- Cheese is a dairy product made by coagulating milk proteins to form curds, which are then processed into various textures and flavors.
- Incorporating certain cheeses into a balanced diet can aid weight loss due to their high protein content and relatively low fat levels.
- Varieties such as cottage cheese, Parmesan, goat cheese, part-skim mozzarella, and quark are particularly beneficial for those seeking to manage their weight.
 Cheese is a versatile dairy product celebrated for its rich flavors and significant nutritional benefits. It is a concentrated source of essential nutrients, including high-quality proteins, calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins like B12 and A. These components contribute to muscle maintenance, bone health, and various metabolic functions. However, cheese is also calorie-dense, with fat content varying widely among different types. For instance, triple cream cheeses can contain up to 36% fat, while options like cottage cheese may have as low as 4% fat.
Cheese is a versatile dairy product celebrated for its rich flavors and significant nutritional benefits. It is a concentrated source of essential nutrients, including high-quality proteins, calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins like B12 and A. These components contribute to muscle maintenance, bone health, and various metabolic functions. However, cheese is also calorie-dense, with fat content varying widely among different types. For instance, triple cream cheeses can contain up to 36% fat, while options like cottage cheese may have as low as 4% fat.
The high saturated fat and sodium levels in many cheeses have been associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, moderation is key; incorporating cheese into a balanced diet can provide nutritional advantages without excessive calorie intake. Opting for lower-fat varieties and being mindful of portion sizes can help maximize health benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Nutritional Benefits of Cheese
Cheese offers a range of nutritional benefits, making it a valuable addition to many diets. It is a rich source of high-quality protein, essential for muscle repair and overall growth. The calcium and phosphorus in cheese contribute significantly to bone health, aiding in the prevention of conditions like osteoporosis. Vitamins such as B12 and A, found in various cheeses, support neurological function and vision, respectively. Additionally, certain cheeses contain probiotics that promote gut health. For example, mozzarella contains beneficial bacteria that may enhance immune response and reduce inflammation. However, it’s important to consume cheese in moderation due to its calorie density and varying fat content. Selecting lower-fat options and being mindful of portion sizes can help integrate cheese’s nutritional benefits into a balanced diet.
Top Cheeses for Weight Loss
Incorporating certain cheeses into a weight loss regimen can be beneficial due to their favorable nutritional profiles. Cottage cheese stands out with approximately 24 grams of protein and 180 calories per cup, promoting satiety and muscle maintenance. Parmesan, known for its intense flavor, allows for smaller servings, aiding in calorie control. A single tablespoon adds robust taste with minimal calories. Here are some cheeses that align well with weight loss goals:
1. Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese is widely recognized as a valuable dietary option for weight loss due to its high protein content and low calorie density. Studies indicate that the protein in cottage cheese promotes satiety, which can help reduce overall calorie intake and support weight management goals (1). Additionally, research on the dehydration and rehydration properties of cottage cheese highlights its nutrient retention, making it a practical option for inclusion in low-calorie diets (2). This combination of nutritional benefits and practicality makes cottage cheese a standout choice for those aiming to lose weight while maintaining muscle mass.
Nutrition Value of Cottage Cheese in Table
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value (approx) |
| Calories | 98 kcal | 5% |
| Protein | 11 g | 22% |
| Fat | 4.3 g | 6% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.7 g | 8% |
| Cholesterol | 17 mg | 6% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.4 g | 1% |
| Fiber | 0 g | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.7 g | – |
| Calcium | 83 mg | 6% |
| Sodium | 364 mg | 15% |
| Potassium | 104 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 67 IU | 1% |
| Iron | 0.1 mg | 1% |
2. Part-Skim Mozzarella
Part-skim mozzarella is an excellent choice for weight-conscious individuals due to its balance of high protein content and reduced fat levels. Scientific studies emphasize its role in weight management diets, highlighting that its protein supports muscle maintenance and promotes satiety, reducing overall calorie intake (3). Additionally, low-moisture part-skim mozzarella is noted for its lower calorie density compared to full-fat versions, making it a versatile option for healthy eating plans while maintaining key nutrients like calcium and casein proteins. These factors combine to position part-skim mozzarella as an optimal cheese for those aiming to manage weight effectively.
