patches on the skin, can appear for various reasons, primarily due to prolonged sun exposure. While they are commonly associated with aging, different types of age spots can develop based on underlying causes and skin conditions. Knowing the specific type can help in choosing the right prevention and treatment methods. Below, we explore the most common types of age spots and what sets them apart.
- Solar Lentigines
- Liver Spots
- Seborrheic Keratosis
- Freckles (Ephelides)
- Melasma
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
- Moles (Nevi)
Common Causes of Age Spots
Age spots, also known as liver spots or sun spots, are flat, darkened areas that typically appear on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. While they are most common in older adults, age spots can develop at any age, particularly for those who spend a lot of time outdoors. Understanding the causes behind these pigmentation changes can help in preventing and managing them effectively. Here are some of the most common factors that contribute to the development of age spots.
- Sun exposure
- Ultraviolet (UV) light exposure (including tanning beds)
- Skin aging
- Genetics/hereditary predisposition
- Hormonal changes
- Excess melanin production
- Damage to pigment-producing skin cells (melanocytes)
- Fair skin
- Being over 40 years old
- Frequent sunburns
- Prolonged sun exposure over many years
Best herbs for Age Spots
Using herbs to care for age spots instead of medication offers several compelling advantages. Herbal remedies are increasingly recognized for their efficacy and safety in managing various aging-related conditions, including skin aging. Unlike synthetic medications, herbs such as Ginseng, Ginkgo Biloba, and other phytochemicals have been shown to possess potent anti-aging properties, including antioxidant effects and the ability to improve resistance to DNA damage, which are crucial in managing age spots. Additionally, herbal treatments are perceived to be milder and safer, with fewer side effects compared to conventional medications, making them a preferred choice for many individuals. The natural compounds in herbs can inhibit the degradation of collagen and elastin, essential for maintaining skin health and reducing the appearance of age spots. Furthermore, the holistic approach of herbal medicine, which often includes multiple beneficial compounds, can address not just the symptoms but also the underlying causes of skin aging, providing a more comprehensive treatment. Therefore, the use of herbs presents a natural, effective, and safer alternative to traditional medications for the care of age spots.
1. Safflower
Safflower oil shows promise as a natural remedy for age spots due to its unique composition and properties. Rich in linoleic acid and vitamin E, safflower oil offers potent antioxidant benefits that can help protect the skin from UV damage and oxidative stress, which are primary causes of age spots. The high content of linoleic acid may also aid in skin lightening and improving hyperpigmentation, potentially reducing the appearance of existing age spots. Additionally, safflower oil contains compounds like serotonin derivatives and acacetin that can help lighten dark patches and even out skin tone. Its moisturizing properties and ability to strengthen the skin barrier may further contribute to overall skin health, potentially preventing the formation of new age spots.
What Research Says?
- Based on research carried out by Langmuir, Solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN)-based hydrogel formulations significantly improve the solubility and skin penetration of quercetin and luteolin found in safflower petals extract. This increased solubility and penetration enhance the antioxidant activity of these compounds, making them more effective in preventing skin damage.
How to use
To use safflower for age spots, apply pure safflower oil directly to the affected areas twice daily after cleansing. Gently massage the oil into the skin until absorbed. For a more potent treatment, mix safflower oil with a few drops of lemon essential oil or vitamin E oil. Alternatively, create a mask by combining safflower oil with honey and turmeric powder, applying it for 15-20 minutes before rinsing. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for several weeks to see noticeable results. Always perform a patch test first to ensure no adverse reactions.
Potential side effects of safflower
Safflower oil can cause gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps in some individuals. It may also lead to allergic reactions, especially in people sensitive to plants in the Asteraceae family. High consumption can potentially increase blood sugar levels. In rare cases, it might cause skin irritation when applied topically. Excessive intake may contribute to inflammation due to its high omega-6 fatty acid content.
Who should avoid safflower
Pregnant women should avoid safflower as it may cause uterine contractions and miscarriage. People with bleeding disorders or scheduled for surgery should refrain from using safflower due to its blood-thinning effects. Individuals with diabetes should use caution as it may affect blood sugar levels. Those allergic to ragweed and related plants should avoid safflower. People with liver disease or gallbladder problems should consult a healthcare provider before use.
Interaction with medications
Safflower can interact with blood-thinning medications, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding. It may interfere with diabetes medications, affecting blood sugar control. Safflower might also interact with medications metabolized by the liver, altering their effectiveness. It can potentially enhance the effects of certain cholesterol-lowering drugs. Always consult a healthcare provider before using safflower alongside any medications, especially those for blood clotting, diabetes, or heart conditions.
