| Corkwood Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Corkwood |
| Scientific Name: | Ochroma pyramidale |
| Origin | Tropical America; throughout the West Indies, and from southern Mexico, through Central America and into Venezuela, Colombia, Brazil, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia |
| Colors | Initially green turning to brown as they mature |
| Shapes | Cylindrical, ellipsoid, slightly curved capsule, longitudinally sulcate, loculicidal, 15 cm long and 8 mm wide, ribbed, 5-valved, dehiscent, densely woolly hairy inside |
| Name | Corkwood |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ochroma pyramidale |
| Native | Widely distributed in tropical America; throughout the West Indies, and from southern Mexico, through Central America and into Venezuela, Colombia, Brazil, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. It is planted in many tropical countries, including tropical Africa (e.g. Cameroon and Zimbabwe) and South Africa. It has locally become naturalized |
| Common Names | Balsa Wood, Ajaka, Baranda, Basilic des moines, Basilic sacre, Bidai, Brinda, Bryanda, Gaggera, Hsiang tsai, Kala tulsi, Kamangi, Kaphrao, Katriin, Kom ko dong, Krishna tulasi, Loko-loko, Maeng-luk, Manjari, Mreah preu, Mreahs prow, Nalla tulasi, Parnasa, Patrapuspha, Ruku-ruku, Sacred balm, Saph’au, Sheng luo le, Sulasi, Suvasa tulasi, Tarp hao, Te marou, Thai basil, Trittavu, Tulasa, Tulasi chajadha, Tulsi, Tunrusi |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Kurkhout Albanian: Dru tape Amharic: Bushiwudi (ቡሽዉድ) Arabic: Falayn (فلين), balzan haramiatan (بلزا هرمية) Armenian: Khts’anap’ayt (խցանափայտ) Azerbaijani: Mantar Bengali: Sōlā (সোলা) Brazil: Pau-de-balsa Bulgarian: Korkovo dŭrvo (корково дърво) Burmese: Corkwood-ˈkôrkˌwo͝od Chinese: Ruǎnmù (软木), Qing mu (輕木), Bai se mu, Bai shai mu Croatian: Corkwood Czech: Lehké dřevo, balzovník jihoamerický Danish: Corkwood, Balsa, Balsatræ, Balsatræ Dominican Republic: lana Dutch: Kurkboom, Balsa, Balsahout English: Corkwood, West Indian balsa, Balsa, Bois flot, Corkwood, Downtree, Downtree, Balsa, Balsa wood, Balsa tree, Down tree, Cork tree Esperanto: Korko, Balzo Estonian: Korgipuu Filipino: Corkwood Finnish: Corkwood, Balsa, Balsapuu, balsa, French: Bois de liege, Balsa, Patte-de-liève, Balsa, Bois de balsa, bois flot, bois liège Galician: Balsa Georgian: Korp’is khe (კორპის ხე), balsa (ბალსა) German: Korkholz, Balsabaum, Balsa, Balsaholz, Pyramiden, Pyramidenbalsabaum Greek: Fellós (φελλός) Gujarati: Kakrkavuḍa (કkર્કવુડ) Haitian: Mawodenn, flè mahodèm; koton swa Hausa: Katako Hebrew: קורקווד , בלזה Hindi: Corkwood-ˈkôrkˌwo͝od Hungarian: Parafa, Balsafa Icelandic: Korkur Indonesian: Kayu gabus, Balsa Irish: Corc-choill, Balsa Italian: Corkwood, Balsa, Legno di balsa, legno sughero Japanese: Korukuuddo (コルクウッド), Ba ru sa (バルサ) Javanese: Corkwood Kannada: Kārkvuḍ (ಕಾರ್ಕ್ವುಡ್) Kazakh: Trotuar (тротуар) Komi: Balʹsa (Бальса) Korean: Koleukeu (코르크), balsa (발사) Kurdish: Corkwood Lao: Mai khok (ໄມ້ຄອກ) Latin: Corkwood Latvian: Korķa koksne Lingua Franca Nova: Balsa Lithuanian: Kamštinė mediena, Kūginė balza Macedonian: Pluta drvo (плута дрво) Malagasy: Corkwood Malay: Corkwood Malayalam: Kēārkkvuḍ (കോർക്ക്വുഡ്), bālsa (ബാൽസ) Maltese: Sufra Marathi: Korkavud (कॉर्कवुड) Mongolian: Uisen mod (үйсэн мод) Nepali: Karkavud (कर्कवुड) Norwegian: Corkwood, Balsatre Oriya: କର୍କଉଡ୍ Pashto: کورک ووډ Persian: چوب چوب پنبه, درخت بالسا Polish: Drewno korkowe, Ogorzałka wełnista Portuguese: Sobreiro, Algodoeiro, Algodão bravo, Pau de balsa, Balsa, Madeira de balsa, pata-de-lebre, pau-de-jangada, topa, pão-de-balsa Punjabi: Kārkavuḍa (ਕਾਰ੍ਕਵੁੱਡ) Quechua: Yawar wiqi Romanian: Corkwood, Balsa Russian: Probkovoye derevo (пробковое дерево), Balʹsa (Бальса Serbian: Corkvood (цорквоод) Sindhi: سائيڪو