Nutrition Value of Part-Skim Mozzarella in Table
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value (approx) |
| Calories | 280 kcal | 14% |
| Protein | 28 g | 56% |
| Fat | 17 g | 22% |
| Saturated Fat | 11 g | 55% |
| Cholesterol | 54 mg | 18% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.1 g | 1% |
| Fiber | 0 g | 0% |
| Sugar | 1 g | – |
| Calcium | 731 mg | 56% |
| Sodium | 620 mg | 26% |
| Potassium | 95 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 420 IU | 8% |
| Iron | 0.3 mg | 2% |
3. Feta Cheese
Feta cheese is a noteworthy choice for weight loss due to its nutrient density and lower calorie content compared to many other cheeses. Studies have highlighted its high protein levels, which enhance satiety and contribute to reduced calorie consumption (4). Moreover, feta cheese is rich in beneficial fats, including conjugated linoleic acid (6), which may aid in fat metabolism and support weight management efforts (5). Its lower sodium alternatives also make it a healthier option for individuals managing dietary salt intake while still reaping its nutritional benefits (6).
Nutrition Value of Feta cheese in Table
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value (approx) |
| Calories | 264 kcal | 13% |
| Protein | 14 g | 28% |
| Fat | 21 g | 27% |
| Saturated Fat | 15 g | 75% |
| Cholesterol | 89 mg | 30% |
| Carbohydrates | 4.1 g | 1% |
| Fiber | 0 g | 0% |
| Sugar | 4 g | – |
| Calcium | 493 mg | 38% |
| Sodium | 917 mg | 38% |
| Potassium | 62 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 422 IU | 8% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 3% |
4. Parmesan Cheese
Parmesan cheese, often regarded for its rich, nutty flavor, can be a surprising ally in a weight-loss diet. With its high protein content and low carbohydrate profile, Parmesan cheese can help promote satiety, preventing overeating and supporting effective weight management. Studies have shown that protein-rich foods like Parmesan help regulate hunger hormones, thereby reducing overall calorie intake. Furthermore, its combination of healthy fats and proteins contributes to a feeling of fullness, making it an excellent option for those looking to control their appetite while still enjoying flavorful meals (7). Parmesan’s dense nature also means you can enjoy small portions to satisfy cravings without consuming excessive calories. However, it is essential to consume it in moderation, as it does contain sodium, which could contribute to high blood pressure if overconsumed. In addition to its satiating properties, Parmesan contains beneficial probiotics that support gut health, adding another layer of nutritional benefit (8). Thus, when incorporated wisely into a calorie-controlled diet, Parmesan cheese can be a flavorful and healthful choice for those aiming to lose weight.
Nutritional values of Parmesan cheese (per 100 grams):
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
| Calories | 431 kcal |
| Protein | 38.0 g |
| Fat | 29.0 g |
| Saturated Fat | 19.0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 4.1 g |
| Sugars | 0.9 g |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Calcium | 1184 mg |
| Sodium | 1800 mg |
| Potassium | 180 mg |
| Vitamin A | 463 IU |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg |
| Iron | 0.9 mg |
5. Goat Cheese
Goat cheese, known for its tangy flavor and creamy texture, is a popular choice for those looking to manage their weight. It offers a unique set of benefits that make it suitable for weight loss diets. One of the key advantages of goat cheese is its composition of medium-chain fatty acids, which are metabolized more efficiently than the long-chain fatty acids found in cow’s cheese. This means that goat cheese can promote satiety, helping individuals feel full faster and potentially eat less overall, a key factor in weight management (9). Additionally, goat cheese is lower in fat compared to many other cheeses, yet it still provides important nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which support overall health (10). It is also known for being easier to digest for some people, particularly those who are sensitive to cow’s milk. However, it is important to be mindful of its calorie density and sodium content, as excessive consumption could counteract its benefits for weight loss (11). When incorporated in moderation, goat cheese can be a flavorful and satisfying addition to a balanced diet for weight management.