2. Pomegranate

Pomegranate shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its rich antioxidant content and unique properties. The fruit’s high concentration of polyphenols, particularly ellagic acid and punicalagin, provides potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that can help combat oxidative stress and sun damage, primary causes of age spots. Pomegranate’s ability to promote cell rejuvenation and tissue repair may aid in reducing the appearance of existing age spots and preventing new ones from forming. Its natural UV protection properties can further shield the skin from sun-induced hyperpigmentation. Additionally, pomegranate’s capacity to stimulate collagen production and enhance skin elasticity contributes to overall skin health and a more youthful appearance. The fruit’s antimicrobial benefits may also help in maintaining clear skin.
What Research Says?
- As per studies undertaken by Nutrients, Pomegranate is rich in polyphenols, which have strong antioxidant properties. These antioxidants can help in reducing oxidative stress, a key factor in the formation of age spots.
How to Use
To use pomegranate for age spots, apply fresh pomegranate juice directly to the affected areas using a cotton ball twice daily. Alternatively, create a paste by grinding pomegranate seeds with a bit of lemon juice and apply it to the spots for 15 minutes before rinsing. For a more potent treatment, mix pomegranate seed oil with a few drops of vitamin E oil and massage into the skin nightly. You can also make a face mask by combining pomegranate juice, honey, and yogurt, applying it for 20 minutes twice weekly. Consistency is key for visible results.
Potential side effects of pomegranate
While generally safe, pomegranate can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, including itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Excessive consumption may lead to digestive issues such as diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting. In rare cases, it can cause low blood sugar. Topical application of pomegranate extract may cause skin irritation or rashes in sensitive individuals. Always perform a patch test before applying pomegranate products to larger skin areas.
Who should avoid pomegranate
Individuals with pomegranate allergies should avoid it entirely. Those with low blood pressure should use caution, as pomegranate may further lower blood pressure. People scheduled for surgery should stop consuming pomegranate at least two weeks prior due to its potential blood-thinning effects. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare provider before using pomegranate supplements. Those with kidney problems should avoid excessive consumption due to its high potassium content.
Interaction with medications
Pomegranate can interact with various medications. It may enhance the effects of blood pressure medications, potentially causing hypotension. Pomegranate can interfere with the liver’s ability to process certain drugs, including statins and some antibiotics, potentially increasing their side effects. It may also interact with blood thinners like warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. Always consult a healthcare provider before consuming pomegranate alongside any medications, especially those for blood pressure, cholesterol, or blood clotting.
3. Ginseng
Ginseng shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its unique composition and beneficial properties for skin health. Rich in antioxidants, particularly ginsenosides, ginseng can help combat oxidative stress and free radical damage, which are primary causes of age spots. Ginseng extracts and compounds can inhibit melanogenesis, the process responsible for skin pigmentation, both in vivo and in vitro. Ginseng’s ability to promote collagen production and improve skin elasticity may also contribute to reducing the appearance of age spots and improving overall skin tone. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties can help soothe irritated skin and reduce redness, which may indirectly benefit those with age spots. Ginseng can enhance skin moisture retention and protect against UV damage, both of which are crucial in preventing and treating age spots.
What Research Says?
- According to studies performed by Aging and disease and IJMS, Ginseng and its active components, such as ginsenosides, have been shown to have significant anti-aging effects, including the protection and rejuvenation of skin.
- Research undertaken by Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences and Journal of Medicinal Food reveals Ginseng extracts can improve skin conditions by increasing hyaluronic acid synthesis, aquaporin expression, and collagen production, which are crucial for maintaining skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles.
- Findings from research done by Food & Function and Nutrients show the antioxidant properties of ginseng help in reducing oxidative stress, which is a major factor in skin aging and the formation of age spots.
How to Use
To use ginseng for age spots, incorporate it into your skincare routine through various methods. Apply ginseng-infused creams or serums directly to affected areas twice daily after cleansing. For a more potent treatment, use Korean red ginseng extract mixed with a carrier oil and massage into the skin nightly. You can also brew ginseng tea and use it as a toner by applying it with a cotton pad. For internal benefits, consume ginseng tea or supplements daily, following recommended dosages. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for several weeks to see noticeable results. Always perform a patch test before widespread use.
Potential side effects of ginseng
Ginseng can cause side effects such as headaches, insomnia, and nervousness, especially when taken in high doses. Some users may experience digestive issues like diarrhea or upset stomach. In rare cases, it can lead to more severe reactions like rapid heartbeat, high blood pressure, or allergic reactions. Prolonged use may result in ginseng abuse syndrome, characterized by hypertension, nervousness, and insomnia. Always start with lower doses to assess tolerance.
