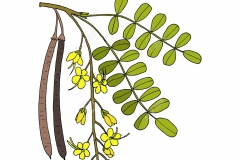
| Amaltas Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Amaltas |
| Scientific Name: |
Cassia Fistula |
| Origin |
South-East Asia, and was introduced throughout the tropics |
| Colors |
Green when young turning to dark brown as they matures |
| Shapes |
Pendulous, cylindrical, indehiscent pod, up to 60-100 cm long and 1.5-2 cm wide |
| Flesh colors |
Blackish |
| Taste |
Sweet |
| Health benefits |
Intestinal Disorders, Skin disorders, Constipation, Common Cold, Immunity Booster, Beneficial for cardiac problems, Fever, Wounds, Relieves flatulence, Fights inflammation, Cure for erysipelas, Helps cure dyspepsia, Treat a chronic cough, Helps diabetics, Relieves urinary problems |
Cassia fistula commonly known as Amaltas, golden rain tree, canafistula is a slow growing, flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. The plant is native to South-East Asia, and was introduced throughout the tropics. It have escaped cultivation in Costa Rica, Guyana, and French Guiana, and are naturalized in many parts of the tropics including the West Indies, Mexico, Ecuador, Belize, and parts of Micronesia. It is considered as an invasive in Queensland, Australia. Apart from Amaltas it is also known as Golden Shower, Purging Cassia, Golden Chain Tree, Indian Laburnum, golden shower tree, pudding pipe tree, Cassia fistula, Ai-kadus, Alash, Ali, Amultas, Bahava, Bahawa, Bereska, Cana pistula, Chaiya-pruek, Garmala, Girimalah, Girmala, Golden rain tree, Golden rain, Guolong liang, Indian Laburnum, Kakke, Khuun, Kiar, Kirwara, Konnai and Konnei.
Genus name comes from the Greek name for a genus of leguminous plants which provide the senna leaves and pods important in pharmacy. Specific epithet means hollow like a pipe. The name C. fistula is thought to originate from the ancient Greek name kassia or casia, for an aromatic and fragrant plant, as the species has a long history of herbal use; the pith of its long, woody pods yields a purgative medicine. The flower is National flower of Thailand and State Flower of Kerala, India. It is a popular plant used as ornamental and for herbal medicine. Dried fruit has medicinal properties and is now widely grown in tropical and subtropical areas around the world.
Plant description
Amaltas is a slow growing, medium sized, tropical, deciduous or evergreen tree that grows about 9-20 m tall and 3-5 m wide upon maturity. The plant is found growing in rain forest (on terra firma), riverine and gallery forest (including flooded riverbanks and várzea), seasonally dry forest, woodland, wooded grassland (savanna and cerrado), dry scrub, thickets and coastal areas, dry, deciduous forest, low altitudes, parks, gardens, and urban areas. The plant prefers to grow in a deep, well-drained, moderately fertile sandy loam. It seems to favor calcareous and red, volcanic soils, but is also found on sandy and loamy soils. Bark is grey, smooth to slightly ridged and slender when young and changes to a darker grey-brown when mature. Stems and young twigs are sparsely to densely hairy.
Leaves
Leaves are smooth, ovate shape, hairy below, alternate, pinnate, and deciduous, with 3-8 pairs of leaflets. The leaf can range from 15 – 60 cm long, with each leaflet ranging from 7 – 15 cm long, and 2-7 cm broad. The leaves will fall periodically, only to be replaced with new foliage. Leaves are absent at flowering time. Leaves usually drop in April as a introduction to flowering which occurs from May to early July. The leaves on this tree are green year round, and remain green until they fall off and are replaced.
