The tree reaches maturity and begins flowering at 10 to 15 years of age, while flowering and fruiting times differ according to geographic location. Timber and wood of the tree are fine grained, hard, and durable. Ripe fruit is green while the edible mesocarp is soft, juicy, and bright orange. The mesocarp has a turpentine flavor and may taste sweet to slightly bitter. The seeds or kernels of the tree are classified as oil seeds.
African Mango Facts
| African Mango Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | African Mango |
| Scientific Name: | Irvingia gabonensis |
| Origin | Northern tip of Angola, including Congo, DR Congo, Nigeria, Côte d'Ivoire |
| Colors | Green when ripe |
| Shapes | Ellipsoid to cylindrical drupe, occasionally nearly spherical, slightly laterally compressed |
| Flesh colors | Bright orange |
| Taste | Sweet to slightly bitter |
| Health benefits | Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, Weight Loss, Battling High Cholesterol, Antioxidants, Increases Energy, Boosts Circulation, Protects Heart Health, Anemia Curing, Detoxifies the Body, Bone Strengthening, Prevent Heart Attacks, Relief from constipation, Suppress Your Appetite |
| Name | African Mango |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | African Mango |
| Native | Humid forest zone from the northern tip of Angola, including Congo, DR Congo, Nigeria, Côte d’Ivoire and south-western Uganda |
| Common Names | Bread tree, African wild mango, wild mango, bush mango, African mango, Dika Nut, Abesebuo, Andok, Boborou, Bush mango, Dika, Duika, Ebi, Eniok, Esele, Mango-bravo, Mopae, N’corobaque, Ntwa, Ogbono, Ogwe, Oro, Pekie, Ugiri, Uncorobaque, Upupa, Uyo, chocolatier, dika du gabon, dika nut tree, dikabread-tree, dikanut-tree, dikanuß, irvingia, manguier sauvage, odika, rainy season bush-mango, sweet bush-mango, árbol chocolate, Dikabread tree, Iba-tree, Odika, Agbono, Bread Tree, Dikka, Duiker Nut, Etima, Iba-tree, Kaka, Odika, Andok oba, Boboi, Boborae, Boboru, Bojep, Bopala, Dibiue mutshi ditoke, Dika-bread tree, Diuka mahogany, Keega, Kpeh, Kpele, Mahogany, Manguier sauvage, Mbei, Meba |
| Name in Other Languages | Cameroon: Andok Congo Democratic Republic: Meba, mueba Côte d’Ivoire: Boboru, wanini English: African mango seed, African mango tree, African wild mango, Bread tree, Dika bread, Dika nut, Dikka, Duiker nut, Native mango, Wild mango, Wild mango nut, Dikabread-tree, Dikanut-tree, Rainy season bush-mango, Sweet bush-mango, French: Bobo, Dika du Gabon, Mangue du Gabon, Mangue sauvage, Manguier du Gabon, Manguier sauvage, Oba, Odika, Sioko, Chocolatier, Dika, Ogbono, chocolatier du Gabon, irvingie du Gabon German: Dikanuß, Wilder Mangobaum, Dikabaum Hausa: Biri, Goron Italian: Dica Japanese: Afurika mango no ki (アフリカマンゴノキ) Nigeria: Oba, oro Polish: Mango afrykańskie Sierra Leone: Bobo Spanish: Arbol chocolate, Irvingia Yoruba: Oro |
| Plant Growth Habit | Large, long-lived, evergreen tropical trees |
| Growing Climates | Evergreen dense, moist, lowland rain-forest, canopied jungle, gallery forests and semi-deciduous forests |
| Plant Size | About 40 m (130 ft.) in height with a straight bole of up to 1 m (3 ft. 3 in)in diameter |
| Bark | Outer bark is smooth or covered with scales with grey to yellow-grey color |
| Leaf | Leaves alternate, simple and entire; stipules up to 4 cm long, unequal, forming a cone protecting the bud, caducous, leaving an annular scar on the branches |
| Flowering season | February to March |
| Flower | Bisexual, regular, 5-merous, small; pedicel up to 5 mm long; sepals free, 1–1.5 mm long; petals free, 3–4 mm long, yellowish white |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Ellipsoid to cylindrical drupe, occasionally nearly spherical, slightly laterally compressed |
| Fruit Color | Green when ripe |
| Flesh | Bright orange pulp, soft, juicy |
| Seed | 2.5–4 cm long and 1.5–2.5 cm wide |
| Propagation | By seed |
| Available Forms | Jelly, jam, juice and sometimes even wine |
| Taste | Sweet to slightly bitter |
| Plant Parts Used | Fruit, seeds, bark and leaves |
| Season | Two fruiting seasons:
|
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
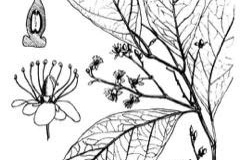
African mango is a large, long-lived, evergreen tropical tree that normally grows about 40 m (130 ft.) in height with a straight bole of up to 1 m (3 ft. 3 in) in diameter. It has buttresses to a height of 3 m (9.8 ft.). The plant is found growing in evergreen dense, moist, lowland rain-forest, canopied jungle, gallery forests and semi-deciduous forests. The outer bark is smooth to scaly with grey to yellow-grey color. The crown is evergreen, spherical and dense.