Who should avoid ginseng
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid ginseng due to potential risks to fetal development. Individuals with hormone-sensitive conditions, such as certain cancers or endometriosis, should consult a healthcare provider before use. People with diabetes should monitor blood sugar levels closely when using ginseng. Those with heart conditions, bleeding disorders, or autoimmune diseases should exercise caution. Children and individuals with schizophrenia should avoid ginseng unless under medical supervision.
Interaction with medications
Ginseng can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of blood thinners like warfarin, increasing bleeding risk. Ginseng can interact with diabetes medications, potentially affecting blood sugar levels. It may also interfere with the effectiveness of certain antidepressants and stimulants. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining ginseng with any medications, especially those for heart conditions, blood pressure, or mood disorders.
4. Astragalus

Astragalus shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its unique properties and beneficial effects on skin health. Rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids and saponins, astragalus can help combat oxidative stress and free radical damage, which are primary causes of age spots. Research has demonstrated that astragalus can promote tissue growth and boost overall skin health, potentially aiding in the treatment of wrinkles and age spots. Its ability to enhance collagen synthesis and improve skin elasticity may contribute to reducing the appearance of age spots and improving overall skin tone. Additionally, astragalus has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, which can help maintain clear and healthy skin. Some studies have also indicated that astragalus can protect against UV damage, a crucial factor in preventing and treating age spots.
What Research Says?
- As research performed by Aging and disease and Phytotherapy Research suggests Astragalus membranaceus has been shown to have significant anti-aging effects, including increasing telomerase activity and exhibiting antioxidant properties, which can help in reducing oxidative stress, a key factor in the formation of age spots.
- Research completed by Frontiers in Nutrition and Phytomedicine indicates Studies indicate that Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) can decrease malondialdehyde (MDA) content and increase superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, which helps in mitigating oxidative damage and potentially reducing age spots.
How to Use
To use astragalus for age spots, apply a topical cream or serum containing astragalus extract directly to the affected areas twice daily after cleansing. Look for products with at least 6% astragalus extract for optimal results. Alternatively, create a DIY treatment by mixing astragalus powder with a carrier oil like jojoba or coconut oil and apply to the spots. For internal benefits, consume astragalus tea or take supplements following recommended dosages. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for several weeks to see noticeable results. Always perform a patch test before widespread use and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential side effects of astragalus
While generally considered safe, astragalus can cause side effects in some individuals. These may include mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea, diarrhea, or bloating. Some users might experience a rash or allergic reactions, particularly those with legume allergies. In rare cases, it can lead to increased urination or nasal symptoms. High doses may potentially affect blood sugar levels or blood pressure. Always start with lower doses to assess tolerance.
Who should avoid astragalus
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid astragalus due to insufficient safety data. Individuals with autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, should consult a healthcare provider before use, as astragalus may stimulate the immune system. People with bleeding disorders or scheduled for surgery should avoid astragalus due to potential blood-thinning effects. Those with diabetes or taking medications that affect blood sugar should use caution and monitor their levels closely.
Interaction with medications
Astragalus can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of immunosuppressant drugs, interfering with their intended purpose. Astragalus can interact with medications that affect blood clotting, potentially increasing bleeding risk. It may also interfere with drugs metabolized by the liver, such as certain antidepressants or statins. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining astragalus with any medications, especially those for immune disorders, blood clotting, or diabetes.
5. Reishi Mushroom
Reishi mushroom shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its unique composition and beneficial properties for skin health. Rich in antioxidants, particularly triterpenoids like ganodermanondiol, reishi mushroom can help combat oxidative stress and free radical damage, which are primary causes of age spots. Ganodermanondiol from reishi can effectively inhibit melanin production by suppressing tyrosinase activity and expression, potentially reducing hyperpigmentation and discoloration of the skin. Additionally, reishi mushroom’s anti-inflammatory and skin-hydrating properties, attributed to its high concentration of polysaccharides, can improve overall skin health and appearance. These polysaccharides help retain moisture, improve skin barrier function, and may contribute to reducing the appearance of age spots and other signs of aging.
What Research Says?
- According to investigations conducted by Journal of Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Reishi mushroom has demonstrated measurable anti-aging properties, particularly in heart, liver, and brain tissues. These effects are attributed to its ability to modulate the immune system, scavenge free radicals, inhibit oxidative stress, and prevent neurodegenerative diseases caused by oxidative stress. Bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides and triterpenes are suggested to play a role in these anti-aging activities
How to Use
To use reishi mushroom for age spots, incorporate it into your skincare routine through topical application and internal consumption. Apply a reishi-infused serum or cream directly to affected areas twice daily after cleansing. Look for products containing at least 6% reishi extract for optimal results. You can also create a DIY mask by mixing reishi powder with honey and applying it for 15-20 minutes. For internal benefits, consume reishi tea or take supplements following recommended dosages. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for several weeks to see noticeable results. Always perform a patch test before widespread use and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential side effects of Reishi Mushroom
Reishi mushroom can cause several side effects, including nausea, dry mouth, dizziness, and stomach upset. Some users may experience skin rashes, headaches, or insomnia. More serious side effects can include liver toxicity, with reports of liver damage in some cases. Prolonged use may lead to bloody stools. Allergic reactions are also possible, particularly in individuals sensitive to mushrooms. It’s important to monitor for any adverse reactions when using reishi mushroom supplements.