Nutritional values of goat cheese (per 100 grams):
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
| Calories | 364 kcal |
| Protein | 22.0 g |
| Fat | 30.0 g |
| Saturated Fat | 20.0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 1.0 g |
| Sugars | 0.1 g |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Calcium | 298 mg |
| Sodium | 500 mg |
| Potassium | 180 mg |
| Vitamin A | 350 IU |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg |
| Iron | 0.8 mg |
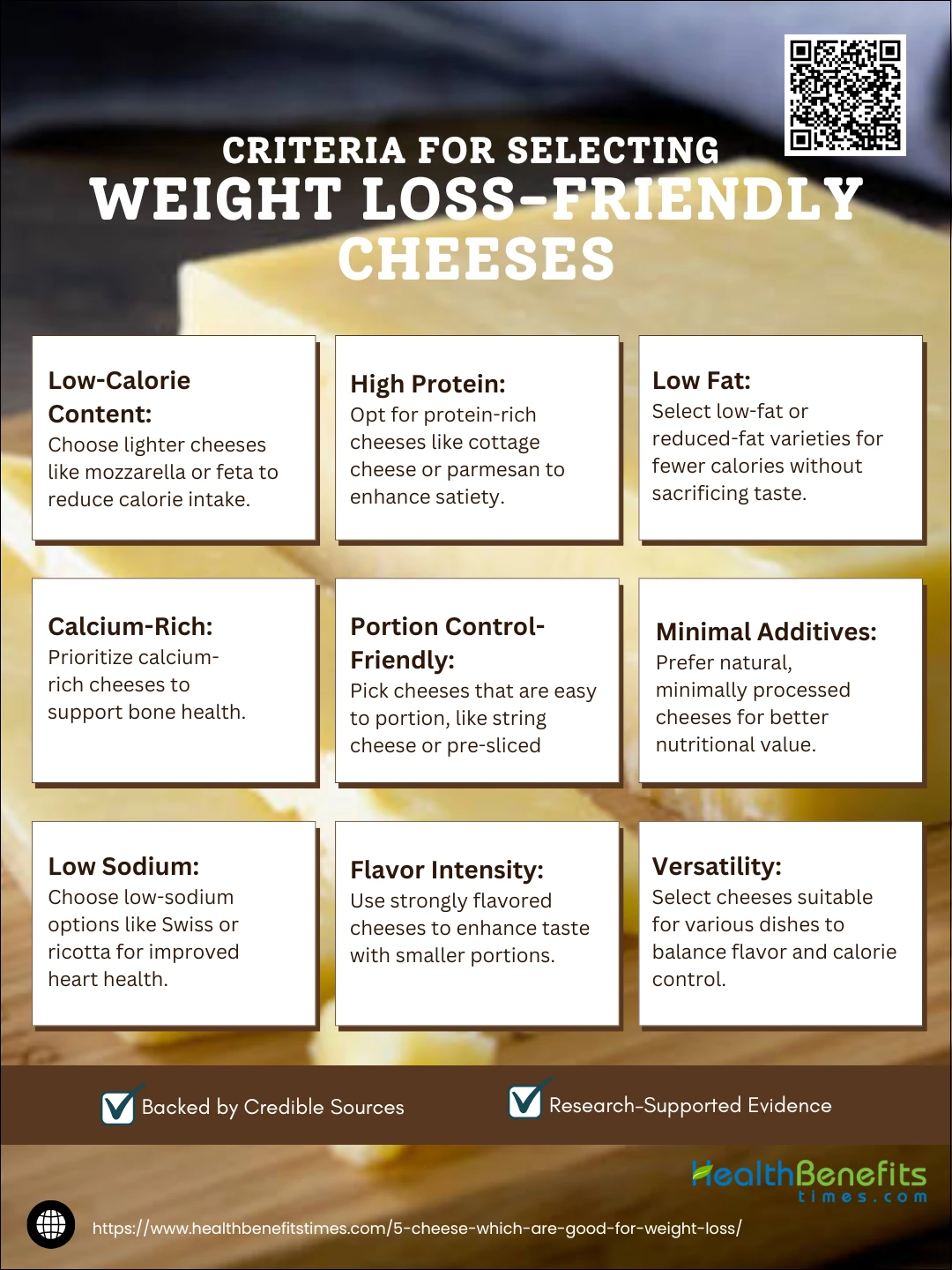
 Criteria for Selecting Weight Loss-Friendly Cheeses
Criteria for Selecting Weight Loss-Friendly Cheeses
Cheese can be part of a healthy diet, even if you’re trying to lose weight. However, not all cheeses are created equal. The best cheeses for weight loss are those that are lower in calories, fats, and sodium but still high in protein and essential nutrients like calcium. Understanding how to select the right cheese can make your meals both satisfying and weight-loss friendly. Below are the key criteria to consider:
- Low-Calorie Content: Opt for cheeses with fewer calories per serving, such as mozzarella or feta, which are lighter compared to cheddar or brie.
- High Protein: Look for cheeses that offer a high protein content to support muscle maintenance and keep you feeling full longer. Cottage cheese and parmesan are excellent choices.
- Low Fat: Choose low-fat or reduced-fat varieties of cheese to limit calorie intake while still enjoying the flavor.
- Calcium-Rich: Select cheeses that are rich in calcium to support bone health, a vital factor in any balanced diet.
- Portion Control-Friendly: Go for cheeses that are easy to portion, like string cheese or pre-sliced options, to avoid overeating.
- Minimal Additives: Choose natural, minimally processed cheeses over highly processed ones with added flavors, sodium, or preservatives.
