| Ativisha Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Ativisha |
| Scientific Name: | Aconitum heterophyllum |
| Origin | Western Himalayas and it is found in Gurhwal, Kumaon and Kashmir |
| Shapes | Seedpods are 16-18 mm, shortly hairy, erect |
| Taste | Acrid, bitter, pungent |
| Health benefits | Treats Diabetes and Leucorrhoea, Treats Mumps & Parotitis, Heals Constipation, Treats Piles, Prevents Vomiting, Great for detoxification, Treats Ingestion, Mal-absorption, Cough & Bronchitis, Common Cold & Flu, Treats Diarrhea, Fever Management |
| Name | Ativisha |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Aconitum heterophyllum |
| Native | Western Himalayas and it is found in Gurhwal, Kumaon and Kashmir |
| Common Names | Himalayan monkshood, Monk’s hood, Indian atees |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Atis Assamese: Aatich Bengali: Ataich, Ataicha (আতাইচা) Bhoti: Ais Canarese: Atibaje Chinese: Yi Zi Hao Cutch: Ativista English: Indian Atees, Greenish Himalayan Monkshood Gujarati: Ativakhani kali, Ativish, Ativishani Kali (અતીવીષની કાલી) Hindi: Ateesarand, Ateicha, Atis, Atvika, Atees, arand, ateicha, arand, mohra, padish, patis Kannada: Ativisha, Atibage, Athihage, Athibaje (ಅತಿಬಜೆ), Athivishe (ಅತಿವಿಷೆ) Konkani: Atibaje Malayalam: Atividayam, Ativitayam, Ativitayam (അതിവിടയം), Atthiranam (ஆட்திரணம்) Marathi: Ativish, Atvisha Nepali: Atis, bikh Oriya: Atushi (ଅଟୁଶି) Persian: Vajjeturki, Bazziturki Punjabi: Atis, Atisa, Atees Sanskrit: Ativisha, Kashmeera, Shuklakanda, Bhangura, Vishva, Visha, Ghunapriya, Ghunavallabha, Peetavallabha, Shishubhaishajya, Shrungi, Shophahaa, Mahaushadham, shyamakanda, Ativishaa (अतिविषा), Bhanguraa (भङ्गुरा), Amrita (अमृता), Aruna (अरुणा), Ataicha, Atisaraghni, ativisa, bhringi, ghunaisa, kashmira, kasmira, madri, mahoshadha, mridvi, pankura, prativisa, prativisha, pravisha, shishubhaishyajja, shokapaha, shringi, shringika, shuklakanda, shveta, shvetakanda, shvetavacha, shyamkanda, sisubhaisajya, sitashringi, suklakanda, surala, upavishaaka, upvisha, vallabha, vira, virupa, visakhya, visha, visharupa, vishva Siddha: Athividayam Tamil: Athividayam (அதிவிடயம்), Atividayam, Atividyam, Ativisam, Mathiri, Pankurai, adivitaiyam, akuculapu, adhividayam, adivitaiyam, akuculapu, alakavetam, alecuveppam, alecuveppu, alecuvitaiyam, alecuvitayam, ariyan, ariyavitaiyam, ariyavitayam, arttiram, aruna, arunai, athividayam, athividyam, ati vitayam, ati-vadayam, ati-vidayam, aticaracuracamaraci, aticarakkini, ativacam, ativacampu, ativadayam, ativaka, atividyam, ativitai, ativitaiyam, ativitam, ativitayam, attakatitam, attam, attatam, attiranam, avirukam, cattivinacini, cinki, cirinki, cukkilakentam, cukkulakantam, kalacu, kalacuvetam, kalacuvitaiyam, kalakavetam, kalarcipatam, kalarcupatam, kalarcuvatam, kantacukkilam, kenta 1, kukkilam, kunakkacikam#, kunakkacikam@, kunapalam, kunapalan, kunattam, kunavallapai, kunetakam, kunettam, mantiri, matiri, matirivitaiyam, nattuativitaiyam, pankaram, pankurai, pankuram, upavitai, upavitam, vicu, vicuvacan, vicuvam, vicuvankatti, vicuvatikkam, visapaka, vitam, vitaru, vitayam, yankura Telugu: Atis vasa, Ativasa (అతివస్స), athivaasa, atirasa, ativasu Tibbi: Atees Tibetan: Bon na, bon na dkar po, bon-na-dkar-po Unani: Atees Urdu: Atees, atis shirin, beesh |
| Plant Growth Habit | Herbaceous perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Alpine to sub-alpine open slopes, common on grassy meadows, upper oak/coniferous forest, also glacial riverine, rocky moist areas, alpine dry scrub, open grass, shady moist alpine slopes |