Who should avoid Reishi Mushroom
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid reishi mushroom due to insufficient safety data. Individuals with bleeding disorders or scheduled for surgery should not use reishi, as it may increase bleeding risk. People with low blood pressure should exercise caution, as reishi can further lower blood pressure. Those with liver problems or a history of liver disease should avoid reishi due to potential hepatotoxicity. Individuals with autoimmune diseases should consult a healthcare provider before use, as reishi may stimulate the immune system.
Interaction with medications
Reishi mushroom can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of blood thinners like warfarin, increasing bleeding risk. Reishi can interact with medications that affect blood sugar levels, potentially causing hypoglycemia in diabetics. It may also interfere with immunosuppressant drugs, reducing their effectiveness. Reishi can interact with certain chemotherapy drugs and may affect liver enzyme levels, potentially altering the metabolism of other medications. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining reishi with any medications.
6. Ginkgo biloba

Ginkgo biloba shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its unique composition and beneficial properties for skin health. Rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids and terpenoids, ginkgo biloba can help combat oxidative stress and free radical damage, which are primary causes of age spots. Research has demonstrated that ginkgo biloba extract provides potent antioxidant protection and skin-soothing effects, which may help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. Its ability to improve circulation and increase skin hydration can contribute to overall skin health and a more youthful appearance. Additionally, ginkgo biloba has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may help in reducing skin discoloration and promoting a more even skin tone. Some studies suggest that topical application of ginkgo biloba extract can increase skin moisture retention and smoothness while reducing roughness, potentially improving the appearance of age spots.
What Research Says?
- Research efforts by Antioxidants and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews show that Ginkgo Biloba has been shown to improve memory, cognition, and overall quality of life in patients with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, as well as in general aging-related cognitive decline.
- As demonstrated by research from Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Pharmacopsychiatry, It enhances cerebral blood flow, reduces blood viscosity, and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which contribute to its neuroprotective effects.
- Research initiated by Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews suggests some studies suggest that Ginkgo Biloba may have a positive effect on vision in patients with age-related macular degeneration, although the evidence is not conclusive and further research is needed.
- According to the research carried out by Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, Ginkgo Biloba is generally considered safe with no significant side effects compared to placebo. However, the evidence for its efficacy in treating dementia and cognitive impairment is inconsistent and unreliable.
How to Use
To use Ginkgo Biloba for age spots, apply a topical cream or serum containing standardized Ginkgo extract (24-32% flavonoids and 6-12% terpenoids) directly to affected areas twice daily after cleansing. For internal benefits, take 120-240 mg of standardized Ginkgo extract daily, divided into 2-3 doses. Look for products specifically formulated for skin care. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for at least 4-6 weeks to see noticeable results. Additionally, you can brew Ginkgo tea and use it as a toner. Always perform a patch test before widespread use and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential side effects of Ginkgo Biloba
Ginkgo Biloba can cause side effects such as headaches, dizziness, stomach upset, nausea, and diarrhea. Some users may experience allergic skin reactions or palpitations. In rare cases, it can lead to increased bleeding risk. There have been reports of internal bleeding in some individuals. Long-term use or high doses may potentially cause more severe issues like liver toxicity. Always start with lower doses to assess tolerance.
Who should avoid Ginkgo Biloba
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Ginkgo Biloba due to insufficient safety data. Individuals with bleeding disorders or scheduled for surgery should not use it due to increased bleeding risk. People with epilepsy should avoid Ginkgo as it may trigger seizures. Those with diabetes should consult their doctor before use. Children should not take Ginkgo as its safety in this population hasn’t been established. People allergic to alkylphenols should also avoid it.
Interaction with medications
Ginkgo Biloba can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of blood thinners like warfarin, increasing bleeding risk. Ginkgo can interact with antidepressants, particularly SSRIs and MAOIs, potentially causing serotonin syndrome. It may interfere with the effectiveness of seizure medications and alter blood sugar levels when taken with diabetes medications. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining Ginkgo with any medications.