- Low Sodium: If sodium is a concern, prefer cheeses with lower salt content like Swiss or ricotta to reduce bloating and improve heart health.
- Flavor Intensity: Strongly flavored cheeses like blue cheese or aged cheddar allow you to use less without compromising taste, reducing overall calorie consumption.
- Versatility: Select cheeses that can be used in a variety of dishes, ensuring they enhance your meals without excessive calories.
 How to Eat Cheese during Weight Loss
How to Eat Cheese during Weight Loss
Cheese can be part of a healthy weight-loss diet when consumed mindfully and in moderation. By choosing the right types of cheese and incorporating them strategically into your meals, you can enjoy their rich flavors without hindering your progress. Below are some practical ways to include cheese in your weight-loss journey:
- Practice Portion Control: Stick to recommended serving sizes, typically around 1 ounce or 1-2 tablespoons. Use a kitchen scale or measuring spoons to avoid overeating.
- Pair with Nutrient-Dense Foods: Combine cheese with vegetables, whole grains, or lean proteins to create balanced meals that keep you full and energized.
- Choose Low-Calorie Cheeses: Opt for lighter options like cottage cheese, mozzarella, or feta, which are lower in calories and fat.
- Use Cheese as a Flavor Booster: Incorporate small amounts of strong-flavored cheeses like blue cheese or parmesan to enhance taste without needing a large portion.
- Avoid Overly Processed Cheeses: Stick to natural cheeses and avoid processed options, which often contain unhealthy additives and excess sodium.
- Eat Cheese as a Snack: Enjoy cheese with healthy accompaniments like apple slices, cucumber sticks, or whole-grain crackers for a satisfying snack.
- Opt for Low-Fat or Reduced-Fat Varieties: Choose low-fat versions of your favorite cheeses to reduce calorie and fat intake while still enjoying the taste.
- Incorporate Cheese in Cooking: Use cheese in recipes like salads, soups, or casseroles in moderation, ensuring it complements the dish rather than dominating it.
- Monitor Sodium Intake: Pay attention to the sodium content of the cheese you choose, especially if you’re managing salt intake for overall health.
- Savor It Mindfully: Eat cheese slowly and enjoy its texture and flavor. Mindful eating helps you feel more satisfied with smaller portions.
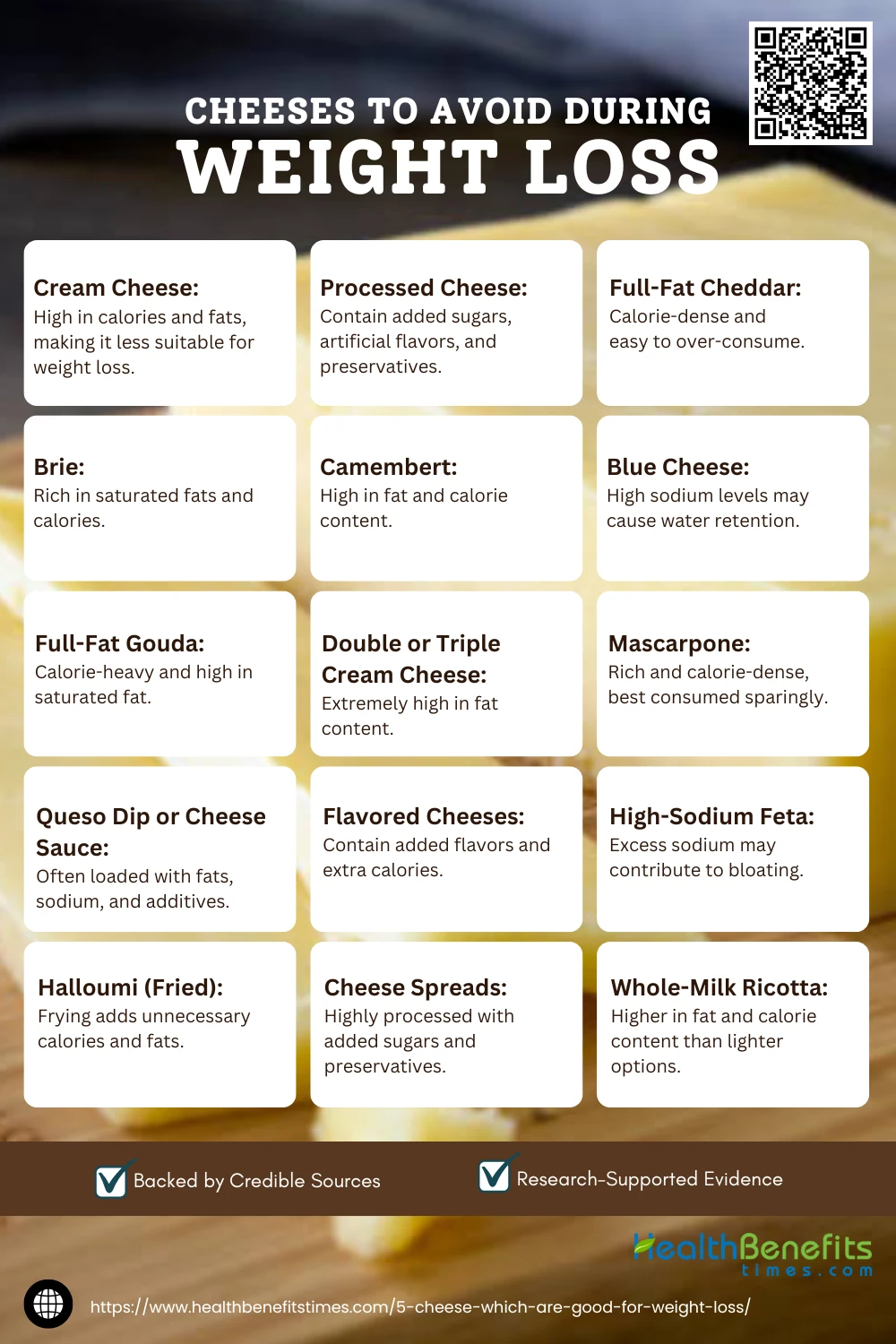
Cheeses to Avoid During weight Loss