| Soil | Sandy loam and slightly acidic soil, with pH about 6, has been found to be the best |
| Plant Size | Usually 15 – 90 cm tall, occasionally reaching 200 cm |
| Root | Roots is conical or cylindrical, about 2 – 7.5 cm long (maximum) and 0.4 – 1.6 cm thick (maximum) |
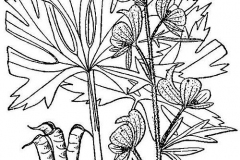
| Stem | Stem erect, leafy, 1-3ft., simple or rarely branched from the base, glabrous below and puberulous above |
| Leaf | Ovate-heart-shaped to rounded, usually 5-10 cm in length, sharply toothed but largely heteromorphous, the upper clasping the stem. All leaves have large rounded teeth. Lowest leaves are deeply lobed and long-stalked. |
| Flowering season | August to September |
| Flower | Flowers are large, hooded, white–violet in colour and occur in slender racemes or lax leafy panicles. Corolla is hairy. Carpels are five in number, containing 10–18 follicles. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Seedpods are 16-18 mm, shortly hairy, erect |
| Propagation | Seeds, tuber segments or young leafy stems can be used |
| Flavor/Aroma | |
| Taste | Acrid, bitter, pungent |
| Plant Parts Used | Root, underground stems, seeds, rhizomes |
| Season | September to October |
| Health Benefits |
|
Roots
The plant roots are tuberous and paired. The shape of the roots is conical or cylindrical, about 2 – 7.5 cm long (maximum) and 0.4 – 1.6 cm thick (maximum). When the plant starts tapering to end, the thickness is gradually reduced. The color of the roots is yellowish and greyish white externally. The scars of fallen rootlets and with a rosette of rudimentary leaves form a wrinkle marks in the external surface. The roots are starchy and white with a surface pointed to the center with 4 – 7 yellowish to brown dots arranged concentrically, towards the end of fibro-vascular bundles. It is odorless, bitter and has no tingling sensation.
Stem
Stem erect, leafy, 1-3ft., simple or rarely branched from the base, glabrous below and puberulous above.
Leaves
Leaves are ovate-heart-shaped to rounded, usually 5-10 cm in length, sharply toothed but largely heteromorphous, the upper clasping the stem. All leaves have large rounded teeth. Lowest leaves are deeply lobed and long-stalked.
Flowers
The flowers are hooded, large, and white to violet colored. They are present in lax leafy panicles or slender racemes with very variable bracts which are either small linear, small ovate, or large ovate. It has hairy corolla. Carpels are five in number, containing 10–18 follicles. Flowering and fruiting occur from August to October in the third year of growth.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by seedpods that are 16-18 mm long, shortly hairy and erect.
Health benefits of Ativisha
Listed below are some of the well-known health benefits of using Ativisha
1. Fever Management
Ativisha is used to manage the fever. It has antipyretic action, which helps to alleviate and prevent the fever. It is commonly used for managing the fever in infants and children in Ayurvedic pediatric medicine. It acts as diaphoretic and induces perspiration, which helps to lower the fever.
2. Treats Diarrhea
Ativisha has antidiarrheal action. It acts as an absorbent, which reduces the liquid content of the stool and binds the stool. Additionally, it decreases the frequency of the loose stools. For this, it is commonly used along with nutgrass and dried ginger powders. Pulverized Ativisha can be consumed three to four times a day with a minimum of two to three hours to treat fever.
