| Chinese asparagus Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Chinese asparagus |
| Scientific Name: | Asparagus cochinchinensis |
| Origin | Southern part of Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu and other provinces to the eastern, central and southern parts of Southwest China. Chinese asparagus is also found in Korea, Japan, Laos, and Vietnam |
| Colors | Whitish, ripening to red |
| Shapes | Globose berry, 5–6 mm in diameter |
| Taste | Sweet, bitter |
| Health benefits | Support for fever, cough, hemoptysis, diabetes, constipation, swollen, throat pain, impotence and cancer |
| Name | Chinese asparagus |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Asparagus cochinchinensis |
| Native | Southern part of Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu and other provinces to the eastern, central and southern parts of Southwest China. Chinese asparagus is also found in Korea, Japan, Laos, and Vietnam |
| Common Names | Chinese Asparagus, Cochinchinese Asparagus, Shiny Asparagus, Wild Asparagus |
| Name in Other Languages | Chinese: Tian Men Dong (天门冬 ), Tian men dong (天門冬 ) English: Chinese Asparagus, Cochinchinese Asparagus, Shiny Asparagus, Wild Asparagus Japanese : Kusa Sugi Kazura (クサスギカズラ), Nangoku Kusa Sugi Kazura, Tachi-Tenmondo, Nangoku kusa sugi kazura (ナンゴククサスギカズラ), Temmondou (テッモンドウ) Khmer : Tumpèang Korean : Cheun Mun Dong (천문동) Portuguese: Espargo De Jardim Russian : Sparzha Blestiashchaia (Спаржа блестящая) Swedish: Kinesisk sparris, Taiwan : Tian Men Dong, Chōnmuntong Vietnam : Thiên Môn Ðông, Thiên Môn, Tút Thiên Nam, Tóc Tiên Leo, Dây Tóc Tiên, Mè Nằm, Nằm Săm, Co Sin Sương, Sùa Sú Tùng, Dù Mào siam |
| Plant Growth Habit | Evergreen or deciduous perennials or subshrubs, sometimes herbaceous climbing plant |
| Growing Climates | Thinly forested slopes, roadsides and waste fields from near sea level. It is also found near seashores all over Japan |
| Soil | Full sun on deep, well drained, fertile, loamy soil but is partially shade tolerant and drought tolerant and can grow in dry, sandy soils |
| Plant Size | 2.5 m long |
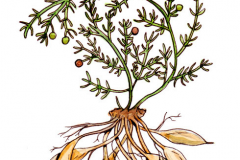
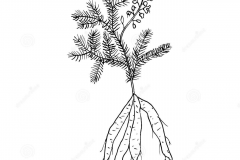
| Root | Tuberous root is spindle-shaped and expanded in the middle or near the end. The enlarged part is 3-5 cm long and 1-2 cm thick |
| Stem | Smooth, often curved or twisted, up to 1-2 m long, branches angulate or narrowly winged |
| Leaf | Leafy branches are usually in clusters of 3, flattened or slightly sharp triangulates due to midrib keel, slightly sickle-shaped, 0.5-8 cm long, ca. 1-2 mm wide; Scaly leaves on stems extend at base into stiff spines 2.5-3.5 mm long, with shorter or inconspicuous spines on branches |
| Flowering season | May to June |
| Flower | Bisexual, yellowish-white, 6–7 mm long, 1–3, arising from axils of cladodes; pedicels 7–8 mm long, jointed in the middle or above; male and female flowers separate with perianth in six segments; stamens six, fi laments arising from base of perianth segments, anthers versatile and the ovary is oblong. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Globose berry, 5–6 mm in diameter |
| Fruit Color | Initially whitish, ripening to red |
| Seed | Seed one, small and black |
| Propagation | By sowing and division propagation |
| Taste | Sweet, bitter |
| Plant Parts Used | Root, tuber |
| Season | August to October |
| Other Facts |
|
| Precautions |
|
Plant Description
Chinese asparagus is an evergreen or deciduous perennials or subshrubs, sometimes herbaceous climbing plant that normally grows about 2.5 m tall. The plant is found growing in thinly forested slopes, roadsides and waste fields from near sea level. It is also found near seashores all over Japan. The plant grows well in full sun on deep, well drained, fertile, loamy soil but is partially shade tolerant and drought tolerant and can grow in dry, sandy soils. Tuberous root is spindle-shaped and expanded in the middle or near the end. The enlarged part is 3-5 cm long and 1-2 cm thick. Stems are smooth, often curved or twisted, up to 1-2 m long, branches angulate or narrowly winged.
