Amerikaanse zeeraaf, Atlantic croacker, Atlantic croaker, Corvina, Croaker, Crocus, Hardhead, Roncadina, King Billies, Hard Heads, Grumblers and Silver weakfish are the popular names from which Atlantic Croaker is known by. Scientifically known as Micropogonias undulates, is a marine ray-finned fish species which belongs to Sciaendia family and is closely associated to black drum (Pogonias cromis), the spot croaker (Leiostomus xanthurus), the red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus), the silver perch (Bairdiella chrysoura), the weakfish (Cynoscion regalis) and the spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus). Atlantic croaker is found commonly in sounds & estuaries from Massachusetts to Gulf of Mexico. Believed to be also live on coasts of Southern Brazil and Argentina.
Description
Atlantic croaker is the loudest in the drum family. Also referred as a hardhead as it has smaller ones called pin heads. From August to October during spawning season, turns deep golden color. In the beginning of the August, tiny young comes to the Chesapeake Bay and travel to low salinity or freshwater creeks. It moves to deeper parts of tidal rivers for winter. With the adults, juveniles leave the Bay following autumn. When grown fully upto 2 or 3 years, it reaches between 1 to ½ feet long and 4 to 5 pounds. On average, they are ½ to 2 pounds. It could tolerate wide range of environments and also adapt well to captivity.
Appearance
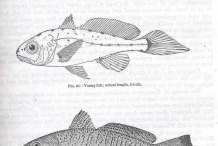
It has a silvery body with a pinkish glow and silvery or brassy white belly. On its back, it has brassy brown spots form faint and irregular stripes. It measures about 18 to 20 inches long but could be upto 24 inches. It has 3 to 5 pairs of small barbels on its chin. The tail fin is slightly pointed and has deep notch in dorsal fin.
Reproduction and Life cycle
They reach sexual maturity about one year old along Gulf Coast. Spawning season is in fall with a peak between August and October. In the spawning season, females releases from 1,00,000 and 2 million eggs, each about 0.35 mm in diameter.
The larvae drift towards land after hatching. On soft bottoms such as mud, they are abundant having large amount of detritus to feed on. They could live upto eight years. Striped bass, spotted seatrout, shark, humans and other croakers are their predators. Due to predation, more than 95% of the population of Atlantic croaker dies every year.
Feeding Behaviour
Atlantic Croaker prey upon mollusks, bristle worms, small fish and crustaceans. The larvae consume pteropods, tintinnids, ostracods, pelecypods, naupliar, egg, copepodid and adult stages of copepods.
Predators
Weakfish, bluefish and striped bass prey on Atlantic croaker.
How to Eat
- It could be fried, baked, broiled and microwaved.
- Skinned fillets for pan frying and also poaching.
- Atlantic croaker could be breaded and dusted with flour or cornmeal and also pan-fried.
- It could be marinated, sautéed or grilled, broiled and roasted.
- Meat could be steamed whole.
Other Facts
- Usually Atlantic croakers are known as hardheads and small croakers are known to be pin heads.
- It is well known as recreational anglers.
- Croakers belong to the drum family that includes weakfish, sport, black drum, red drum and spotted seatrout.
- All drums make croaking or loud drumming by vibrating its swim bladders with the use of special muscles.
- In August 2007, Chesapeake Bay recorded Atlantic croaker which weighed 8 pounds, 11 ounces and measured 27 inches long.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=169283#null
https://www.seafoodsource.com/seafood-handbook/finfish/croaker
https://tpwd.texas.gov/huntwild/wild/species/croaker/
https://www.chesapeakebay.net/S=0/fieldguide/critter/atlantic_croaker
http://www.inlandseafood.com/seapedia/atlantic-croaker
http://www.asmfc.org/species/atlantic-croaker
Comments
| Atlantic Croaker Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Atlantic Croaker |
| Scientific Name: | Micropogonias undulatus |
| Origin | Native to coastal waters in the western Atlantic Ocean |
| Colors | Silvery-pink |
| Flesh colors | Firm, pink |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Calories | 192 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients | Vitamin B-12 (Cobalamine) (76.25%) Selenium (61.45%) Isoleucine (44.08%) Tryptophan (41.14%) Lysine (40.88%) |
| Name | Atlantic Croaker |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Micropogonias undulatus |
| Native | Native to coastal waters in the western Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic croaker is found on the Atlantic coast from Massachusetts southward and throughout the Gulf of Mexico. They prefer estuaries and bays through the spring and summer, then travel offshore in the fall to breed. |
| Common/English Name | Amerikaanse zeeraaf, Atlantic croacker, Atlantic croaker, Corvina, Croaker, Crocus, Hardhead, Roncadina, King Billies, Hard Heads, Grumblers, Silver weakfish |
| Name in Other Languages | Danish: Atlantisk trommefisk, Ørnefisk, ÿrnefisk; Dutch: Amerikaanse zeeraaf, knorrepos, Ombervis; Finnish: Rumpukala; French: Tambour brésilien; German: Adlerfisch, Atlantischer Umber, Westatlantischer Umberfisch; Greek: Kránios; Italian: Scienidi; Japanese: Guchi, Ishimochi, Nibe; Mandarin Chinese: Bōwén róng xū shíshǒuyú (波紋絨鬚石首魚), Bōwén róng xū shí shǒu yú (波纹绒须石首鱼), 线纹绒须; Polish: Mikun; Portuguese: Corvina, Corvina-branca, Corvina-de-corso, Corvina-de-linha, Corvina-de-lista, Cururuca, Cururuca-lavrada, Rabeta-brasileira; Spanish: Corbina, Corvina, corvinon brasileno, Corvinón brasileño, Gurrubata, Roncadina; Swedish: Havsgös; Turkish: Iskine, Mavrusgil baligi |
| Size | 1-1/2 feet long |
| Body Color | Silvery-pink |
| Weight | 4-5 pounds |
| Flesh | Firm, pink |
| Meat texture | Snow white with reddish tint |
| Flavor | Sweet subtle |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Primary Product Forms | Fresh (most common): Whole, head off, Steaks, Fillets Value-added: Breaded portions |
| Major Nutritions | Vitamin B-12 (Cobalamine) 1.83 µg (76.25%) Selenium, Se 33.8 µg (61.45%) Isoleucine 0.737 g (44.08%) Tryptophan 0.181 g (41.14%) Lysine 1.367 g (40.88%) Valine 0.824 g (39.02%) Threonine 0.686 g (38.98%) Histidine 0.457 g (37.09%) Leucine 1.288 g (34.85%) Protein 15.83 g (31.66%) |
| Calories in 1 fillet (87 g) | 192 Kcal. |