7. Gynostemma Pentaphyllum
Gynostemma pentaphyllum has been shown to have potent antioxidant properties, which can help combat oxidative stress – a key factor in skin aging and the formation of age spots. A study demonstrated that Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract can prolong the viability of mouse dermal fibroblasts damaged by UVC light-induced oxidative stress, indicating its potential to retard skin aging. The herb’s ability to scavenge free radicals and protect against UV radiation damage further supports its potential in addressing age-related skin concerns. Additionally, Gynostemma pentaphyllum has anti-inflammatory properties and may promote longevity, which could contribute to overall skin health and potentially help in reducing the appearance of age spots.
What Research Says?
- Studies conducted by Journal of Ethnopharmacology indicate Gynostemma pentaphyllum has been traditionally used to treat aging and related conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic syndrome.
How to Use
To use Gynostemma Pentaphyllum for age spots, consider both topical and internal applications. Apply a cream or serum containing Gynostemma extract directly to affected areas twice daily after cleansing. For internal benefits, consume Gynostemma tea or take supplements following recommended dosages, typically 150-300 mg daily. Look for standardized extracts containing at least 80% gypenosides. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for at least 8-12 weeks to see potential results. Additionally, you can create a DIY face mask by mixing Gynostemma powder with honey and applying it for 15-20 minutes twice weekly. Always perform a patch test before widespread use and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential side effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum
Gynostemma Pentaphyllum can cause side effects such as severe nausea and increased bowel movements. Some users may experience digestive issues, including diarrhea. In rare cases, it may lead to allergic reactions. While generally considered safe for short-term use (up to 4 months), long-term effects are not well-studied. Some people might experience temporary symptoms when starting use, which often subside with continued consumption or reduced dosage.
Who should avoid Gynostemma Pentaphyllum
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Gynostemma Pentaphyllum due to potential risks and insufficient safety data. Individuals with autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis, should consult a healthcare provider before use, as it may stimulate the immune system. People with bleeding disorders or scheduled for surgery should avoid it due to potential blood-thinning effects. Those with diabetes should use caution and monitor blood sugar levels closely.
Interaction with medications
Gynostemma Pentaphyllum can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of blood thinners, increasing bleeding risk. Gynostemma can interact with diabetes medications, potentially affecting blood sugar levels. It may interfere with immunosuppressant drugs, reducing their effectiveness. Those taking medications for heart conditions, blood pressure, or cholesterol should consult a healthcare provider before use. Always inform your doctor about all supplements you’re taking.
8. Goji Berry
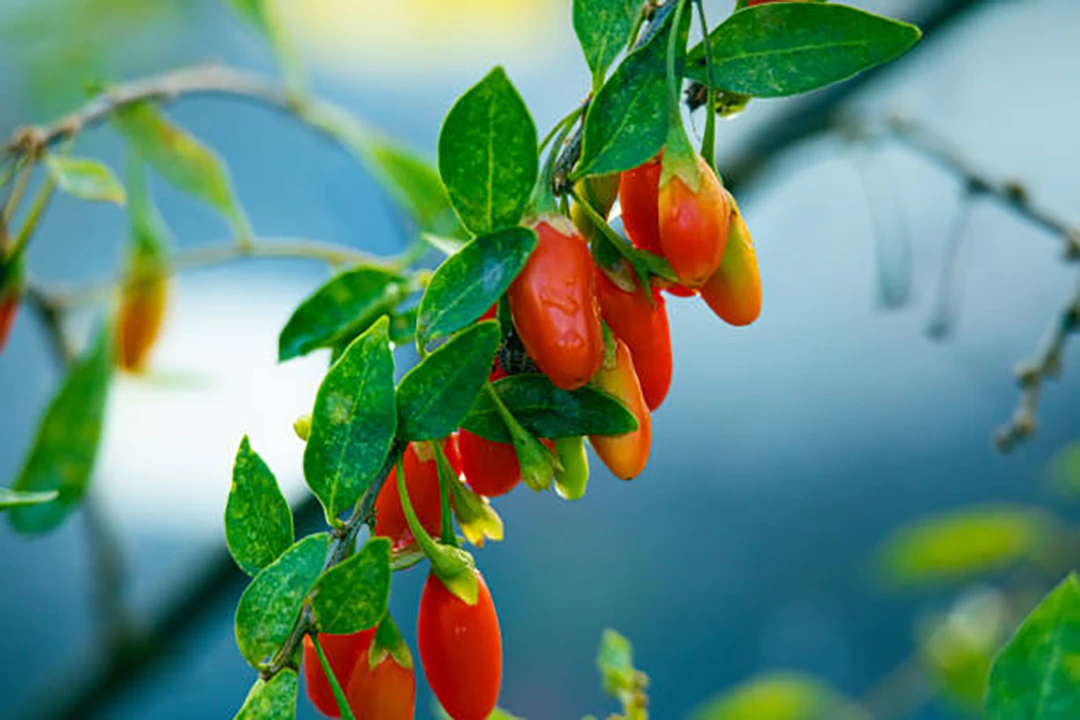

Goji berry shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its unique composition and beneficial properties for skin health. Rich in antioxidants, particularly carotenoids like beta-carotene, lutein, and lycopene, goji berry can help combat oxidative stress and free radical damage, which are primary causes of age spots. Goji berry extract can effectively down-regulate tyrosinase activity and melanin content, which are responsible for skin coloration, potentially helping to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tones. Additionally, goji berry’s high concentration of vitamins, especially vitamin C, contributes to its antioxidant abilities and may help diminish oxidative stress on the skin. The berry’s ability to decrease the level of skin-damaging molecules and promote the longevity of fibroblasts, which produce collagen and elastin, further supports its anti-aging effects.