Leaves
Leaves are alternate, elliptic, simple and entire, one margin is often a little rounder than the other, acuminate, stipules are up to 4 cm long, unequal, forming a cone protecting the bud, caducous, leaving an annular scar on the branches. Petiole is up to 5 mm long. Blade is elliptical, 4.5–8 cm long and 2–4 cm wide, base cuneate, apex acute or indistinctly acuminate, thinly leathery, pinnately veined. They have a glossy top and are dark green in color.
Flowers
Flowers are bisexual, regular, 5-merous and small in slender, clustered racemes or small panicles above the leaves and about as long as them, or on the branchlets and younger branchlets. Pedicel is up to 5 mm long; sepals free, 1–1.5 mm long; petals free, 3–4 mm long, yellowish to greenish-white; stamens 10, inserted below disk, free, equal, filaments 4–5 mm long, disk 1.5 mm in diameter, bright yellow, nectariferous, ovary superior, 2-celled, style 1–2 mm long. Flowering normally takes place from February to March.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by an ellipsoid to cylindrical drupe, occasionally nearly spherical, slightly laterally compressed, 4–6.5 cm long and 4–6.5 cm wide, smooth. Fruits are green when ripe with a bright orange, fibrous pulp surrounding a large seed. It is soft, juicy, and sweet to slightly bitter with one woody stone. Stone consists of seed that are 2.5–4 cm long and 1.5–2.5 cm wide. The plant has two fruiting seasons from April to July and from September to October.
Health benefits of African Mango
Most people are familiar with African Mango as a diet supplement. Some of the most exciting research surrounding African Mango indicates that it also shows promise for addressing several common and serious health problems often related with obesity. Listed below are some of the well-known benefits of African mango
1. Diabetes
Diabetes is considered as one of the distressing condition affecting 25.8 million people in the USA alone, a growing number of them children, teens and young adults. Two separate researches showed that African mango reduced or even normalized blood glucose levels in some subjects. African Mango appears to reduce fasting blood sugar levels, as well as having a beneficial effect on insulin resistance and glycemic index control in obese diabetic patients.
2. High Blood Pressure
During a study of African Mango seed extract and its effect on the body weight and blood lipids, routine health checking of the test subjects exposed a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure in the group receiving the extract.
3. Weight Loss
One of the reasons why this exotic fruit has received so much attention in recent years is because of its superficial effects on weight loss. Flesh of the fruit is not used for these purposes, but a number of studies have been done on the extract from the nut of the African mango. Research has found that not only can the active ingredients help to reduce overall cholesterol levels, but they can also stimulate metabolism and considerably increase passive fat-burning. When this extract is used frequently, it has been known to cause weight loss. It is also known to suppress appetite, which is another way to prevent overeating and create a calorie deficit.
4. Battling High Cholesterol
In Accordance to the CDC, nearly 71 million American adults suffer from high cholesterol – a condition where there are elevated levels of triglycerides and LDL (“bad” cholesterol) in the blood. In several studies, including one of the ones investigating benefits of I. gabonensis in managing diabetes, African mango was shown to reduce overall plasma lipids (fat in blood) by lowering LDL cholesterol and raising levels of beneficial HDL fats.