3. Common Cold & Flu
Ativisha powder should be mixed in Basil Leaf Juice and honey. It can be given to children for treating common cold and infections of upper respiratory tract. This mixture gives relief from nasal blockage, running nose, fever, sneezing and nasal irritation. It also prevents secondary infections.
4. Cough & Bronchitis
Ativisha powder along with Pistacia Integerrima and honey helps to treat bronchitis and cough. It helps to clear the lungs, reduces inflammation and modulates the mucus secretions. The root bark powder of Ativisha can be given to patients particularly children to provide relief from cough, nasal blockage, running nose, sneezing, and nasal irritation.
5. Mal-absorption
Ativisha has stomachic, digestive, and metabolism enhancer actions, which encourages digestion and metabolism. Ativisha helps to digest food and promotes a proper assimilation of the foods, which helps to treat mal-absorption syndrome.
6. Treats Ingestion
Decoctions of Ativisha, dry ginger, Cyperus Rotundus, and Tinospora cordifolium can be eaten together to digest all the undigested food you had, and it gives you better relief. Sometimes the food we consumed would not digest because of low digestive fire that develops the Ama formations, which means the toxic and it leads to ingestion. Ativisha helps to digest the toxins with its digestion and appetizer properties.
7. Great for detoxification
Ativisha is an excellent herb for general detoxification of the body. Root powder can be given to children for clearing out worms in the body. It can also detoxify the blood and improves immunity.
8. Prevents Vomiting
According to Ayurveda, vomiting occurs when the three doshas are imbalanced, particularly Pitta and Kapha. The imbalance is caused by improper eating habits and eating excessive foods such as sour, cold diet, raw or uncooked food, heavy diet, pungent, sharp, and cause burning sensation.
These habits lead to toxic due to improper digestion formation in the body and cause indigestion. As Ativisha has digestive properties, it helps digest the foods that created Ama and caused vomiting and give you complete relief from the conditions. The balancing properties of Ativisha such as appetizer, digestion, and Tridoshas called Vata, Pitta, and Kapha are the reasons for this effect.
9. Treats Piles
Because of the inactive lifestyle we are living today, Piles become the most common issue developed due to chronic constipation. When Vata dosha becomes imbalanced in the body, constipation is created.
These conditions lead to Pile mass formation when ignored or untreated. Ativisha helps manage constipation, thus preventing piles formation.
10. Heals Constipation
Powder of Ativisha root, fruit rind of chebulic myrobalan, rhizome of the sweet flag, leadwort root, fruit of Piper longum, salt of sodium & potassium, and costus rhizome are mixed and consumed with warm water two times a day at 3 to 6 grams as dose.
11. Treats Mumps & Parotitis
Decoction extracted from an equal amount of roots of Ativisha, Ashwagandha, Musli, Guduchi (stem), and Atibala can be taken a day thrice as a dose of 14 – 28 ml for parotitis and mumps.
12. Treats Diabetes and Leucorrhoea
Half teaspoon of dried and powdered mixture of roots of Ativisha, leaves of Ajuga parviflora, and roots of Podophyllum hexandrum is given two times a day in early morning and night after food for three months as a carminative and to treat diabetes and leucorrhoea.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Ativisha
- Abdominal Diseases: Make a decoction of Aconitum Heterophyllum roots. Consume two teaspoons of this decoction before going to bed for two weeks. It cures Abdominal Problems.
- Diarrhea: Finely powder equal quantity of dry Ginger, Beal fruits, Nutmeg and Ativisha together. Take 2 pinches of this powder with water thrice a day.
- Indigestion: Take equal quantity of Sweet Flag, Asafetida, Ativisha, Ginger, Black Pepper and Long Pepper. Grind them to make powder. Take 2 g of it with lukewarm water once a day.
- Fever: Take 100 g Caesalpinia Bonduc seeds with 15 g Ativisha seeds. Powder them. Take quarter teaspoon of the powder with same quantity of Sugar. Have it twice a day.
Traditional uses and benefits of Ativisha
- Dried root is analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antiperiodic, aphrodisiac, astringent, cholagogue, febrifuge and tonic.
