Prickly ashes possess chelerythrine which is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid and effective anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial activity. Native Americans use it to ease pain of rheumatism and toothache. The oil extracted from herb has xanthoxylin which provides stimulating, cleansing, antirheumatic and diaphoretic properties. It is used to treat various disorders such as painful throats, upset stomachs, skin infections and throbbing muscles. Moreover, bark of Prickly ash is used to promote saliva secretion and treat various health ailments. In the end of 19th century, eclectic doctors use it as a medication for digestive problems and strengthen nervous system and also cures cholera. Herbalists used the bark to cure rheumatic problems and improve body’s ability to counteract various physical problems. North American people chew both berries and bark to alleviate toothaches and rheumatism. Mesquakie used leaves, berries, bark of root and bark of trunk. Berries and bark possess strong expectorants which make it syrup for cough, cure for tuberculosis and hemorrhages.
Plant
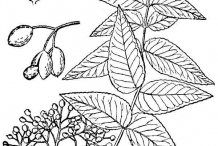
Southern prickly ash is a shrub or spiny tree which is inherent to Southeastern United States. This spiny tree grows to the height of 10 to 17 meters with distinctive spined thick and corky lumps which are 2 to 3 cm long on bark. It bears leathery and glabrous leaves which are pinnately compound and measures 20 to 30 cm long. It has 7 to 19 leaflets and each leaflet measures about 4 to 5 cm long. Flowers are dioecious, small and white in color with diameter 6 to 8 mm. Fruits is two valved capsule which measures 6 mm in diameter having a rough surface. It has several small black seeds. The tree requires abundant water and sunlight.
Traditional uses
- It is useful to treat cramps, chronic rheumatic conditions, intermittent claudication and rheumatic symptoms.
- The berries are useful for circulatory disorders.
- When the bark and leaves are chewed, it causes numbness of mouth, tongue and teeth which provides relief from toothache.
- Fruits possess stimulant, diaphoretic properties and is used as a tonic for stomach and digestive ailments.
- It is useful for ague, fevers and poor circulation.
- Bark and roots are used to comfort pain due to toothache.
- Chew the bark to promote copious salivation.
- Rub fruit on skin such as mouth or lips to produce temporary sensation loss.
- The tincture or tea prepared from bark is used to treat dyspepsia, rheumatism, dysentery, kidney and heart problems.
- Consume tea prepared from inner bark for treating itchy skin.
- In United States, it is used for typhoid, chronic rheumatism, impurity of blood and skin diseases.
- It is used as a tonic for cramps, colic, lethargy and cholera.
- Powdered bark is used to heal the wounds.
- Southern prickly ash is helpful for blood circulation problems in fingers and legs, menstrual cramps, sores, toothache, ongoing joint pain and ulcers.
- Boil the inner bark with root of sarsaparilla and drink it to gain strength during illness.
- Bark was used by Comanches to treat sore throat, fever and toothache.
- In 19th century, it is used to stimulate circulatory system and cure arthritis.
- In Ayurvedic medicine, it is used for headache, toothache, ear and eye conditions, colic, dyspeptic symptoms, fever, diarrhea, worm infestation, asthma, coughs, fever, leprosy and paralysis.
- The tincture helps to stimulate blood flow to stiff and painful joints and promotes supply of nutrients and oxygen to the areas and eliminates waste products.
- Combine the decoction with ginger which promotes circulation.
- It provides relief from gas, diarrhea and tones digestive health.
- Apply it topically to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease and leg ulcers.
- In South Africa, it is used as a treatment for rheumatic conditions.
- Use it internally to heal varicose eczema and skin ulcers.
Precautions
- It lowers the absorption of gut iron.
- It might cause bruising, sun sensitivity and bleeding.
- It could interfere with cardiac glycoside therapy and blood clotting drugs.
- It starts menstrual period and harm the pregnancy so, it should not be used by pregnant women.
- Avoid by breast-feeding women because it causes colic in nursing infant.
- Southern Prickly Ash might affect liver.
- Overdoses causes increase cardiac function, salivation and elevation of blood pressure.
- If used internally, it causes inflammatory stomach conditions.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=28850#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/62606/
http://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Zanthoxylum+clava-herculis
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/a/ashpr077.html
https://www.medicinenet.com/southern_prickly_ash/supplements-vitamins.htm
http://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/a/ashpr077.html
http://www.cloverleaffarmherbs.com/prickly-ash/
Comments
| Southern Prickly Ash Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Southern Prickly Ash |
| Scientific Name: | Southern Prickly Ash |
| Origin | Native to Southeastern United States |
| Shapes | 6 mm diameter, two valved capsule |
| Name | Southern Prickly Ash |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Zanthoxylum clava-herculis |
| Common/English Name | Toothache tree, Tingle tongue, Hercules’ club, Pepperwood, Percules-club pricklyash, Prickly Ash, Southern Prickly-ash, Frêne Épineux Américain, Fresno Espinoso del Sur, Frêne Épineux du Sud, Prickly Ash, Sea Ash, Prickly Yellow Wood, Toothache Tree, Xanthoxylum, Zanthoxylum clava-herculis, Zanthoxylum |
| Soil | Well-drained |
| Plant Size | 10 to 17 m tall |
| Leaf | Glabrous, leathery, pinnately compound, 20 to 30 cm long |
| Flowering Season | Mid-spring |
| Flower | Dioecious, small, white, 6 to 8 mm diameter |
| Fruit shape & size | 6 mm diameter |
| Plant parts used | Bark, berry |
| Seed | Black |