Leaves
Leafy branches are usually in clusters of 3, flattened or slightly sharp triangulates due to midrib keel, slightly sickle-shaped, 0.5-8 cm long and 1-2 mm wide; Scaly leaves on stems extend at base into stiff spines 2.5-3.5 mm long, with shorter or inconspicuous spines on branches.
Flowers
Chinese asparagus flowers usually in 2 axillary, light green; Pedicels are 2- 6 mm long, joints usually midway, sometimes variate; Male flowers: perianth 2.5-3 mm long; Filaments are not adnate to perianth segments; Female flowers are similar in size to male flowers. The flowering period of Chinese asparagus (Asparagus cochinchinensis) is from May to June, and the fruiting period is from August to October.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by globose berries, 6-7 mm in diameter with single seed. They are initially whitish, ripening to red.
Different function and purpose of Chinese asparagus
Decoration application
Chinese asparagus can be used as a small pot, and it is suitable for indoor ornamental pot, and it is also a good leaf arrangement for bouquet. Chinese asparagus is commonly used in a thousand barrel basin, placed on a few high frames, green leaves fine and soft hanging down like a waterfall, with a sense of movement. It can also be suspended to appreciate.
The international popular cultivation of Chinese asparagus, branches into upright shape, dense leaflet composition such as foxtail, beautiful. Potted Chinese asparagus is suitable for decorating family rooms or halls, and can also be cut stems and leaves as lining leaves for Flower arrangement.
Medicinal value
Chinese asparagus (Asparagus cochinchinensis) is used medicinally for the treatment of fever, cough, vomiting blood, lung impotence, lung carbuncle, sore throat, thirst, constipation, urination. Root tuber is a common Chinese medicine, which has the effect of moistening dryness, clearing fire and relieving cough.
Traditional uses and benefits of Chinese asparagus
- The plant has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for over 2,000 years.
- Root is harvested when the plant is dormant and is dried for medicinal use.
- Dried root is antibacterial, anti-helminthic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiseptic, antitussive, diuretic, expectorant, nervine, sialagogue, stomachic, nervous stimulant and tonic.
- The plant is a traditional Chinese medicine used for treating lung- and spleen-related diseases.
- Dried root is a tonic with antifebrile, antitussive and diuretic activity.
- Chinese asparagus is often used for the treatment of fever, cough, hemoptysis, diabetes, constipation, swollen and throat pain.
- Prolonged usage is recommended for the treatment of impotence.
- The plant also has a folk history for the treatment of cancer.
- Chinese asparagus has been traditionally used for the treatment of cancer in Korea and China.
- It also has anti-inflammatory activity and may have therapeutic potential in a variety of immune-related cutaneous diseases.
- Chinese asparagus is often decocted with other herbs (Rehmannia glutinosa, Scrophularia ningpoensis, Stemona tuberosa, Trichosanthes kirilowii, Schisandra sinensis, Adenophora verticillata, Angelica sinensis, Panax ginseng and Ophiopogon japonicus) in various medicinal formulations.
- It is used in the treatment of a wide range of ailments including pulmonary diseases, impairment of the body fluid, consumptive ailments such as cough, hematemesis, sore throats and constipation and diabetes mellitus.
- It is taken internally in the treatment of fevers, debility, sore throats, coughs etc.
- It is often decocted with other herbs and used in the treatment of a wide range of ailments including diabetes mellitus.
- It is commonly used in restorative recipes together with Rehmannia glutinosa and Codonopsis javanica.
- The root is harvested when the plant is dormant and is dried for later use.
- The plant has a folk history for the treatment of cancer, modern research has detected anti-tumor activity and it is now being studied for the treatment of lung cancer.
- The roots and stems are used in traditional Chinese and Korean medicine.
Culinary Uses
- The fusiform tubers are washed to remove the bitterness and the fibrous core removed, and the tubers are then boiled before being consumed
- Tubers are also eaten after preserving in sugar as sweet conserves
- The fruit has also been reported to be edible.
- Tubers are cooked and consumed, it tastes like asparagus.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Asparagus+cochinchinensis
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/ASPCC
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-274989
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asparagus_cochinchinensis
https://en.hortipedia.com/Asparagus_cochinchinensis
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Asparagus+cochinchinensis
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200027560
https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/integrative-medicine/herbs/chinese-asparagus