What Research Says?
- Research executed by Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity reveals Goji berries have strong antioxidant properties that can be beneficial in treating skin disorders associated with aging, including age spots. The antioxidant activity helps in reducing oxidative stress, which is a key factor in skin aging.
- As shown by research done by Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Goji berry extracts can be effectively incorporated into cosmetic formulations. These formulations remain stable under various conditions and exhibit good skin adhesion, making them suitable for topical treatments aimed at anti-aging, including the reduction of age spots.
- Research organized by Food & Function suggests Goji berries enhance the activities of antioxidant enzymes and reduce oxidative damage, which can contribute to the reduction of age-related skin conditions like age spots. The berries also improve stress tolerance and extend lifespan in model organisms, indicating their potential in mitigating aging symptoms.
How to Use
To use goji berry for age spots, incorporate it into your skincare routine both topically and internally. Apply a goji berry-infused serum or cream directly to affected areas twice daily after cleansing. Create a DIY face mask by blending dried goji berries with honey, applying it for 15-20 minutes twice weekly. For internal benefits, consume 1-2 tablespoons of dried goji berries daily or drink goji berry tea. Look for skincare products containing goji berry extract for added benefits. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for at least 8-12 weeks to see potential results. Always perform a patch test before widespread use and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential side effects of Goji Berry
Goji berries can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, leading to symptoms like tingling in the mouth, skin rashes, or itchiness. Some people may experience digestive issues such as stomach aches, nausea, or diarrhea, especially when first consuming them. In rare cases, excessive consumption may lead to increased bleeding risk. High intake of goji berry tea has been linked to potential liver toxicity.
Who should avoid Goji Berry
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid goji berries due to insufficient safety data and potential risks to fetal health. Individuals with known allergies to other fruits, especially those sensitive to peaches or plants in the Solanaceae family, should exercise caution. People with diabetes, high blood pressure, or bleeding disorders should consult their healthcare provider before consuming goji berries. Those scheduled for surgery should discontinue use at least two weeks prior.
Interaction with medications
Goji berries can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. They may enhance the effects of blood thinners like warfarin, increasing bleeding risk. Goji can interact with diabetes medications, potentially causing blood sugar to drop too low. It may also interfere with medications for high blood pressure, heart conditions, and drugs metabolized by the liver. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining goji berries with any medications.
9. Rhodiola Rosea
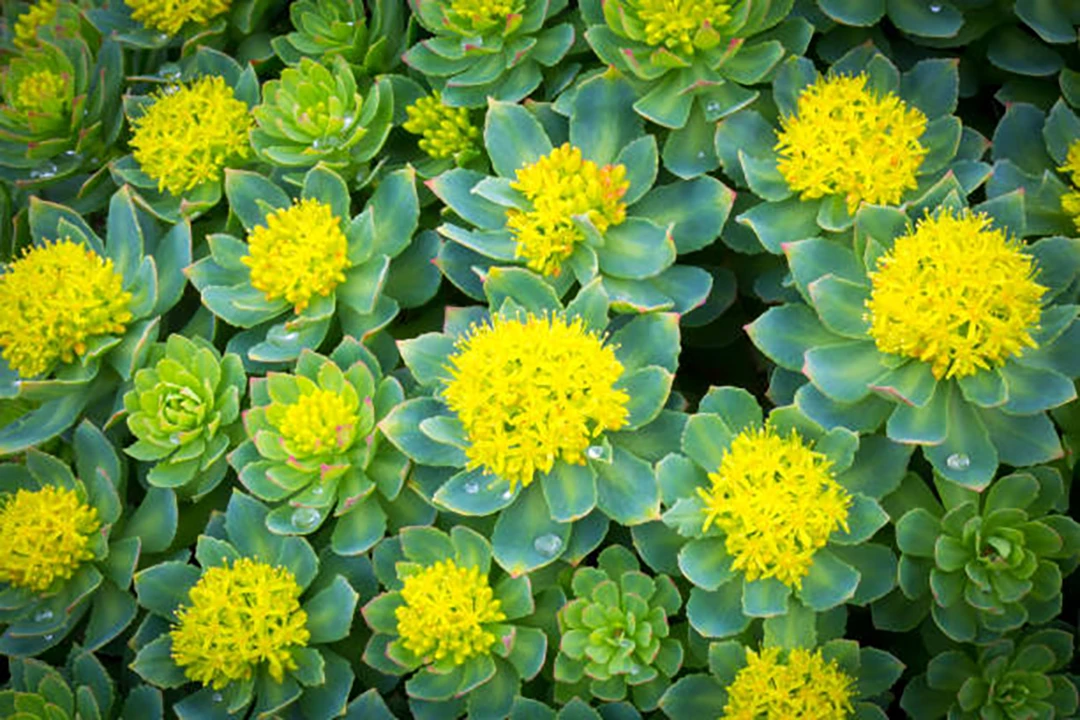

Rhodiola rosea has been shown to have potent antioxidant properties, which can help combat oxidative stress – a key factor in skin aging and the formation of age spots. Rhodiola rosea extract can effectively scavenge free radicals, reduce lipid peroxidation, and protect against UV damage, all of which are crucial in preventing and reducing age spots. The herb’s ability to increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes and protect against oxidative insults in keratinocytes further supports its potential in addressing age-related skin concerns. Additionally, Rhodiola rosea has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties and may promote longevity, which could contribute to overall skin health and potentially help in reducing the appearance of age spots.