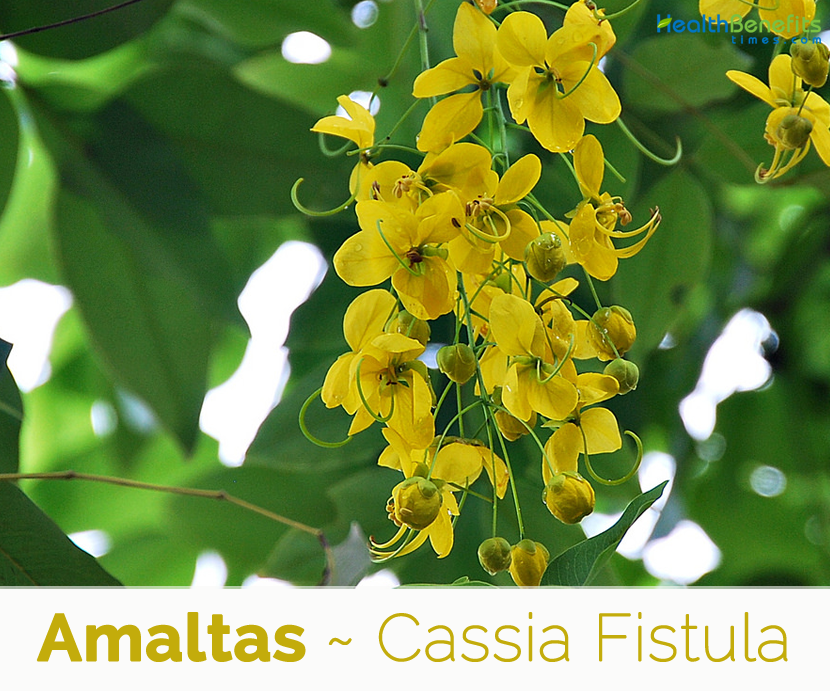
Flower
Flower is showy, bright yellow in color, pentamerous and slightly zygomorphic in shape, and growing from pendulous 20 to 40 cm long racemes, each flower 4–7 cm in diameter with five yellow petals of equal size and shape. They are borne on terminal, drooping racemes about 30-60 cm long which can be grouped by 3. Flowering normally takes place from April to July.
Fruit
Fertile flower are followed by pendulous, cylindrical, indehiscent pod, up to 60-100 cm long and 1.5-2 cm wide, with a pungent odor and containing several seeds. Fruits are initially green turning dark brown as they mature. Seeds are lenticular, ellipsoid, 8-9 mm long, glossy light brown in color and lustrous. When fresh the pods contain a black pulp which on drying adheres to the septa. Sticky brown pulp inside the pods has been used in herbal medicines. Maturing of the fruits starts from December to March.
Health benefits of Amaltas
Cassia fistula, that goes by the name Amaltas, is not only a very beautiful tree but also extremely beneficial to the human body. This tree, with medium sized leaves and bright yellow flowers, has been used for its medicinal properties since time immemorial. Here are some of the countless health benefits that this tree offers
1. Intestinal Disorders
Application of Cassia Fistula pulp externally around the navel area can help children suffering from flatulence by ensuring evacuation. Pulp can also be mixed with almond or linseed oil for easing bowel movement problems.
2. Skin disorders
Leaves of cassia fistula tree can effectively provide relief from skin irritation, swelling and pain. You may use the juice and paste of its leaves to treat skin problems such as ringworm and inflammation in the hand or feet caused due to cold conditions. Rubbing leaves of cassia fistula on problematic areas of the skin can also be very effective.
3. Constipation
Pulp obtained from this tree, also known as cassia pulp, is known to be an effective laxative. Soak 50 grams of cassia pulp in water overnight and strain it. Mix 25 grams of sugar in it and use it to treat constipation. The pulp of Cassia Fistula is a mild and harmless purgative.
4. Common Cold
Cassia fistula is also effective in treating common cold. Inhalation of smoke from burning cassia fistula root can treat a running nose. The smoke is known to stimulate nasal discharge and thus provide relief.
5. Immunity Booster
Bark and fruits of this tree have great antioxidant properties and hence, can boost immunity of the body. Regular consumption of the extracts from the bark and fruits can improve natural immune response.
6. Beneficial for cardiac problems
Amaltas leaves have heart-healthy properties. Prepare a decoction of the leaves and have it morning and evening. It helps reduce the unhealthy LDL cholesterol and makes the heart muscles strong. This improves the heart health.
7. Fever
Decoction of Amaltas is useful for treating fever. Prepare a decoction by boiling the leaves of the tree in water. Filter and cool before having it. This will help you get relief from fever. This is one of the best cassia fistula medicinal uses.
8. Wounds
Cassia Fistula acts as great remedy for treating wounds. The herb promotes tissue regeneration and the juice extracted from the leaves is also used for dressing wounds.
9. Relieves flatulence
When you have digestion problem, or you eat food that produces gas, gas might collect in your stomach and intestines, and this will cause pain. Use the pulp of the fruit to get relief. Make a paste of the fruit pulp and apply this around the navel. You will soon get relief from your gas.
