Iberis amara is used since 80 a.d. in homeopathy to treat gastrointestinal problems. The bitter candytuft contains glucosinolates, flavonoles and curcurbitacines that are anticonvulsive and anti-inflammatory. Especially the curcurbitacines are responsible for the bitter taste of the bitter candytuft. The different chemical compounds are able to relax the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract or they innervate the muscles. Being able to relax and innervate is a special property of that plant compounds. The fruit is a small pod that bears the seeds that have a high concentration of curcurbitacine. They are used in homeopathy against cardiac insufficiency Iberis amara prefers nutrient poor and calcerous soils.
Plant Description
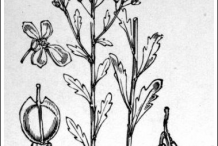
Annual Candytuft is an herbaceous, annual or occasional biennial plant that grows about 15-30 cm (6-12 inches) tall and 20- 40 cm (8-16 inches) wide. The plant is found growing in bare patches of south facing chalk grassland, particularly in rabbit scrapes, but can also be found in quarries, wasteland and as an arable weed. The plant is lost from sites devoid of bare ground but as the seed can remain viable in the soil for many years it can reappear following disturbance. The plant prefers well-drained calcareous soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. It can tolerate mildly acid soils as well. The stem is upright with splayed branches and downy-haired at the edges.
Leaves
Leaves are elongating cuneiform and obtuse. The lower leaves are often spatulate and narrow toward the petiole. The upper leaves are sessile, usually with 2 to 4 blunt teeth at wide intervals and a ciliate margin.
Flower and Fruit
The stemmed flowers are arranged in racemes; there are 4 orbicular, diagonally splayed sepals approximately 2 mm long with white or reddish membranous margins and 4 obovate-elongate white petals, the outer ones approximately 6 mm, the inner ones 3 mm long. The plant has 2 short and 4 long stamens and a superior 4-carpled ovary; the carpels are fused. The fruit is a small pod, 4 to 5 mm long, almost circular with wide-winged fruit sides and a tough margin. Each of the 2 chambers has only 1 seed. The seeds are semi-ovoid, 2.5 to 3 mm long, flat and approximately 1 mm thick. They are usually narrow-winged at the margin, brown and smooth.
Traditional uses and benefits of Annual Candytuft
- Little used in modern herbalism, rocket candytuft is a bitter-tasting tonic, aiding digestion and relieving wind and bloating.
- It is traditionally taken to treat gout, rheumatism and arthritis.
- All parts of the plant are antirheumatic and antiscorbutic.
- Seeds are considered very useful in the treatment of asthma, bronchitis and dropsy.
- Common homeopathic remedy is made from the seeds.
- It has always been used for gout, rheumatism and kindred ailments.
- All parts of the plant are antirheumatic and antiscorbutic.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Annual Candytuft
- Gastroparesis: Take equal amounts of Wild Candytuft, Angelica root, Milk Thistle fruit, Caraway fruit, Licorice root, Peppermint, Chamomile flower, Chelidonium Majus and Lemon Balm Leaves. Grind them together. Take one tsp powder with lukewarm water once a day. OR Prepare a decoction of above given herbs. Drink half cup twice a day.
Culinary Uses
- Seeds are sometimes used as a source of mustard.
- Both the leaves and flowers of candytuft can be eaten raw and have a taste similar to that of a sweet broccoli.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=23144#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/225/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=19648
http://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Iberis+amara
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/109377
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/c/canbit17.html
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2859697
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=IBAM
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iberis
https://www.uaex.edu/yard-garden/in-the-garden/docs/candytuft.pdf
Comments
| Annual Candytuft Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Annual Candytuft |
| Scientific Name: | Iberis amara |
| Origin | Western, central and southern Europe |
| Shapes | Small pod, 4 to 5 mm long, almost circular with wide-winged fruit sides and a tough margin. |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Health benefits | Treat gout, rheumatism and arthritis |
| Name | Annual Candytuft |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Iberis amara |
| Native | Western, central and southern Europe |
| Common Names | Hyacinth Candytuft, Rocket Candytuft, Clown’s Mustard, White Candytuft |
| Name in Other Languages | Chinese: Qūqū huā (屈曲花) Danish: Hvid sløjfeblomst, Bitter Sløjfebblomst Dutch: Bittere scheefbloem English: Annual candytuft, Bitter candytuft, Rocket candytuft, Wild candytuft, Gruetzblume, teraspic, Hyacinth Candytuft, Hyacinth flowered candytuft, Finnish: Katkerasaippo, Lumisaippo French: Iberis amer, Thlaspi blanc, Téraspic, Ibéris amer, Iberis cilié, Ibéris à feuilles ciliées German: Bittere Scheifenblume, Grützblume, Bitterer Bauernsenf, Grüzblume Korean: Seoyangmalnaengi Norwegian Bokmål: Prydsløyfe Nynorsk, Norwegian: Prydsløyfe Polish: Ubiorek gorzki Swedish: Blomsteriberis, Katkerasaippo |
| Plant Growth Habit | Herbaceous, annual or occasional biennial |
| Growing Climate | Hillsides and in cornfields, yards, roadsides, wasteland, culturally-influenced land |
| Soil | Prefers well-drained calcareous soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. It can tolerates mildly acid soils |
| Plant Size | 15-30 cm (6-12 inches) tall and 20- 40 cm (8-16 inches) wide |
| Leaf | Alternate, lowest soon withering, middle and upper leaves stalkless, narrowly obovate, sparse-toothed at tip (sometimes with short margins), margin sparsely hairy, 3-veined |
| Flowering Periods | Jun to July |
| Flower | Arranged in racemes; there are 4 orbicular, diagonally splayed sepals approximately 2 mm long with white or reddish membranous margins and 4 obovate-elongate white petals |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Small pod, 4 to 5 mm long, almost circular with wide-winged fruit sides and a tough margin. Each of the 2 chambers has only 1 seed. |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Seed | Brown smooth semi-ovoid, 2.5 to 3 mm long, flat and approximately 1 mm thick |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, stem, root, seeds |
| Precautions |
|