When trying to lose weight, it’s important to avoid certain types of cheese that are high in calories, saturated fats, and sodium, as these can hinder your progress. Cheeses like cream cheese, processed cheese slices, and full-fat varieties of brie, camembert, or cheddar are often calorie-dense and easy to overconsume. Processed cheeses, in particular, often contain added sugars, artificial flavors, and preservatives, making them less nutritious. Additionally, cheeses that are heavily salted, such as blue cheese or feta, may contribute to water retention and bloating. While these cheeses can still be enjoyed occasionally in small portions, they are best minimized or replaced with lower-calorie, high-protein options for regular consumption during weight loss.
- Cream Cheese
- Processed Cheese Slices
- Full-Fat Cheddar
- Brie.
- Camembert
- Blue Cheese
- Full-Fat Gouda
- Double or Triple Cream Cheese
- Mascarpone
- Queso Dip or Cheese Sauce
- Flavored Cheeses
- High-Sodium Feta
- Halloumi (Fried)
- Cheese Spreads
- Whole-Milk Ricotta
 Conclusion
Conclusion
In conclusion, different types of cheese, such as cottage cheese, Parmesan, and goat cheese, offer a variety of nutritional benefits, but they also come with distinct characteristics. Cottage cheese is low in calories and fat while being rich in protein and calcium, making it a great option for those seeking a lighter, nutrient-dense dairy product. Parmesan, on the other hand, is much higher in calories and fat, particularly saturated fat, but it is an excellent source of protein and calcium, though it should be consumed in moderation due to its high sodium content. Goat cheese is similarly rich in fat and protein and provides a good amount of calcium, though it can be quite caloric. Its lower lactose content may make it a preferable choice for those who are sensitive to lactose. Overall, cheese can be a valuable addition to a balanced diet when consumed in moderation, with each type offering its own set of nutrients to complement different dietary needs.
References:
- Natural Grocers. Going Veggie.
- Arulkumar, M., et al. (2024). Investigation of the dehydration and rehydration behavior of osmotic pretreated paneer slices (Indian cottage cheese) and its modeling approach. Wiley Online Library.
- Swaminathan, A.V., Govindasamy-Lucey, S., et al. (2024). Impact of preacidification on the functionality and insoluble calcium levels of Low-Moisture Part-Skim Mozzarella made from high-casein milk. Journal of Dairy Science.
- Changes in the rheological properties of Iranian UF-Feta cheese during ripening.
- Compositional and functional characteristics of feta-type cheese made from micellar casein concentrate.
- Cambridge University Press. Accelerated ripening of Feta cheese with heat-shocked cultures or microbial proteinases.
- American Dairy Association. (n.d.). 5 Tasty Low-Calorie Cheeses.
- Cleveland Clinic. (2021, September 2). Parmesan Cheese: Nutrition Info and Health Benefits.
- (n.d.). Health Benefits of Goat Cheese.
- (n.d.). Is Goat Cheese Good for You?.
- (n.d.). Is Goat Cheese Good for You? Here are Some Benefits and Side-Effects.