10. Fights inflammation
You get relief from inflammation and pain such as gout and rheumatism by having the leaves of the cassia fistula tree. Fry some leaves in mustard oil and have it once daily. For gout, boil the root in milk and have it once daily. This is one of the effective cassia fistula medicinal uses.
11. Cure for erysipelas
Erysipelas occurs due to a bacterium group a Streptococcus. You will experience blister-like condition with raised red patches on the skin. Make a paste of the leaves and mix it with equal amounts of ghee. Apply this mixture to the affected parts to get relief.
12. Helps cure dyspepsia
When you have an upset stomach, it can cause pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen. Symptoms include nausea and bloating. You can get relief from these symptoms by having the decoction of the leaves of the Cassia fistula tree.
13. Treat a chronic cough
Preparation made from the fruit pulp of the cassia fistula tree is good for relieving chronic cough symptoms. Make a mixture of the pulp of the fruit with a few teaspoons of ghee. Have this in the morning and night for two weeks. Your cough will disappear. If people have bronchitis, you can use the paste of the fruit with milk to get relief. Find bronchitis symptoms and treatment.
14. Helps diabetics
Amaltas is useful for diabetics in controlling the sugar levels in the blood. The action of the cassia fistula helps improve the insulin sensitivity and thus helps control the level of sugar in the blood.
15. Relieves urinary problems
When people have pain passing urine and can only do so by making an effort, the use of Amaltas helps to relieve the pain. It helps them pass urine with ease. Make a paste of the root of the cassia fistula tree by soaking it in water overnight. Mix this with ghee and have this daily in the morning. This will relieve your distress. This is one of the effective cassia fistula medicinal uses.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2iw9NojpgXA
Traditional uses and benefits of Amaltas
- The five parts – roots, bark, fruit, flower, and leaf – are mixed with water to form a paste and applied to ringworm, scabies, and skin disorders stemming from impurities in the blood.
- Heated leaves are used as a poultice over swollen joints.
- Liquid from leaves stone-ground with vinegar is applied to treat leprosy and other skin diseases.
- Juice from crushed leaves is applied liberally as a remedy for herpes facialis.
- Pulp is taken either alone or mixed with an equal amount of tamarind fruit pulp to promote regular bowel movements.
- Paste from pulp is applied around the navel of infants to alleviate colic and bloated stomach.
- Pulp paste is rubbed onto the navel to treat urinary disorders, pain around the urethra and during urination, and blood in the urine.
- Liquid from boiling the pulp is used as ear drops to clear infections.
- Milk in which roots have been boiled is taken as a remedy for flatulence.
- Powdered seeds can be used in the treatment of amoebiasis and bark extracts against inflammation.
- Pods are used against malaria, blood poisoning, anthrax, diabetes, and dysentery.
- Bark and leaves are used in the treatment of various skin conditions, broken bones, and tropical ulcers.
- Ripe pods and seeds are widely used in both traditional and conventional medicine as a laxative.
- In modern medicine, the fruit pulp is sometimes used as a mild laxative in pediatrics.
- Fruit pulp is rich in pectins and mucilage.
- Aqueous fraction of the pods has produced a significant decrease in glycaemia.
- Aqueous and methanolic bark extracts have shown significant anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
- An alcohol extract of the leaves has shown antibacterial activity in vivo against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, plus accelerated wound healing.
- Pods are used as a remedy for malaria, blood poisoning, anthrax, diabetes and dysentery.
- Decoction of this is taken as a cure for kidney stones, as a vermifuge and as a laxative.
- Pulp is extracted from the pods by bruising them and then boiling them in water, after which the decoction is evaporated.
- Bark or leaves are widely applied to skin problems.
- Broken bones and tropical ulcers are bandaged with bark scrapings and leaf sap.
- Heartwood is traditionally applied as an anthelmintic.
- Decoction of the roots is applied to purify wounds and ulcers.
- Roots are used to treat fevers in India.
- Poultice of leaves are used for insect bites, swelling, rheumatism and facial paralysis.
- Juice of leaves is useful as dressing for ringworm, relieving irritation and relief of dropsical swelling.
- Its leaves and bark mixed with oil are applied to pustules, insect bites.
- Its root is also useful in fever, heart diseases, retained excretions and biliousness.
- It is also used in cardiac disorders biliousness, rheumatic condition, hemorrhages, wounds, ulcers and boils and various skin diseases.
- Extract of the root lowered the blood sugar level up to 30 %.