5. Antioxidants
Antioxidants are essential in fighting free radicals – oxidizing agents which damage cells in our bodies, leading to aging and disease. An analysis of the Irvingia gabonensis plant has shown African Mango to be a potent source of antioxidants.
6. Increases Energy
As energy increases body works more. It increases the level of energy in a body to do more activities than usual. When we indulge in doing more activities it results in burning of fat.
7. Boosts Circulation
With a decent amount of iron in this fruit, having some of this sweet treat is outstanding for providing a boost to circulation, which delivers resources and oxygen wherever the body needs it most.
8. Protects Heart Health
The active ingredients in the extract of this fruit’s seed are able to reduce cholesterol levels and encourage the metabolism, both of which can lead to lower blood pressure and a reduced risk of coronary heart diseases.
9. Pregnant Nutrition and Anemia Curing
African mango has a high portion of zinc and minerals of which work well for pregnant woman and anemia suffer. Consume African mango moderately and do not excessively eat while you don’t know the right and a balanced portion from a nutritionist. Also, for first-trimester pregnancy, a mother soon to be will feel easy to vomit and have no appetite to eat food. It is time to serve them mango as it is so fresh and healthy.
10. Detoxifies the Body
African mango encourages healthy weight management. It helps in cleansing the colon and detoxifies the body as well as supply the body with nutrients. It can cleanse and eliminate waste and toxins. There is no cramping in the stomach when your body releases bile after intake of African mango which is a major occurrence in many cleansers.
11. Bone Strengthening
Milk is not only one source of potassium and K vitamin to strengthen your bones and cells healthy. African mango amazingly has an almost same proportion of potassium and K vitamin to optimal potassium absorption into the blood and cells. If you want to have such strong and solid bones, try to consume more mango and others fruit from now on.
12. Prevent Heart Attacks
Potassium, vitamin, and fiber are three most important contents in African mango which cooperate together to prevent the heart attack. Consuming more potassium along with natrium less is the best daily diet option. Automatically, it will also reduce the cardiovascular disease which encourages heart attack.
13. Relief from constipation
Most people have experienced constipation at some point in their lives. Not only is constipation very uncomfortable but it can also lead to weight gain. Because African mango is rich in soluble fiber it can add bulk to stools, which can help alleviate constipation.
14. Suppress Your Appetite
African mango is one of the best supplements to deal with the real problem behind your inability to lose weight: your hunger. When you are hungry, cutting back on your food intake is nearly impossible, as you continually feel the need to eat. The African mango supplement deals with the problem by producing more leptin in your body. Leptin is a hormone that tells your body, “Alright, pal, no more food. You’ve had enough!” When you are overweight, your body is less sensitive to the leptin produced by your body, so it takes longer for your appetite to be satisfied. However, when your body produces more leptin, it will feel full much more quickly – therefore making the African mango your best friend when dieting.
Traditional uses and benefits of African mango
- Its bark is a purgative for treating gastrointestinal and liver conditions, sterility, hernias, and urethral discharge.
- It is also an aphrodisiac and used in the treatment of diarrhea and dysentery, body pains, toothache, sores, and wounds.
- It is considered by some to be a powerful aphrodisiac and to be beneficial in cases of senility.
- It is used in an enema, or added to a baked banana in order to relieve diarrhea and dysentery.
- When applied externally, it is ground up with water for rubbing on to the body for easing pains.
- It is used in mouth-washes for relieving toothache, made into a poultice and applied to sores and wounds.
- Bark is mixed with palm oil for treating diarrhea and for reducing the breast-feeding period.
- Shavings of the stem bark are consumed by mouth to treat hernias, yellow fever, and dysentery, and to reduce the effects of poison in French Equatorial Africa.
- Antibiotic properties of the bark help heal scabby skin, and the boiled bark relieves tooth pain.
- The Mende tribe in Sierra Leone grinds the bark into a paste with water and applies the product to the skin for pain relief.
- Powdered kernels act as an astringent and are also applied to burns.