Sinhala: Kōkvuḍ (කෝක්වුඩ්) Slovenian: Plutovina Spanish: Bosque de tapón, Balsa, Madera de balsa, Balzovec, guano, balsa, balso real, cajete, cojejo, corcho, gatillo, lana, tambor, lanilla, pochote Sudanese: Corkwood Swedish: Korktrad, Balsa Tajik: Kandakorj (кандакорй) Tamil: Kārkvuṭ (கார்க்வுட்), Mirutuvāṉa maram (மிருதுவான மரம்) Telugu: Corkwood (kôrkwo͝od) Thai: Corkwood (kôrkwo͝od) Turkish: Mantar ağacı kerestesi Udmurt: Balʹsa (Бальса) Ukrainian: Probkovi dereva (пробкові дерева), Bal’sove derevo (Бальсове дерево) Urdu: کارک ووڈ Uzbek: O’rmon daraxti Vietnamese: Gỗ bần Welsh: Corcwood Zulu: Ukhuni |
| Plant Growth Habit | Deciduous or evergreen, fast growing, short lived, medium-sized tree |
| Growing Climates | Moist, lowland, limestone forest, margins of lakes or in disturbed areas, rare in the older forest |
| Soil | Found mainly on fertile, bottom-land soils along the sides of streams |
| Plant Size | 60 to 90 ft. high and 2.5 to 4 ft. in diameter. On the best sites may reach a height of 80 ft. and a diameter of 2.5 ft. in 5 years. It has been known to grow even faster on very rich soils |
| Bole | Straight, usually short, cylindrical, up to 100(–180) cm in diameter, with short buttresses in older trees |
| Bark | Bark surface is smooth, grey-white mottled |
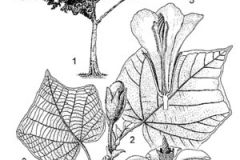
| Leaf | Simple, spirally arranged towards the ends of the twigs. Lamina is broadly cordate, 10-26 cm long and 14-30 cm wide, thin coriaceous ± entire or angularly lobed |
| Flower | Solitary, lateral or axillary, on a stout, fleshy pedicel 7 mm diameter and 10 cm long. Calyx is tubular to funnel-shaped, 7 cm long, apically with 5 dilated lobes 1.5-2 cm long |
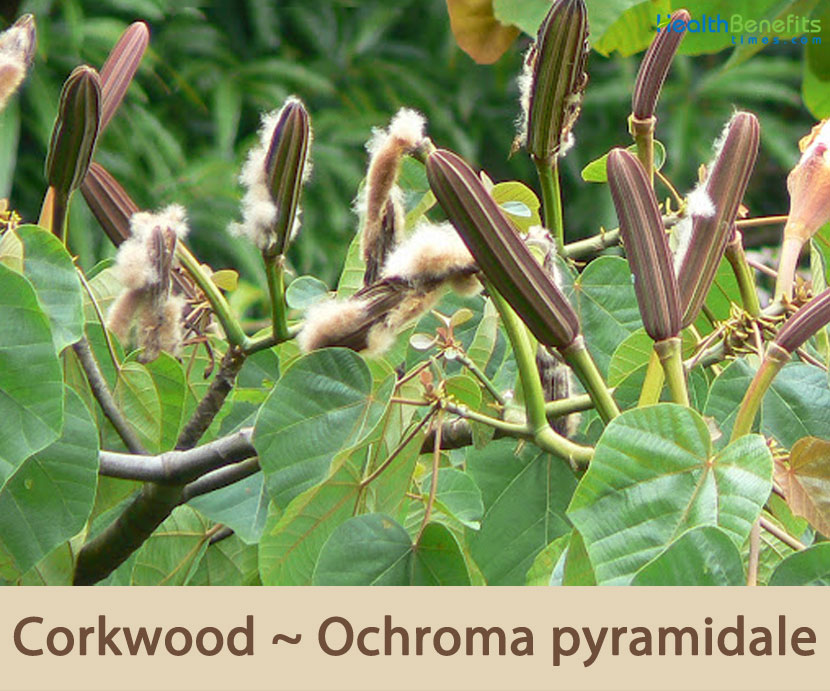
| Fruit Shape & Size | Cylindrical, ellipsoid, slightly curved capsule, longitudinally sulcate, loculicidal, 15 cm long and 8 mm wide, ribbed, 5-valved, dehiscent, densely woolly hairy inside |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to brown as they mature |
| Seed | Black, pear-shaped, 4–5 mm long and 1.5 mm wide, embedded in a mass of brown woolly hairs |
| Propagation | By seed |
| Lifespan | Around 30 to 40 years in the wild |
| Traditional Medicinal Uses |
|
Plant Description
Balsa tree or Corkwood is a deciduous or evergreen, fast growing, short lived, medium-sized tree that normally grows about 60 to 90 ft. tall and 2.5 to 4 ft. in diameter. On the best sites it may reach a height of 80 ft. and a diameter of 2.5 ft. in 5 years. It has been known to grow even faster on very rich soils. Bole is straight, usually short, cylindrical, up to 100(–180) cm in diameter, with short buttresses in older trees. Bark surface is smooth, grey-white mottled. Crown is spreading and large. Branchlets are stellate and hairy. The plant is found growing in moist, lowland, limestone forest, margins of lakes or in disturbed areas and is rare in the older forest. The tree is mostly found on fertile, bottom-land soils along the sides of streams. It is classified as a hardwood despite the wood itself being very soft. It is the softest commercial hardwood and is widely used because it is light weight.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, spirally arranged towards the ends of the twigs. Lamina is broadly cordate, 10-26 cm long and 14-30 cm wide, thin coriaceous ± entire or angularly lobed. Apex is obtuse to acuminate, base rounded to cordate, persistently densely stellate-tomentose below, glabrescent above, midrib and main veins slightly raised to sulcate above, strongly prominent below; venation 5-7-palmate at the base, mid vein with 4-6 lateral veins. Petiole is terete, 2-4 mm diameter and 12-20 cm long, moderately stellate-tomentose even on mature leaves, ± dilated apically; stipules ± deltoid, to 10 mm long, densely tomentosa and caduceus.