- Ashes from burnt pods mixed with little salt are used with honey taking 3- 4 times to relieve cough.
- Heated pods are applied to swellings on the neck due to cold.
- Amaltas fruits are used in the treatment of diabetes.
- Seeds are useful in jaundice, biliousness, skin disease and in swollen throat.
- Fruit pulp is used for constipation, colic, and urinary disorders.
- Powder or decoction of the bark is administered in leprosy, jaundice, syphilis and heart diseases.
- Stem bark is used against amenorrhea, chest pain and swellings.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Amaltas
- Insect bites: Take Root bark. Grind them. Make paste with water. Apply it on the affected part.
- Blisters: Take the leaves. Boil them. Apply it on Blisters.
- Abscess: Take the equal quantity of bark and leaves. Grind them. Make paste with Sesame oil. Apply it on Abscess.
- Skin: Take equal quantity of bark and leaves. Grind them. Make paste with Sesame oil. Apply it on the affected part. OR take the flowers. Grind them properly. Add lime juice. Mix it well. Apply on the affected area. OR use bark oil.
- Constipation: Take the leaves. Grind them properly with water. Take one tablespoon with cooked rice daily. OR take bark. Soak it in water. Strain it. Drink the water once a day. OR take out the pulp of the fruit. Soak one tablespoon in a glass of water overnight. Strain it. Add sugar for taste. Drink it in the morning daily. For Children Only: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in warm almond oil. Massage the abdomen and navel rounded area.
- Diabetes: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in a jug of water. Leave it for 2 hours. Drink it twice a day.
- Emacitation: Take the fresh flowers. Clean them properly with water. Boil two flowers in a glass of milk. Drink twice a day.
- Flatulence: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in a glass of water. Drink it early in the morning. For Children Only: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in mustard oil. Heat it for a minute. Apply slightly warm oil around the navel at night.
- Stomach ache: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in a glass of water. Drink it early in the morning. For Children Only: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in mustard oil. Heat it for a minute. Apply slightly warm oil around the navel at night.
- Itching: Take the flowers. Grind them properly. Add lime juice. Mix it well. Apply on the affected area.
- Jaundice: Take the flowers. Grind them properly. Add one tablespoon honey in one tablespoon paste. Have it once a day.
- Leucorrhoea: Take the flowers. Grind them properly. Add one tablespoon honey in one tablespoon paste. Have it once a day.
- Anemia: Take the flowers. Grind them properly. Add one tablespoon honey in one tablespoon paste. Have it once a day.
- Rheumatism: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Grind it with some water. Boil it on a low flame. Leave it for two hours. Apply it on the affected parts.
- Joint pain: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Grind it with some water. Boil it on a low flame. Leave it for two hours. Apply it on the affected parts.
- Stomach Diseases: Take some flowers. Soak them in a jug of water overnight. Drink it early in the morning. For Children Only: Take out the pulp of the fruit. Mix it in mustard oil. Heat the oil for a minute. Apply slightly warm oil around the navel.
- Ascaris: Take a handful of leaves. Boil them. Extract them properly. Add sugar according to your taste. Take one tablespoon with Luke warm water daily.
- Cold: Take Golden Shower Root. Burn. Inhale the smoke once a day.
- Fever: Inhale the smoke of burnt Golden Shower Root twice a day.
- Intestinal diseases: For Children: Apply pulp of Golden Shower Fruit on abdomen.
- Constipation: Take Golden Shower fruit pulp, Wine Grapes pulp, Fennel, Rose, Coriander seeds. Mix them in a jug of water. Soak overnight. Strain. Drink twice a day.
- Swelling: Take 5 grams each of the bark of Drumstick, Indian Beech, Berberis Aristata and the root of Golden Shower. Grind with some urine of cow. Apply on the affected area.
- Stomach ache: Take Golden Seal, Meadowsweet and Chamomile in equal quantity. Grind them together. Have one teaspoon with lukewarm water.
- Constipation: Prepare a decoction of Terminalia Chebula and add 1 teaspoon of Cassia Fistula in it. Consume it before bed time.
- Gout: 5-10 g roots are boiled in a glass of milk and taken twice a day for few days.
- Skin diseases: Cassia fistula leaves paste is applied externally.
- Constipation: 10-15 grams fruit pulp is soaked in half liter water at night. Next morning the pulp is mashed. This is filtered and filtrate is taken orally to get relief from constipation.