What Research Says?
- Findings from studies performed by Phytotherapy Research indicate Rhodiola rosea contains phenolic compounds such as rosavin, rosarin, rosin, tyrosol, and salidroside, which exhibit strong antioxidant activities. These compounds help in reducing oxidative stress, which is a significant factor in skin aging and the formation of age spots.
- Research performed by IJMS shows the anti-aging properties of Rhodiola rosea are attributed to its ability to modulate oxidative stress and improve mitochondrial function. This can potentially slow down the aging process of the skin and reduce the appearance of age spots.
How to use
To use Rhodiola Rosea for age spots, consider both topical and internal applications. Apply a cream or serum containing Rhodiola Rosea extract directly to affected areas twice daily after cleansing. Look for products standardized to contain 3% rosavins and 1% salidroside. For internal benefits, take 250-700 mg of Rhodiola Rosea extract daily, divided into 1-2 doses. Start with a lower dose and gradually increase as needed. Consistency is key, so continue the treatment for at least 8-12 weeks to see potential results. Additionally, you can brew Rhodiola Rosea tea and use it as a toner. Always perform a patch test before widespread use and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Potential side effects of Rhodiola Rosea
Rhodiola Rosea can cause side effects such as dizziness, dry mouth, and excessive saliva production. Some users may experience sleep disturbances, especially if taken late in the day. In rare cases, it can lead to jitteriness, anxiety, or agitation. High doses may cause headaches or mild digestive issues like nausea or stomach upset. Most side effects are generally mild and tend to subside with continued use or dose adjustment.
Who should avoid Rhodiola Rosea
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Rhodiola Rosea due to insufficient safety data. Individuals with bipolar disorder should not use it as it may trigger manic episodes. People with autoimmune disorders should consult a healthcare provider before use, as Rhodiola may stimulate the immune system. Those with low blood pressure should exercise caution, as Rhodiola can further lower blood pressure. Individuals with diabetes should monitor blood sugar levels closely when using Rhodiola.
Interaction with medications
Rhodiola Rosea can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of antidepressants, particularly MAOIs and SSRIs, potentially causing serotonin syndrome. Rhodiola can interact with blood pressure medications, potentially causing hypotension. It may interfere with blood sugar control medications and affect the metabolism of drugs processed by the liver. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining Rhodiola with any medications.
10. Turmeric
Turmeric shows promising potential in addressing age spots due to its unique composition and beneficial properties for skin health. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, is a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent that can help reduce the appearance of age spots and improve overall skin health. Curcumin has been found to inhibit melanin production, which may help lighten hyperpigmentation and even out skin tone. Its potent antioxidant properties fight free radicals, protecting the skin from oxidative stress and UV damage, which are primary contributors to the formation of age spots. Additionally, turmeric’s soothing properties can reduce skin irritation and inflammation associated with age spots, promoting skin rejuvenation and overall health. The combination of these effects makes turmeric a promising natural option for those looking to address age spots and improve their skin’s appearance.
What Research Says?
- According to the findings from research conducted by Phytotherapy Research, Turmeric and curcumin have shown therapeutic benefits for various skin conditions, including acne, atopic dermatitis, and facial photoaging, which suggests potential benefits for age spots as well.
- Studies executed by IUBMB indicate Curcumin’s antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative stress, which is a contributing factor to skin aging and the formation of age spots.