- Stems of the tree have been used as chewing sticks to help clean teeth.
- Preparations made from the bark are used to treat hernia and yellow fever and as an antidote for poisoning in Cameroon.
- Kernels are used to treat diabetes.
- It is used for countering the ailments relating to ear like tympanic lining infections.
- It is a good herbal cure for Obesity.
- It helps in reducing our food intake, burning body fat which leads to the loss in body weight in a reasonable fashion.
- African Mango is effective in countering Obesity; it habitually regulates the body Metabolism.
- Maintained rate of Metabolism is directly proportional to low-level of Cholesterol in the body.
- It is effectual in controlling diabetes by managing body blood sugar level.
- It is beneficial in combating jaundice, which has an adverse effect on the entire human body but majorly on liver, kidneys and heart.
- It is beneficial in promoting proper gastrointestinal action, which helps in improving digestion and avoiding acidity.
- It is a good herbal treatment possessing painkilling and antimicrobial characteristics, which help in treating sores and preventing infections in wounds.
- African Mango is fruitful in counteracting hernias, which leads to dislocation of the organs from its actual position.
- It bears constipating properties, which is favorable in ceasing ailments like loose motions i.e. dysentery and diarrhea.
- Leaves are boiled in water and taken as a tea for the treatment of intestinal worm infestation in humans in rural areas in eastern Nigeria.
- B of the tree consists of important antioxidant and anti-inflammatory ingredients which could be of use in treating various neurodegenerative diseases.
- Leaves of the tree are combined with the stem bark of other plants and boiled in water and taken as a tea to treat spleen infections.
Culinary uses
- Edible seeds are used in soups and as a food flavoring.
- Seed is also used for the preparation of odika, also known as dika bread or Gabon chocolate.
- Fruits are yellow and fibrous, with palatable pulp that can be used for fruit drinks and jams.
- Kernel is an important source of vegetable oil.
- The fruit pulp is palatable and can be used for a fruit drink and for jam production.
- Seeds can be ground or crushed and used as a thickening and flavoring agent in soups and stews.
- They can also be made into a cake called “dika bread” for preservation.
- Edible oil is extracted from the seed is used in cooking.
Other Facts
- Pulp is also used to prepare a black dye for cloth.
- In some areas, the tree is planted to provide shade for crops.
- Wood is tough, very heavy, very hard, durable, and resistant to termite attack.
- Tree is normally preserved on farms when woodland is cleared in order to provide shade for crops, particularly cocoa and coffee.
- Wax has been extracted from the plant which has been found useful as an assistant in making medicinal tablets.
- Both the bark and the roots contain tannins.
- Fruit pulp is used to prepare a black dye for cloth.
- Fat extracted from the seed is suitable for soap-making and other industrial uses.
- Sap-wood is light brown, the heart-wood a slightly darker or greenish-brown.
- It has a fine moderately close grain and a good polished finish can be achieved.
- It is not easy to cut, which limits its usefulness for native people who often only have simple implements.
- It is used for street paving.
- Canoes can be made from the trunk, and pestles for yam-mortars.
- Pulp is used for making jam, jelly, and juice and is consumed as a dessert throughout western and central Africa.
- The leaves are used as food for livestock by farmers.
- The wood is used for making walking sticks and supports for thatched roofs.
- Young trees are used for making poles and stakes, while branches are made into walking sticks or thatched roof supports.
- Dead branches are used as firewood.
- Twelve year-old trees in Nigeria have yielded 1060 fruits (180 kilos) per tree.
Precautions
- Excess consumption of African mango can result in sleep problems, headaches, and flatulence.
- Allergies to this fruit also exist, although they are rare.
- African mango supplements may cause sleep disturbance for some people.
- Diabetic patients should avoid the consumption of African mango supplements and those as well, who are scheduled for surgery.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Irvingia+gabonensis
https://www.drugs.com/npp/african-mango.html
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?20449
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irvingia_gabonensis
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Irvingia_gabonensis_(PROTA)
https://wikivisually.com/wiki/Irvingia_gabonensis
http://163.247.128.32/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=20449
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/IRVGA
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2866788
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/28877