- Chronic cough: 12-24 grams ghee is prepared from the decoction of fruit pulp and taken twice a day.
- Acidity or gas: Massage a slightly warmed up fruit pulp around the navel area in a circular motion in multiples of seven for about 10 minutes. Doing this daily for a month cures.
- Skin eruptions due to impure blood: Soak Aamaltas fruit pulp and some tamarind in a cup of water overnight. Next morning mash them well, strain out the pulp and drink the water. Do it for a month to get complete relief. It also makes the skin glow.
- Constipation: Soak 10 to 20 grams of fruit pulp in a glass of water overnight. Filter the water in the morning and drink it. This is a very gentle laxative.
- Alopecia areata or baldness: Apply a paste made by mixing ash of Amaltas leaves with some goat’s milk. This is very effective for loss of hairs from the scalp, eyebrows, and beard.
- Piles: Boil 10 grams each of Aamaltas fruit pulp, harad, and munakka and drink this decoction at bedtime for some days.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: decoction of the pulp is taken with 2 grams each of dry ginger, harad, and giloy powders.
- Amenorrhea: A paste of the leaves is used for treating amenorrhea while a plaster of leaves is used for treating chilblain.
Culinary Uses
- Tender leaves can be made into a soup and taken for constipation.
- Bark is an ingredient in betel paste, the slightly narcotic masticatory that is popular in some areas of Asia.
- Flowers are edible and can be fried.
- Young leaves and flower buds are cooked as a vegetable.
- Pulverized seeds are used as a laxative.
- Pulp is used as an ingredient in spiced Indian tobacco.
- Flowers and buds are also eaten as food.
Dosage
- Fruit pulp: 5 to 10 gm.
- For Purgation: 10 to 20 gm.
- Root bark decoction: 50 to 100 ml.
- Flower: 5 to 10 gm.
Other facts
- Bark yields tannins and dyestuff.
- Wood is used in charcoal making and as material in construction, fence post, carts, etc.
- Tree can be planted for the restoration of degraded lands and restoration of woodland.
- Since it is not palatable to domestic animals, it may be suitable for the reforestation of areas which have become overgrazed.
- Seeds of Cassia fistula are a potential commercial source of seed gum, a potential binder for the pharmaceutical industry.
- Water soluble gum isolated from the seeds has been evaluated for its binding properties for formulations of tablets.
- Wood is used for many products and tools including wheels and shafts of carts, turnery, tool handles, ploughs, harrows and rollers, house building posts, rice pounders, bows, for boat spars, and bed plates for machinery; also for tent poles and tent pegs, toys and carvings.
- Wood is used to make a good quality charcoal.
- Cassia fistula is attractive to bees, butterflies and/or birds.
- Flowers are used in religious ceremonies in India and Bangladesh.
- Flower is National flower of Thailand and State Flower of Kerala, India.
- Golden tree twigs are commonly lopped for fodder.
- Postal stamp was issued by the Indian Postal Department to commemorate this tree.
Amaltas Perfumes
That said, to me the best way of indulging in the heady blooms of Amaltas throughout the year is distilling their fragrance into a perfume. It’s easily done at home:
Ingredients
- 2 cups of freshly picked Amaltas flowers
- 2 cups of Distilled water
- An empty perfume bottle (for storing)
Direction
- Wash the flowers very well.
- Put the flowers and distilled water into a heavy-bottomed pot and heat to a just-below-boiling simmer (don’t cook the flowers – that will ruin the scent).
- Let them simmer for around two hours, checking periodically to make sure the pot hasn’t run out of water.
- Turn off the heat and cool the contents.
- Strain contents through a muslin cloth (or cheesecloth) to remove the solid bits.
- Pour the remaining liquid into an empty perfume bottle.
- Use as you would any regular perfume!
Precautions
- All parts of plant are poisonous if ingested.
- It may cause nausea and dizziness.
- High doses may induce diarrhea and dysentery.
- Herb is not recommended for small kids and pregnant women.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=25749#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/38312/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=9334
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Cassia+fistula
https://www.cabi.org/ISC/datasheet/11434
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=280435
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CAFI3
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-1022
https://www.feedipedia.org/node/325
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Amaltas.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cassia_fistula
https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/duke_energy/Cassia_fistula.html
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Cassia+fistula
http://hort.ufl.edu/database/documents/pdf/tree_fact_sheets/casfisa.pdf
http://www.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Cassia_fistula.PDF
Comments
comments