- It is used in India in the treatment of dyspepsia, diarrhea and coughs.
- It is also used in Tibetan medicine, where it is said to have a bitter taste and a cooling potency.
- It is used to treat poisoning from scorpion or snake bites, the fevers of contagious diseases and inflammation of the intestines.
- It is useful in treating coughs, diarrhea and indigestion.
- It is a valuable drug for infants in dentition, fever and vomiting.
- Traditionally it has been used as an antidote to poisoning.
- Roots are astringent and used in diarrhea, especially in infants, and in dyspepsia, vomiting, cough, irritability of the stomach and colic.
- It is used as a bitter tonic to combat debility after malaria and other fevers.
- It is also used against hysteria, dyspepsia, vomiting, and cough.
- Ativisha is used in Ayurveda for due to scorpion or snake bite.
- It is widely used in treating chronic and recurrent fever.
- It is used in treating bleeding disorders.
- When administered to new mothers, it cleanses and detoxifies breast milk.
- Ativisha is used in treating pediatric disorders.
- It is also used to encounter acute poisoning.
- The powder made from its root is used as anti-fertility agent.
- It can also be used in treating loss of memory, piles, throat diseases and splenic fever.
- It reduces obesity and it also improves diabetic and rheumatic conditions.
- Seeds crushed in honey are applied locally on throat, in tonsillitis.
- Nasal insufflations of roots are beneficial in headache.
- Seed and root are used in ascites.
- Seeds are diuretic; the root decoction reduces burning of urinary tract.
- It increases volume of urine.
Dosage of Ativisha (Aconitum Heterophyllum)
| Under 5 years | Please consult with doctor |
| Grade-Schooler (5 – 12 years) | 600 to 750 mg |
| Teenager (13 -19 years) | 750 to 1000 mg |
| Adults (19 to 60 years) | 1000 to 2000 mg |
| Geriatric (Above 60 years) | 500 to 1000 mg |
| Pregnancy | 250 to 500 mg |
| Lactation | 250 to 500 mg |
| Maximum Dosage | 6 g/day (in divided doses) |
Consumption: Two times a day with honey after food
How to Use Ativisha
Ativisha Powder
- Take 1 teaspoon of Ativisha Powder.
- Add honey to it and take preferably in the morning.
- Use this remedy once a day to get rid of indigestion.
Ativisha Extract
- Take 1-2 pinches of Atis Extract.
- Add honey to it and take preferably in the morning.
- Use this remedy preferably for children to get relief from fever, loose motions, bloating etc.
Ativisha Kwath
- Take 2-3 teaspoons of Ativisha Kwath.
- Add an equal quantity of water and some honey to it.
- Drink it twice a day after meals to get rid of digestive problems.
Ativisha Powder
- Take ½ – 1 teaspoon of Ativisha Powder.
- Add rose water to it.
- Apply evenly to the affected area.
- Let it sit for 8-10 minutes.
- Wash thoroughly with tap water.
- Use this remedy 2-3 times a week to get rid of boils and ulcers.
Ativisha Oil
- Take 1-2 teaspoons of Ativisha oil.
- Add sesame oil and gently massage it on the affected area.
- Use this remedy 2-3 times a week to get rid of pain and inflammation of the joints.
Precautions
- The whole plant is highly toxic, simple skin contact has caused numbness in some people.
- It may cause toxic effect on human body.
- It may cause dryness in the body.
- Its heavy dose has a narcotic effect.
- Aconitum heterophyllum has the ability to make the sympathetic nervous system more sensitive to physiological stimuli.
- Like other Aconitum species for this, no purification process is mandatory.
- Root can be purified by boiling in milk or cow urine before use.
- Excess usage may cause dryness in mouth, tremors and chillness.
- It may also cause nausea, vomiting, convulsions and dehydration.
- The usage of this medicine during pregnancy is restricted.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Aconitum+heterophyllum
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2618818
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/AAOHE
http://temperate.theferns.info/plant/Aconitum+heterophyllum
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Greenish%20Himalayan%20Monkshood.html