How to Use
To use turmeric for age spots, create a face mask by mixing 1 tablespoon of turmeric powder with 2 tablespoons of honey and optionally 1 tablespoon of lemon juice for extra brightening. Apply this paste evenly to your face, focusing on areas with age spots. Leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing off with warm water. Use this mask 2-3 times a week for best results. Additionally, you can incorporate turmeric into your diet or take supplements under medical guidance. For topical use, you can also find skincare products containing turmeric extract. Always perform a patch test before widespread application to avoid potential skin irritation.
Potential side effects of Turmeric
Turmeric can cause mild side effects such as stomach upset, nausea, dizziness, or diarrhea when taken in high doses. Topical application may lead to skin irritation, redness, or allergic reactions in some individuals. Excessive consumption can increase the risk of kidney stones in susceptible people. In rare cases, it may cause abnormal heart rhythm. Long-term use of high doses might potentially lead to liver problems.
Who should avoid Turmeric
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid high doses of turmeric due to potential risks. Individuals with gallbladder problems, bleeding disorders, or diabetes should consult a healthcare provider before using turmeric supplements. People scheduled for surgery should stop turmeric use at least two weeks prior due to its blood-thinning effects. Those with iron deficiency should be cautious as turmeric may interfere with iron absorption. Individuals with hormone-sensitive conditions should also seek medical advice before use.
Interaction with medications
Turmeric can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing side effects. It may enhance the effects of blood thinners, increasing bleeding risk. Turmeric can interact with diabetes medications, potentially causing blood sugar to drop too low. It may interfere with the effectiveness of certain chemotherapy drugs. Turmeric can also affect how the liver processes some medications, potentially altering their effects. Always consult a healthcare provider before combining turmeric supplements with any medications.
FAQs
- How long does it take for herbal remedies to show visible results on age spots?
Answer: The time it takes for herbal remedies to show visible results can vary depending on the individual, the severity of the age spots, and the specific herb used. Typically, consistent use over 8-12 weeks may be required to see noticeable improvements. However, results can vary, and some people might see changes sooner or later than this timeframe.
- Can herbal remedies completely remove age spots?
Answer: Herbal remedies can help lighten age spots and improve the overall appearance of the skin, but they may not completely remove age spots in all cases. The effectiveness depends on factors like the cause of the spots, skin type, and consistency in using the remedy. Combining herbal treatments with proper sun protection may help achieve better results.
- Are there any specific herbs to avoid when using them for age spots?
Answer: While many herbs are generally safe, some, like St. John’s Wort, can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, potentially worsening pigmentation if proper sun protection isn’t used. Additionally, individuals should be cautious of potential allergic reactions and interactions with other skin products. Always conduct a patch test before using any new herbal remedy.
- Can herbal treatments be used alongside conventional treatments for age spots?
Answer: In some cases, herbal treatments can complement conventional treatments for age spots, such as chemical peels or laser therapy. However, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist before combining different treatments to avoid any adverse interactions or skin reactions.
- Can diet affect the effectiveness of herbal treatments for age spots?
Answer: Yes, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support skin health and enhance the effectiveness of herbal treatments. Consuming foods high in vitamin C, E, and other antioxidants can help combat oxidative stress, which is a common cause of age spots.
- Are there any side effects of using herbal oils topically for age spots?
Answer: Topical application of herbal oils may cause skin irritation, redness, or allergic reactions in some individuals. It is always recommended to perform a patch test before using any new herbal oil on a larger area of the skin. If any adverse reaction occurs, discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare professional.
- Can herbal remedies be used for age spots on sensitive skin?
Answer: Some herbal remedies, such as chamomile or aloe vera, are gentle and may be suitable for sensitive skin. However, it’s essential to be cautious, as even natural remedies can cause irritation. Patch testing and consulting a dermatologist can help determine if a particular herbal treatment is appropriate for sensitive skin.
- Are herbal supplements effective in preventing age spots?
Answer: Herbal supplements that contain antioxidants and skin-nourishing compounds may help protect the skin from oxidative stress and UV damage, potentially preventing the formation of new age spots. However, they should be used as part of a holistic approach that includes sun protection and a balanced diet.
- Is it safe to use essential oils directly on age spots?
Answer: Essential oils should generally not be applied directly to the skin without dilution. They should be mixed with a carrier oil, such as coconut or jojoba oil, before application. Direct application of essential oils can lead to skin irritation or allergic reactions, especially on sensitive areas like the face.
- Can herbal treatments for age spots be used on other forms of hyperpigmentation?
Answer: Yes, many herbal treatments that are effective for age spots can also be used to address other forms of hyperpigmentation, such as melasma or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. However, the underlying cause of the pigmentation should be considered, and treatment should be adapted accordingly.