Flowers
Flowers are solitary, lateral or axillary, on a stout, fleshy pedicel 7 mm diameter and 10 cm long. Calyx is tubular to funnel-shaped, 7 cm long, apically with 5 dilated lobes 1.5-2 cm long, appearing deeply carinate externally in dried material, externally stellate-tomentose, internally wooly, decurrent with pedicel and subtended by 3 caducous bracteoles that leave prominent scars. Petals 5, contorted in bud, orange-yellow, clavate, 13 cm long and 5 cm wide, externally stellate-tomentose, glabrescent basally, internally glabrous. Stamens are connate into a glabrous tube 11 cm long, the distal half being slightly dilated and densely covered with sessile long wavy anthers. Ovary is sessile, glabrous, conical, 8 cm high, 5-locular. Style is 15 cm long with an apical twisted cylindrical stigmatic mass 3 cm long and 8 mm wide.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by cylindrical, ellipsoid, slightly curved capsule, longitudinally sulcate, loculicidal, 15 cm long and 8 mm wide, ribbed, 5-valved, dehiscent, densely woolly hairy inside. Seeds are black, pear-shaped, 4–5 mm long and 1.5 mm wide, embedded in a mass of brown woolly hairs.
Different Facts of Balsa tree or Corkwood
- The woolly fiber contained in the seedpods has occasionally been used like kapok as a stuffing material in pillows and mattresses.
- The fiber obtained from the bark has been used to make ropes.
- The grain is straight; texture coarse and even; the luster silky.
- The wood is very soft and weak, but with a good strength to weight ratio, and that from old trees tends to be brittle.
- It is non-durable and prone to attack by Anobium and Lyctus borers, termites and longhorn beetles.
- The wood is very easy to work with hand and machine tools, but sharp tools are needed to prevent crumbling.
- The pulp can be easily bleached without loss of strength, making it suitable for printing and writing papers.
- The extremely lightweight wood is used for floats, buoys, lifejackets and life-belts, surf boards, aircraft construction, ship and boat building, lightweight boxes, toys, model making, laboratory mounting boards, core stock in sandwich construction, surgical splints, packaging of fragile articles and as insulation for temperature, vibration, sound and formerly also for electricity.
- Slightly heavier wood is suitable for matches, Popsicle sticks and toothpicks, and for the production of pulp and paper.
- Trees can commence flowering and producing viable seeds when 3 – 4 years old.
- The tree is sometimes planted as an ornamental or to provide shade.
- Indigenous Peoples carve elegant sculptures, build houses, boats and trays to prepare food, make toys such as stilts.
- The Balsa plant has been used to build vessels for river transportation, which allowed Indigenous Peoples (according to some studies) to navigate great distances.
- Light wood of the Balsa is used mainly to make surfboards and scale airplanes for model airplanes.
Precautions
- Corkwood tree is unsafe when taken by mouth. It can cause death.
- Corkwood tree can cause many side effects including dry mouth, decreased perspiration, dilation of pupils, blurred vision, red, dry skin, increased body temperature, increased heart rate, difficulty urinating, hallucinations, spasms, acute psychosis, convulsions, and coma.
- Overdose poisoning symptoms include sleepiness followed by restlessness, hallucinations, delirium, and manic episodes followed by exhaustion and sleep.
- It’s unsafe for anyone, including pregnant or breast-feeding women, to take corkwood tree.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=21602#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/ochroma_pyramidale.htm
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Ochroma+pyramidale
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/36974
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2401123
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/264296
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Ochroma_pyramidale_(PROTA)
http://www.narc.gov.jo/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=25473
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ochroma
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Ochroma+pyramidale
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=OCPY
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/OCHLA